Cats are very susceptible to viral infections, of which quite a lot are currently known. It should be borne in mind that any viral diseases in cats pose quite a serious danger to your furry pet. Having suspected your pet presence of a virus, there is no need to try to treat the disease yourself, since the medicine and its dosage should be selected by a specialist. Viral diseases in cats pose a mortal danger to the animal. Such diseases must be observed in a veterinary office. Each of these infections can quickly send a beloved cat to the next world, causing a lot of emotional suffering to the owners, but to avoid such a fate, read our article as quickly as possible and call a doctor at home!
Common viral diseases of cats
Viruses cause severe, life-threatening diseases in cats. Infection occurs through air, water, feed, bedding and contact with infected animals. The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- Contact with a virus carrier. Visiting cat shows poses a great danger.
- Transmission of viruses through food, water, and air.
- Failure to comply with zoohygienic conditions.
- Stress factors:
- Transportation.
- Bored content.
- Overheating or hypothermia.
- Poor nutrition.
The following diseases are considered the most common and most dangerous among cats:
- Rabies.
- Panleukopenia
- Aueszky's disease.
- Panleukopenia.
- Viral rhinotracheitis.
- Cat flu.
- Calicivirus.
- Coronavirus peritonitis.
- Leukemia.
- Immunodeficiency in cats.
- Herpes.
Virus
Rabies
The most dangerous viral zoonotic disease is rabies. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is myxovirus.
- Carriers are stray dogs, cats, wild carnivores.
- Infection - through saliva from the bite of a sick animal or defects in the skin and mucous membranes.
- Incubation period. After the bite, the animal is observed for 10 days. If no clinical manifestations occur, the animal is considered healthy.
- Symptoms are nervous phenomena.
- Forms of the disease:
- Violent. Excessive drooling, aggressive behavior, perversion of appetite, paralysis. Photophobia, hydrophobia. After 3-11 days the animal dies.
- Paralytic. Lasts up to 4 days. Paralysis occurs without an aggressive phase.
- Atypical. Symptoms erased. Ends in paralysis and death.
- Diagnostics:
- Lifetime - based on anamnesis, epizootic situation, clinical symptoms.
- Post-mortem - histological examination of the brain.
- Treatment. Injection of specific serum within 72 hours. If symptoms appear, treatment is ineffective.
- Prevention - annual vaccination.
Rabies in a cat
Piroplasmosis
This disease is more common in dogs than cats, but purring creatures can also contract the disease. The disease is transmitted by Babesia ticks, hence its other name – Babesios. In fact, piroplasmosis is a complex disease of animals, with the reproduction of harmful mites that feed on blood in the blood and under the skin of a cat.
Piroplasmosis in cats has mild symptoms, which can be signs of many other diseases. The main signs of piroplasmosis include:
- almost complete refusal to eat;
- general lethargy and indifference of the animal;
- beetroot, red, brown color of urine;
- mucous membranes become yellow;
- Digestive problems appear.
The disease progresses extremely rapidly, and it can only be detected by the results of urine and blood tests.
Treatment should begin in the first two days after infection, because after this period it may no longer have any effect on the disease. Moreover, the treatment itself is carried out with extremely potent drugs that can be toxic. When prescribing them, the doctor is guided by the consideration that the risk of intoxication may be significantly less than the risk of death. Therefore, it is recommended not to start treatment until laboratory results are obtained.
In parallel with potent medications, the doctor will prescribe medications to boost your pet’s immunity and complex vitamins to support the cat’s body. Improvement occurs approximately six to seven days after the start of treatment.
Prevention of piroplasmosis can only be done by protecting the cat from ticks using special means and timely treatment of the pet from parasites.
Aueszky's disease
Cats are the first to get sick; productive animals become infected from them. A person becomes infected through meat. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is herpesvirus.
- Carriers are rodents, infected pigs.
- Infection occurs through eating virus-carrying mice, rats and contact with pigs.
- Incubation period. Up to eight days.
- Symptoms are nervous phenomena.
- Forms of the disease:
- Classic. Excitement gives way to depression. Constant meowing, drooling, vomiting, photophobia, itching, death.
- Atypical. Severe depression, the animal does not meow. Quick death.
- Encephalitic. Signs similar to the classical form. Additionally - aggressiveness, lack of coordination, paralysis.
