What is dysbiosis and what causes it?
Dysbacteriosis (dysbiosis) is not a separate pathology, but a broad term denoting the replacement or death of bacteria that form the natural normal microflora. Their place is filled by pathogenic bacteria and E. coli and begin to develop rapidly.
The process involves all body systems, mucous membranes and muscles.
Factors that provoke dysbacteriosis include:
- Poor living conditions (unbalanced diet, vitamin deficiency, predominance of fats and carbohydrates in food, insufficient indoor air humidification, drafts, dry low-quality food, etc.).
- External reasons (change of residence, unfavorable environmental conditions).
- Disorders of the hormonal system, which can be caused by pregnancy, taking medications (including contraceptives).
- Liver, kidney failure.
- Psycho-emotional stress. Stress can be associated with a change of owners, the appearance of another pet in the house, the loss of offspring and other factors that negatively affect the animal’s psyche.
- Long-term, repeated antibiotic therapy is the most severe case of dysbiosis. As a rule, even one course of antibiotics is harmful to the animal. As a result, normal microflora is replaced by pathogenic microorganisms that are resistant to the effects of medications.
- Worm infestation.
Dysbacteriosis can develop in any animal. Artificially bred cat breeds are most susceptible to this condition - Scottish, British, etc.
Why is dysbacteriosis dangerous? To answer this question, you need to understand what function the intestinal microflora performs. This is a kind of protective barrier that protects the body from the effects of pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
In addition, it stimulates and activates the immune system in kittens, neutralizes and removes toxins from the body, regulates metabolism and the activity of the hormonal system.
If signs of dysbiosis are detected, it is necessary to contact a veterinarian as soon as possible, otherwise the pet’s body will be completely defenseless against pathogenic microorganisms that cause dangerous diseases.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent a deplorable situation and not expose your cat to unpleasant misfortunes, you can follow certain preventive rules that minimize the risk of dysbacteriosis. Don’t forget that sincere love and care are the most important things required from an owner.
- You should choose food for your pet carefully - make sure that the food contains all the essential vitamins and microelements. Don’t forget that cats are big fans of picking up fallen food from the floor; it is also not recommended to allow this to happen. Dysbacteriosis can occur not only due to poor-quality food, but also from swallowed inedible small objects.
- You should be careful when treating with antibiotics. As practice shows, some diseases can be cured without the use of such serious drugs. If the situation forces you to use antibiotics, then you should definitely take care of restoring both the body and the cat’s microflora.
- Periodically it is worth carrying out prophylaxis with probiotics, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. This therapy is absolutely safe for your pet. But the improvement of metabolism and the state of microflora will improve significantly.
Dysbiosis in cats is a clinical syndrome that destroys the immune system and slowly depletes the body. The danger of this condition is that it goes unnoticed for quite a long time, and only breeders with extensive experience in keeping animals can differentiate it from food intoxication.
Symptoms
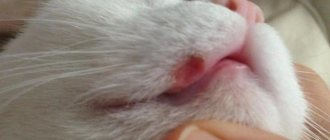
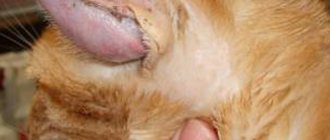
Signs of pathology appear suddenly. The cat looks depressed, sick, and shows no activity. Appetite is absent or reduced, causing the animal to lose weight. The stool is liquid, sometimes with mucus and blood. There may be both diarrhea and constipation.
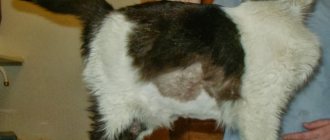
The wool loses its shine and does not look aesthetically pleasing. In representatives of long-haired breeds, the fur coat may thin out significantly.
In some cases, bloating and flatulence are observed. Such a clinical picture gives every reason to suspect dysbiosis, especially if the cat was recently treated with antibiotics.
Dysbacteriosis in cats – Veterinary Service of the Vladimir Region
Dysbacteriosis in cats is a disease characterized by a violation of the mobile balance of microflora that normally populates the intestines.
