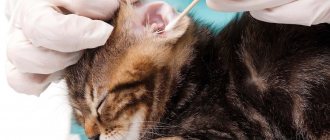
Skin diseases of cats are a common phenomenon, since the upper layer of the epidermis performs a protective function and blocks the access of pathogens to the animal’s body.
But the pet’s immune system is not always able to withstand all external and internal provoking factors.
It is necessary to be attentive to your pet and promptly respond to any changes in its behavior. If a cat scratches its neck until it hurts, you first need to recognize the underlying cause of the disease.
Symptoms and diagnosis of why a cat itches
The general condition of the sick animal is depressed; when licking and scratching the ulcers, the animal may meow pitifully.
Many pathologies can cause annoying itching. But at the same time, you should not confuse the daily combing and licking of the animal, which he does for hygienic purposes.
Alarming symptoms:
- the pet itches constantly, scratching the skin to the point of wounds;
- bald patches appear;
- the pet behaves aggressively;
- the fur falls out in clumps;
- appetite decreases;
- the eyes turn sour;
- ulcers and erosions form;
- dandruff appears.
If painful signs appear, you should contact your veterinarian. Only a specialist can determine the root cause of itching.
Diagnostic methods:
- visual inspection of the cat;
- bacterial culture;
- blood test to identify the allergen;
- cytological examination of skin tissue, which allows us to identify the functionality of cellular elements;
- skin scraping, eye wash, ear and nose swab.
Depending on the data received, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment. Self-medication is not recommended, as this will not only not help the pet, but will also significantly complicate the situation.
The cat scratches itself until it hurts and bleeds: what to do, how and how to treat it
Itchy skin in a cat can signal the presence of a number of pathologies in the pet, ranging from dermatological diseases to the presence of parasites and diseases of internal organs. Therefore, if unpleasant symptoms appear, you should contact your veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Mr. Cat recommends: general information
Itching occurs as a result of irritation of receptors located on the skin. The appearance of such a symptom may indicate the presence of a pathological process in the pet’s body.
To recognize the presence of this manifestation in a cat, it is necessary to carefully examine the condition of the skin. With regular scratching, claw marks, abrasions and dried crusts of blood form on the dermis. In addition, with a pronounced process, the pet will constantly scratch and lick the affected area.
Due to the appearance of itching, the animal's behavior may change - the cat becomes restless, excited, and an apathetic mood may be replaced by aggression.
Itching not only causes discomfort for the pet, but can accompany serious health problems, so the owner should not neglect visiting the veterinarian. When a symptom appears, you should understand the cause that caused it.
Also read the article why a cat may scratch itself if there are no fleas.
The cat scratches itself until it bleeds and is very itchy
There are a number of diseases in which a cat scratches itself until multiple blood crusts and wounds appear. The symptoms can be caused by both external and internal factors.
External diseases include various dermatological and infectious diseases, as well as infection by parasites. Internal factors include pathologies of the kidneys, cardiovascular system, and gastrointestinal tract organs.
Worms (helminths)
Helminthiasis is a large group of diseases caused by invasion by parasitic worms. There are a large number of pathogens that affect the internal organs of cats. Infection, as a rule, occurs through the fecal-oral route, that is, by eating foods that have been in contact with contaminated feces, as well as through contaminated soil and plants.
The parasite that enters the cat’s body, depending on the species, affects organs, most often the gastrointestinal tract.
The clinical picture is represented by the appearance of itching in the area of the anal sphincter, an increase or decrease in appetite, and general signs of intoxication syndrome - the animal becomes restless, sleep is disturbed, lethargy and decreased mobility appear.
As the disease progresses, a change in stool is observed - frequent diarrhea appears, in some cases the presence of the parasite in the stool can be seen with the naked eye.
Another sign of the presence of a parasite in a cat’s body is a deterioration in the quality of the coat - the hairline loses its shine, and increased hair loss is possible.
Inflammation due to bacteria
Severe scratching on a cat’s body can occur due to infection with pathogenic bacteria. Pathology develops when existing wounds and abrasions become infected. An area of local inflammation forms in the affected area, with the development of edema, redness of the dermis, and the appearance of ulcers.
When the immune response decreases, an abscess may occur.