- Gastroenteritis. Severe pain in the abdominal cavity, vomiting, sudden death.
- Diagnostics. It is necessary to distinguish between Aueszky's disease (pseudorabies) and rabies.
- Treatment. In the initial phase use:
- Immunoglobulin Vitafel.
- Immunostimulants - phosphoprenyl, immunofan, gamavit.
- Antibiotics - maxidin.
- Prevention has not been developed.
Panleukopenia
Feline distemper (panleukopenia) is the most dangerous disease with a high mortality rate. Survivors of a four-day illness become virus carriers. In the warmer months, young animals and old cats get sick. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is parvovirus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats, blood-sucking insects.
- Infection is through the air, flea bites, and cat feces. Intrauterine infection.
- The incubation period is 2...10 days.
- Symptoms:
- Vomit. Yellow-green mucous discharge with blood. Foul bloody diarrhea.
- Starvation.
- Cardiovascular failure.
- Body temperature >41°C.
- Conjunctivitis, rhinitis. Dry mucous membranes. Dehydration of the body.
- Coma. Sudden death.
- Diagnosis - clinic and epizootic situation. A blood test shows a drop in the number of leukocytes to 3*103/ml when the norm is 5.5...18.5*103. It is necessary to distinguish panleukopenia from non-contagious enteritis and toxoplasma invasion.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Administration of drugs is parenteral. The tablets cause a gag reflex. Apply:
- Subcutaneous injections of saline to relieve symptoms of dehydration.
- Hemostatic drugs.
- Vitamins of category B, to replenish spent reserves.
- Antibiotics to suppress secondary microflora.
- Diet food. The appearance of appetite is a favorable sign. Rehabilitation nutrition is as follows:
- Limiting carbohydrates at the expense of proteins.
- The first days - kefir and white bread soaked in low-fat meat broth.
- On the third day - specialized ready-made gentle food.
- A four-week ban on raw foods and vegetables is imposed.
Animals that have recovered from the disease acquire stable immunity to parvovirus. Antibodies protect offspring up to twelve weeks of age.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Primary and secondary form
As a rule, a healthy animal, vaccinated according to age, which is properly fed with high-quality feed, has less chance of getting sick. Parvovirus often turns out to be not a separate disease, but a symptom of an underlying pathology. Therefore, primary and secondary catarrhs are distinguished:
- Primary infections include foodborne infections. That is, opportunistic microflora, salmonella, E. coli, anaerobes that develop when poisoned by bad food. This also includes bacterial and mycotic infections that develop when eating moldy foods.
- Secondary parvovirus develops against the background of infectious processes of viral origin.
Another point is the pH of the internal environment. According to this indicator, acid and alkaline inflammation are divided. At first glance, the information is redundant. But it is very important for the doctor. The correctness of diagnosis and its future treatment depends on this knowledge. With the acidic nature of the inflammatory process, fermentation processes develop with the release of carbon dioxide and methane.
Viral rhinotracheitis
The disease affects the organs of vision and breathing. The mortality rate does not exceed 20% of the number of cases. Those who have recovered from the disease develop lifelong immunity. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms: The causative agent is the herpes virus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection - air, discharge from the genitals, eyes, nose. Infection is transmitted through food, contact between people and insects.
- The incubation period is 3...8 days.
- Symptoms:
- Acute form:
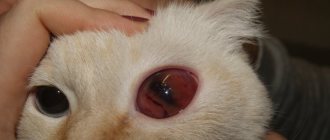
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva. Rhinitis.
- Cough.
- Ulcers on the tongue.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membranes. Redness of the nose.
- Temperature >40°C.
The acute form ends with recovery after a decade.
- Chronic form:
- Constipation.
- Chronic rhinitis lasts for years.
- Bronchitis develops, developing into pneumonia
- Ulcers appear on the skin.
- The nervous system is affected.
- Abortions and stillbirths are recorded.
- Diagnosis: clinic, tests of nasal and eye secretions.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Apply:
- Universal antibiotics.
- Sulfonamides.
- Antihistamines.
- B vitamins. Ascorbic acid.
- Dietary nutrition consists of the use of liquid boiled feed.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Calicivirus
Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasmosis is an infectious disease that is caused by mycoplasmas (pathogens) that poison the cat with waste products of ammonia and hydrogen content. It is possible to become infected with this disease in any way: from airborne droplets to habitual everyday communication. The disease can affect all organs of the animal, even stillborn offspring.