If in a healthy cat in the distal parts of the small intestine and in the large intestine lactobacilli, anaerobic streptococci, E. coli, enterococci and other microorganisms predominate, then with dysbacteriosis the balance between these microorganisms is disturbed, putrefactive, iodophilic or fermentative flora, fungi, mainly of the Gandida type, develop abundantly . With dysbacteriosis in cats, there are microorganisms in the intestines that should not normally be present; a large number of microbes and fungi are detected in the contents of the proximal parts of the small intestine and in the stomach. Instead of non-pathogenic strains of E. coli, pathogenic ones are often found in cats.
Thus, with dysbiosis, quantitative and qualitative changes in the composition of microbial associations in the gastrointestinal tract of a cat are observed.
Etiology.
Clinical dysbiosis in cats is caused by all diseases and conditions that are accompanied by disruption of the processes of hydrolysis and absorption of nutrients in the intestine - dyspepsia, gastritis (gastritis in cats), pancreatitis (pancreatitis in cats), hepatitis (liver disease in cats), enteritis, poisoning in a cat (Poisoning in a cat: first aid), colitis (colitis in cats), gastroenteritis (gastroenteritis in cats), worms in cats, severe stress, hormonal imbalance associated with pregnancy, the use of contraceptives (contrasex), infectious diseases - (feline panleukopenia , salmonellosis in cats, infectious peritonitis in cats, infectious rhinotracheitis - herpes in cats), parasitic (coccidiosis in cats, giardiasis in cats) kidney disease in cats, oncological diseases of the stomach and intestines (oncology in cats).
Often the cause of intestinal dysbiosis in cats is long-term uncontrolled use of antibiotics, sulfonamides, nitrofurans and other antimicrobial agents that suppress normal intestinal microflora and promote the development of those microorganisms that are resistant to these substances.
Pathogenesis . The mechanism of development of dysbiosis in cats is as follows: there is a disruption in the antagonistic activity of the intestinal microflora towards pathogenic and putrefactive microorganisms, its participation in the digestive processes (due to its own enzymes) and the synthesis of certain vitamins.
Toxic waste products of microorganisms and the products of breakdown of nutrients formed in large quantities - organic acids, aldehydes, indole, skatole, hydrogen sulfide, histamine and others, irritate the intestinal wall.
An allergic reaction occurs in the cat's body to unusual products of the breakdown of nutrients, as well as to antigens of bacteria and fungi.
Clinical picture . Dysbacteriosis in cats is characterized by clinical signs of dyspepsia or enteritis. The cat's appetite is reduced, and with severe spastic pain in the intestines it disappears completely (loss of appetite in the cat).
An unpleasant putrid odor emanates from the mouth (bad breath in a cat), vomiting or the urge to vomit is possible (vomiting in a cat). Dysbacteriosis in cats is often accompanied by the development of intestinal flatulence (bloating in a cat).
The cat's abdomen is sharply increased in volume, and upon palpation it is very tense and painful.
Diarrhea that occurs (diarrhea in a cat) may alternate with constipation (constipation in a cat (coprostasis). Feces have a sharp putrid or sour odor and contain undigested food particles. As a result of disturbances in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, the cat experiences symptoms of general intoxication of the body - lethargy, apathy, depression.
With a long course of dysbacteriosis, it is complicated by hypovitaminosis, especially in the body there is not enough B vitamins.
Some types of intestinal dysbiosis, especially staphylococcal, candidomycosis, and proteus, can become generalized and even cause sepsis in the cat.
Diagnosis . To diagnose the disease in modern veterinary clinics, the following methods are used: biochemical blood test (cat blood test), fecal examination and endoscopic examination. The diagnosis of dysbacteriosis in cats is confirmed by repeated studies of fecal microflora (mainly based on the results of coprogram).
If gastrointestinal pathology is suspected, radiography and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound in a cat) are performed.