The clinical picture of the pathology is represented by skin itching, increased body temperature, and decreased activity of the pet. In the absence of effective therapy, the pathological process can lead to the spread of infection.
Pyoderma
Pyoderma is a disease caused by infection of the skin with pathogenic bacteria. The disease can be either independent or secondary.
The main clinical manifestation of the disease is the formation of lesions on the skin with purulent contents. In this case, the cat experiences intense itching, as a result of which it scratches the abscesses until blood crusts form.
Most often, the infectious process is localized in the chin area, on the surface of the limbs, and on the back.
The pathological process can be:
- superficial - the infection affects the upper layers of the skin;
- deep - the deep layers of the dermis are affected, and the disease occurs in a more severe form.
Superficial pyoderma may be caused by the development of:
- impetigo - pathogenic bacteria affect the stratum corneum of the skin with the formation of small abscesses;
- folliculitis - the infection is localized in the cavity of the hair follicles. Most often, this form is observed in kittens.
The clinical picture is represented by an external manifestation in the form of the formation of pustules on the skin, and an unpleasant odor may appear. An inflammatory process forms in the affected area, with redness of the skin, a local increase in temperature, and leakage of exudate, as a result of which the animal’s fur takes on an unkempt appearance and tangles form.
Otitis (ear inflammation)
Otitis media is a disease characterized by the development of inflammation localized in the outer, middle or inner ear. The etiological factor in the development of the disease is:
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- allergic reaction;
- parasite infection.
The clinical picture depends on the cause of the ear inflammation. When infected with a mite, the outer ear is usually affected, with numerous brown crusts, scratches and abrasions appearing on its surface.
An allergic reaction occurs due to contact with an allergen. In addition to skin itching in the ear area and the development of inflammation, general malaise, drowsiness, apathy of the animal, as well as damage to the skin in other parts of the body are possible.
Otitis of a bacterial nature can develop as an independent disease due to a decrease in immune status. A secondary infection occurs when there is damage in the ear.
Ringworm (scratching until it bleeds)
Ringworm is a group of diseases of various etiologies, which manifest themselves in the form of small itchy nodules on the affected area of the skin.
- Ringworm is a disease caused by a fungal pathogen of the genus Microsporum. The clinical picture is characterized by the appearance of one or several areas of bald patches on the animal’s fur. The affected dermis is characterized by dryness and peeling, the presence of small nodules without exudate. Characterized by severe itching and redness at the site of the pathogen. The size of bald spots varies from small islands to large areas of fungal damage. The infection is dangerous for humans - with close contact with an animal, the risk of infection reaches almost 90%.
- Pityriasis rosea is a disease whose etiological factor is infection with a virus and the development of allergies. The nature of the disease is not completely clear. Most often, cats with a pronounced decrease in immune status are susceptible to the disease. Risk factors include advanced age and a period of up to one year, as well as the presence of chronic diseases. The clinical picture is characterized by the formation of flaky pink formations on the skin of a rounded shape on the pet’s skin.
- Pityriasis versicolor is characterized by a fungal infection of the stratum corneum of the skin. The causative agent is a fungus of the genus Pityrosporum. Clinical manifestations are represented by the formation of small multi-colored spots on the surface of the cat’s body, and the occurrence of itching. Elements of the rash may disappear when the ambient temperature drops. The disease is transmitted to humans, so if a pet is infected with this disease, safety measures should be taken.
- Lice, mites and skin parasites
Pediculosis in cats is most often caused by infestation with Felicola subrostratus lice. Parasites have a piercing-sucking apparatus, with the help of which they pierce the skin and feed the pathogen with blood. During damage to the dermis, the louse injects an anticoagulant compound, resulting in the formation of a local inflammatory process, irritation and itching.
Tick-borne infestation is characterized by great diversity:
- the ear mite is localized in the outer ear, but can spread to the inner ear and even to the meninges, causing encephalitis;
- Hair mites cause demodicosis. Pathogens are microscopic parasites, which have recently been classified as opportunistic microorganisms. The disease is characterized by the appearance of bald areas on the cat’s body, and the skin becomes pale and dry. Mild forms of the disease can go away on their own and respond well to treatment. In the case of a generalized infection or in the juvenile form, damage to internal organs may occur;
- subcutaneous mites cause notoedrosis, cheyletiellosis and other ailments;
- The scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei is the causative agent of scabies. The pathogen lives under the skin, makes passages in it, resulting in severe itching.