Mycoplasmosis at the beginning is similar to a standard cold. The cat is sneezing, coughing, suffering from a runny nose, and her eyes are inflamed. But then all the discharge can turn purulent, with the appearance of ulcers on the skin, and the joints suffer greatly.
To cure a disease such as mycoplasmosis, it is very important to consult a doctor at the very first stage, when the cat only seems to have a cold. The disease can be detected in this period only as a result of the necessary tests.
Mycoplasmosis cannot be prevented by vaccinating a cat, so it is necessary to maintain its immunity and not expose it to stress, colds, or hypothermia. Mycoplasmosis is treated by prescribing a course of potent antibiotics, selected by the doctor taking into account the characteristics of a particular animal, drugs are always prescribed that increase the cat’s immunity, and they also give the cat medications that treat the symptoms of the disease: drops in the eyes and nose, expectorants, cough medicines, healing ointments . It also aligns the functions of the pet’s gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system.
To prevent the disease, measures are taken to maintain the pet’s strong immunity through proper nutrition, always with the addition of complex vitamins when feeding the pet naturally.
Calicivirus
The disease affects the respiratory system. They get sick during the cold months. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is calicivirus.
- Carriers are sick cats, virus carriers.
- Infection is through the air and by contact.
- The incubation period is 1...3 days.
- Symptoms resemble those of rhinotracheitis. Calicivirus is complicated by stomatitis, diseases of vision and breathing. The disease lasts 7...21 days. Mortality - 30%.
- Diagnosis - clinic, epizootic situation, blood tests. Anemia and leukopenia are observed.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Apply:
- Universal antibiotics.
- Sulfonamides.
- Nitrofurans.
- Vitamins A, C, B12.
- Hyperimmune serum.
- Dietary nutrition, as for leukopenia.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Calicivirus
Coronavirus peritonitis
Presents a problem for fellinologists running a nursery. Among the many relatively harmless coronaviruses is a deadly one. The disease is difficult to diagnose. It resembles diseases of the brain, eyes, digestive organs and cardiovascular pathologies. Young animals up to two years old and old cats are affected. Mortality is high. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the FIP coronavirus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection - through the air, discharge from the genitals, nose, eyes. Infection is transmitted through food, contact between people and insects.
- The incubation period is 21 days.
- Symptoms:
- Temperature >40°C.
- Symptoms of peritonitis.
- Vomit.
- Ascites.
- The stomach is swollen.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Universal antibiotics are used to destroy the accompanying microflora.
- Prevention. Not developed.
Coronavirus peritonitis
Symptoms
The list of infectious diseases of cats is very long, but the first symptoms of the disease may be of a similar nature. The main features include:
- increased lacrimation:
- heavy salivation;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- copious discharge from the nose;
- inflammation of the eye;
- cough, sneezing;
- the desire to hide from bright light, attempts to constantly be out of sight of the owners;
- fear at the sight of water;
- a sharp loss of interest in food or, conversely, a greatly increased appetite;
- general lethargy, apathy;
- temperature;
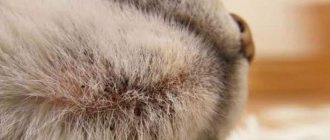
- rash and wounds on the head and torso;
- convulsive twitching of the limbs and the whole body.
If a cat is infected, it depends only on the person whether it will be possible to save the pet by starting treatment at the initial stage of the disease, because infectious diseases are quite difficult to treat effectively.
Leukemia virus
Destroys the immune system, causes the development of cancer. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is FeLV.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection is contact.
- Symptoms:
- Exhaustion.
- Heat.
- Starvation.
- Lethargy.
- Anemia.
- Dermatitis.
- Poor wound healing.
- Forms of the disease. There are three options for the development of events, with an equal degree of probability:
- The immune system produces antibodies, and the cat recovers.
- Asymptomatic virus carriers. A cat is dangerous to other animals. After a long time, the symptoms described above develop, and the animal dies painfully.
- The cancer progresses quickly.
- Diagnostics. Analysis for FeLV. If the result is positive, it is repeated after three months
- Treatment is symptomatic.
- Prevention. Vaccination. Isolation from other infected cats.
Leukemia virus
Diagnosis
The veterinarian takes stool blood tests. Now there are special diagnostic techniques that make it possible to detect in pathological material both the virus and the antibodies produced by the body in response to its introduction. In the event that a litter of kittens is affected and one of them has died, an autopsy is urgently required, followed by sowing of the material. This is not only a diagnosis, but also a chance to develop a suitable therapeutic technique.
If a breeder suspects that one of his pets is a carrier, he can simply take blood from the cat. If there are antibodies specific for FPV, the suspicions are not unfounded. Such animals should be immediately excluded from the reproduction process.
Is there any treatment for parvovirus enteritis in cats? Unfortunately, specific therapy for this disease has not yet been developed. The sooner you see a veterinarian, the better your pet's chance of survival. Many cats recovered with good nutrition, medications for diarrhea and, if necessary, intravenous infusions of buffers. Multivitamin formulations, useful for restoring the general tone of the body of a recovering animal, will not interfere.
How can you prevent the disease? Vaccination is the main method of prevention. The first vaccination is given at the age of eight to nine weeks, and it is repeated after three to four weeks. It is strongly recommended that adult cats be vaccinated annually. You just need to remember that it is not advisable to vaccinate pregnant cats, as there may be negative consequences for the health of unborn kittens.
The veterinarian takes the animal's feces or intestinal scrapings for analysis. Today there are techniques that make it possible to find in this material not only the virus, but also the antibodies that are secreted by the body in response to its introduction. If a litter of kittens is affected, an autopsy and culture of materials is performed. This is not only a diagnosis, but also a chance to develop a suitable diagnostic technique.
Before mating, it is necessary to take blood tests for both the cat and the cat. If specific antibodies are detected in it, then the animal is a carrier of the virus. He is excluded from breeding.
Feline immunodeficiency
This is the feline version of human HIV. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the FIV virus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection is contact.
- The incubation period is long.
- Symptoms:
- Exhaustion.
- Heat.
- Refusal of food.
- Lethargy.
- Anemia.
- Diarrhea.
- Encephalopathy.
- Leukopenia.
- Stomatitis, glossitis, gingivitis.
- Udder tumor.
- Rhinitis, conjunctivitis.
- Pyoderma.
- Dermatitis.
- Wounds do not heal well.
- Diagnostics. Serological tests for FIV.
- Prevention. Isolation from sick cats.
Feline immunodeficiency
Prevention measures
They are quite simple. When you consider how difficult and expensive it can be to diagnose and treat parvovirus in cats, it becomes clear that these measures need to be followed throughout your furry pet's life. Prevention comes down to the following points:
- Timely vaccination against viral and bacterial infections.
- Preventive deworming, the timing must be determined by a veterinarian.
- For feeding you need to use only high-quality feed and fresh products.
- There should always be clean water in the bowl.
Preventive measures are very simple and not difficult to implement.
- Be sure to promptly vaccinate your pet against bacterial and viral infections.
- Feed your pet exclusively high-quality, fresh food and food.
- Carry out deworming treatment according to the schedule drawn up by your veterinarian.
Herpes
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the herpes virus.
- Transmitted intraplacentally.
- The incubation period is 3 days.
- Symptoms:
- Depression.
- Purulent conjunctivitis.
- Keratitis.
- Yellow-green diarrhea.
- Ulcerative stomatitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Stillbirth.
- Treatment is symptomatic.
- Prevention - vaccination.
We invite you to join our Zen channel and group on VKontakte or Odnoklassniki, where new articles for pet owners are published.
Similar articles:
- Ringworm Caution: What Pet Owners Need to Know
- Why are cats overweight?
- Nephritis in cats
Treatment
The worst thing is when the animal is brought in already in serious condition. Then the doctor is faced with the difficult question of how to treat parvovirus in a cat if there is practically no time for diagnosis. Most often, a drip is placed, which allows you to level out dehydration and restore strength to the pet’s body. Depending on the condition of the animal, vitamins, hemostatic and other drugs are added to it.
At the same time, the veterinarian selects antibiotics that are designed to stop the development of pathogenic microflora. Do not forget that both the antimicrobial drug itself and its dosage should be chosen by the doctor. Traditional medicine can help, but you need to agree on the regimen with your doctor, and also not stop traditional therapy.