Other skin parasites are fleas. Settling on the skin of a cat, pathogens cause inflammation due to bites, saliva getting into the wounds, and decomposition of dead individuals. These parasites can cause an allergic reaction and also infect your pet with dangerous diseases. Fleas carry tularemia, hemobartonellosis and other infectious diseases.
It is important to read about why fleas can appear even on an indoor cat.
Allergies
Allergic reactions are an inadequate response of the immune system to the entry of a particular allergen into the body. Pathology is most often recorded for food products, dust, and household chemicals.
The clinical picture is represented by various skin lesions in the form of urticaria or dermatitis. In this case, the cat experiences severe itching, so scratching and sores may appear.
In severe cases, anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm and other life-threatening symptoms may develop.
Hormonal imbalances
- Cushing's syndrome is a pathology caused by an increase in the production of steroid hormones by the adrenal glands, or by the direct systematic administration of glucocorticosteroids in the treatment of various diseases. Adrenal hormones play an important role in many body processes.
When their concentration in the blood increases, a failure occurs in all types of metabolism. The clinical picture is characterized by the development of obesity, severe thirst appears as a result of an imbalance in water-salt balance, and diuresis increases.The development of atrophic changes in muscles, dullness and hair loss, dandruff, and itchy skin are observed.
- Hypothyroidism is a pathology of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland, in which there is insufficient production of thyroid hormones responsible for metabolic activity.
The disease is accompanied by a decrease in the cat's activity, peeling of the skin, itching, and increased body weight. The disease is rare in cats and is most often caused by removal of the thyroid gland or previous radiotherapy for hyperthyroidism. - Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood as a result of damage to the pancreas or glucose tolerance. The disease has a systemic effect on the pet’s entire body, including the skin.
Treating cat itching at home
Treatment for itchy skin depends on the cause of its occurrence. As a rule, therapy includes a set of measures to eliminate the disease.
Complex treatment
Complex therapy involves eliminating the cause of itchy skin, as well as relieving the unpleasant symptom.
If there is inflammation on your pet's skin, you should use anti-inflammatory ointments that are applied to the damaged areas of the dermis. Ulcers should be treated with various antiseptic solutions - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Depending on the pathogen, the doctor prescribes a remedy aimed at its destruction.
An allergic reaction is treated with antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Source: https://MrKot.com/kot-raschesyvaet-sebya
Main reasons
Itching can be caused by both internal and external causes. Most often this is due to the presence of fleas, even if they could not be identified during a visual inspection.
Moreover, irritation on the skin from their bites can persist for 1-1.5 months after the pet has been treated.
The waste products of helminths, as well as the toxins released by them, provoke skin rashes and allergic reactions.
There are other provoking factors that cause an unpleasant symptom. Each of them can be manifested by characteristic itching, but in addition to this, there are other symptoms that make it possible to diagnose the pathology.
Therefore, it is necessary to consider all possible causes and become familiar with their characteristic features.
Helminths
Parasites have a negative impact not only on the digestive organs, but also contribute to the loss of essential nutrients.
As a result, the cat does not receive enough of the necessary components from food, which leads to increased dryness of the epidermis and the appearance of dandruff. This feature provokes itching. Therefore, the pet tries to lick itself more often and more intensely in order to eliminate the unpleasant symptom.
Be sure to read:
Why does a cat shake its ears and head constantly, causes of itching, how to help and what to do
The waste products of helminths, as well as the toxins released by them, provoke skin rashes and an allergic reaction.
Helminthiasis occurs in both adults and kittens. Infection occurs through flea bites and contact with an infected animal.
Parasites can be transmitted to humans and other pets ; treatment should be carried out on everyone at the same time.
Characteristic features:
- faded, matted fur;
- peeling of the epidermis;
- changes in taste preferences due to digestive failure;
- sour eyes;
- unusual behavior.
For prevention purposes, it is recommended to vaccinate or regularly give special suspensions, which can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy.
Ringworm
This fungal disease also causes annoying itching in cats. The provoking factor for development is a lowered immune system and an unbalanced diet.
Ringworm causes annoying itching in cats
Infection can occur through contact with a sick street animal, as well as from an owner who brings spores of a pathogenic fungus on his clothes. Lack of treatment can cause the death of your pet.
The danger of ringworm is that it can be transmitted to humans. Therefore, therapy should be started at the first signs to avoid serious complications.
Additional signs:
- the fur falls out in clumps;
- bald patches appear on the body;
- inflamed areas become covered with scales and become inflamed;
- the pet constantly shows anxiety;
- the wool is greasy, matted, without a healthy shine;
- claws become deformed;
- lack of interest in food;
- In place of bald patches, ulcers form.
The general condition of the sick animal is depressed; when licking and scratching the ulcers, the animal may meow pitifully, as this causes pain.
Lice, ticks, fleas and skin parasites
All external parasites not only bite the animal, causing skin irritation, but also leave behind waste products, which provokes an unpleasant symptom.
All external parasites not only bite the animal, causing skin irritation, but also leave behind their waste products, which causes itching.
Harmful insects are also carriers of infection that penetrates open wounds. As a result, an inflammatory process develops, penetrating into the deep layers of the epidermis.
Parasites can be identified by additional signs:
- restless behavior;
- small rash on the skin;
- apathetic attitude;
- receding hairline;
- ulcers, ulcers;
- hair loss.
To prevent the appearance of parasites, it is recommended to periodically use special wool treatment products.
Allergic reactions
Often the symptom appears when you are allergic to a flea collar, drops, household chemicals or food.
At the same time, the cat scratches not only its neck, but also its ears until it bleeds. An additional symptom is biting and constant licking of the limbs. A small rash also appears on the skin.
To save your pet from suffering, it is necessary to identify the allergen. To do this, you need to analyze what could provoke this reaction.
Be sure to read:
Why does a cat bite and gnaw its tail strongly, sometimes until it bleeds? Should I be worried?
Skin infections
Various skin pathologies are also characterized by annoying itching. This is due to disruption of metabolic processes in the epidermis, the development of inflammatory processes, and the formation of ulcers and ulcers.
The cat, trying to get rid of the itching, scratches its neck even more until open wounds appear, which negatively affects its well-being and behavior.
Additional signs:
- inflamed areas on the skin;
- rash, ulcers, dry scales, scabs;
- dull, matted fur;
- in inflamed areas the skin is much thicker;
- apathetic behavior;
- refusal to eat.
Hormonal and endocrine disorders
The appearance of an unpleasant symptom may be associated with a hormonal imbalance in the pet’s body or a failure of the endocrine system. These disorders are rare, but they should also be taken into account when diagnosing pathology.
The appearance of itching may be associated with hormonal imbalance in the body
Possible reasons:
- disruption of the thyroid gland;
- diabetes;
- Cushing's syndrome.
Additional symptoms: severe peeling of the skin, partial baldness on the sides, matted hair.
Psychological problems
Various stress factors can also negatively affect the well-being of a domestic cat. As a result, itching may occur as a reaction of the body to psychological trauma.
Probable causes;
- moving to a new apartment;
- the appearance of another animal in the house;
- loneliness for several days;
- restriction of movement;
- sudden change in temperature conditions.
To eliminate this unpleasant symptom, it is recommended to surround your pet with care and attention. This will allow him to quickly adapt to new conditions and normalize his psychological state.
Otitis (ear inflammation)
The provoking factor for the development of the disease is excessive accumulation of sulfur as a result of strong growth of hair.
Therapy must be carried out with the approval of a veterinarian based on the established diagnosis
Often the inflammatory process is a consequence of infection by ear mites, which provokes the active reproduction of pathogenic flora.
The pet constantly rubs its ears and shakes its head. In advanced cases, the affected ear becomes inflamed, painful, and emits an unpleasant odor.
If left untreated, the pathological process affects the lining of the brain and can cause the death of the animal.
Cat fleas
Fleas on a cat are perhaps the most common problem in an animal. Even if the cat is domestic and has never been outside or had contact with other animals, this does not guarantee that it has not picked up fleas. After all, even the owner can bring them in from the street, along with shoes or on clothes.
And as soon as abnormal combing of the animal has been noticed, the first thing to do is to examine the cat for the presence of fleas. This procedure is not difficult to carry out. Use two hands to separate the pet's fur on a certain area of the skin. In the parting of the fur, as a rule, you can notice the uninvited “tenants” of the animal. And in advanced cases, fleas can be seen with the naked eye.
Here, the pet owner can make the choice himself, based on his budget and the degree of neglect of the disease.
The main types of diseases that cause itching
All diseases that are characterized by the appearance of an annoying symptom in the neck area can be divided into several main categories.
Types of diseases:
| Name of the group of pathologies | Diseases |
| Parasitic |
|
| Tick-borne |
|
| Allergic |
|
| Bacterial |
|
Treating itching in a cat
For treatment, drugs are used whose action is aimed at eliminating the main cause of the pathological process. Therapy should be carried out with the approval of a veterinarian based on the established diagnosis.
Attention! You should not self-medicate based on your assumptions, since the appearance of a scratch or wound is only a symptom of a concomitant disease.
Basic treatment methods depending on the type of disease:
- Parasitic infections. To eliminate external parasites, the wool is treated with the following types of preparations: Bars, Hartz, Bayer, as well as anti-scabies ointments (ivermectin, aversectin). In case of helminthiasis, Drontal and Prazicide are prescribed. Antihistamines are used to reduce unpleasant itching - Tavegil.
- Fungal pathologies. Bald spots on the neck are treated with Sanoderm and Miconazole ointments, which are used until the pathological signs are completely eliminated. It is also acceptable to use special shampoos such as Sebozol or Nizoral. In particularly difficult cases, the doctor prescribes vaccination using Polivac or Vakderm.
- Bacterial diseases. Antiseptic agents such as Formalin or Miramistin are used to treat wounds. After this, the scratches should be treated with ointments: for dry eczema - naphthalene or Vishnevsky, for wet eczema - Lassara or zinc. To eliminate bedsores, Levomekol ointment is prescribed.
- Allergic reactions. Antihistamines are prescribed: Stop-itching, Suprastin, Tavegil.
Be sure to read:
What to do if a cat licks its fur to bald spots and wounds, what is overgrooming
Depending on the severity and form of the pathology, the doctor may also prescribe immunomodulators, antibiotics, gastroprotectors, probiotics and other types of medications.
Scabies mite
Another option for excessive head scratching in a cat may be a scabies mite. There are several types of scabies mites, and accordingly, treatment for each type of mite is individual. If, in general. The scabies mite is a small, small parasite. It can be seen under a microscope. It feeds on animal skin.
Again, you need to contact your veterinarian. It is necessary to scrape the wounded skin of the animal. Sometimes an analysis is also taken. And it also happens that a not very qualified veterinarian, after a routine examination of the animal, diagnoses “scabies mite.” This approach is not correct. After all, scabies mites can be confused with other similar diseases.
If the doctor did everything correctly and the animal was given this particular diagnosis, then the attending physician will prescribe treatment. In this case, both injections and tablets, and even special drops are used (both for internal and external use). Often, an animal picks up a scabies mite due to a weakened immune system. In this case, the veterinarian may prescribe an immunostimulating drug.
How to help your pet at home
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to use compresses or wipes based on medicinal herbs.
Effective recipes:
- Calendula. Pour 30g of plant collection into 250 ml of water. Boil the mixture for 15 minutes, without letting it boil too much. Leave for 2 hours, peel. Use as a rub, lubricating scratches and wounds on the neck.
- Chamomile. Pour 30 g of herb into 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Cleanse and use as a compress on wounds and ulcers. Use the product 3-4 times a day until complete recovery.
If the cat continues to actively lick the inflamed areas, which interferes with their healing, a veterinary cone or Elizabethan collar should be used.
Prevention
To protect your pet from diseases, you must follow certain rules of prevention:
- Preventive visits to the veterinarian at least once every 6 months.
- Regularly taking antiparasitic medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Apply drops or a collar against fleas and ticks.
- Balance your pet’s diet so that it contains all the necessary vitamins and microelements.
- Regularly change bedding and treat your pet's equipment.
- Avoid contact with street animals.
Inattention to the cat's health and ignoring obvious symptoms can lead to serious complications, and then long-term therapy over several months will be required to restore the animal.
Therefore, at the first signs of disease, you should contact your veterinarian.