Differential diagnosis . Veterinary specialists, when carrying out differential diagnosis, must exclude dysbiosis that occurs against the background of systematic nutritional errors (established on the basis of the collected anamnesis) and dysbacteriosis accompanying acute and chronic infectious and invasive diseases.
Treatment. When dysbacteriosis is established in a cat, stop using antibacterial agents that contribute to its development. They carry out a set of activities aimed at:
- Purgation.
- Improving the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Restoration of beneficial microflora in the intestines.
- Immune support.
- Mental stabilization.
We cleanse the intestines of toxins and waste by prescribing enterosorbents (Smecta, Lignitin).
Some veterinary specialists carry out intestinal cleansing by prescribing phytoelite: a tablet 4-5 times a day (first week) and 3 times a day (second week).
In the third week, the dose is reduced to ½ tablet, which should be given once a day. In the last, fourth week of treatment, give 1 tablet once a week.
To improve the functioning of the digestive organs, we use enzymatic preparations - Mezim, Cholenzym.
If your cat has diarrhea, give rice decoctions.
In order to restore the population of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines, we treat with probiotics. Among the probiotics, veterinary specialists usually prescribe the following:
Lactobifid, Lactoferon, Fortiflora, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Baktisubtil
These products should be used under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Among the antihistamines, cats are prescribed diphenhydramine, tavegil, trexil, suprastin, fenkarol, kestin, claritin, etc. in therapeutic doses.
Immunity support is carried out by using neoferon in the form of injections. This immunomodulator is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
The treatment regimen is determined by a veterinarian. The herbal preparation “Cat Bayun” in tablets or in the form of an infusion will help stabilize the psyche.
The cat's feeding diet is prepared in such a way that a significant proportion of it consists of sour milk products: yogurt, acidophilus, bifidokefir, bifilife, bifidok, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, etc.
In case of dysbacteriosis that has arisen against the background of an underlying disease of the digestive tract (enteritis, colitis, etc.), it is necessary to eliminate this pathology and restore the normal functioning of the stomach and intestines.
Prevention of dysbacteriosis.
In order to prevent dysbiosis in cats, animal owners should take the following preventive measures:
- Treat for helminthic diseases twice a year.
- Vaccinate against infectious diseases present in the region of residence.
- Timely detect and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- After a course of antibiotic therapy for certain diseases of the digestive system, conduct a course of treatment with probiotics.
Source: https://vetvo.ru/%D0%B4%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%B1%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B8 %D0%BE%D0%B7-%D1%83-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%88%D0%B5%D0%BA.html
Treatment
If the diagnosis of dysbacteriosis is confirmed by laboratory tests, then do not panic. This phenomenon is not very pleasant and it creates a certain danger for the body. However, the pathology is not transmitted to other animals and humans, is successfully treated and does not cause complications.
Therapy lasts 1-2 months and is complex. Treatment is aimed at:
- cleansing the gastrointestinal tract;
- restoration of natural microflora;
- normalization of metabolism;
- strengthening the immune system;
- stabilization of the psycho-emotional background.
If the symptoms are pronounced, the cat is given activated charcoal, Smecta. In general, drug treatment includes vitamin therapy, antihistamines, and drugs that strengthen the immune system. Hormonal pills, including contraceptives, are prohibited!
Cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out using the drug “Fitoelita”. The dosage is determined individually by the veterinarian.
To restore the microflora, the pet is prescribed a special light diet. The diet consists of fermented milk products. Such nutrition restores microflora. The colonization of lacto- and sour-lactic bacteria has a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Prebiotics will become a nutrient substrate for beneficial microorganisms that displace pathogenic bacteria. They should also be in the diet. It is advisable to include foods such as bananas, asparagus, and Jerusalem artichoke in the cat's menu. Of course, it is unlikely that the fluffy will show interest in such food, but it is still worth adding them little by little to dishes.
Lactoferon is used only if it is recommended by a specialist.
To strengthen the immune system, a solution of Neoferon is indicated, which is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
It is very important to help your cat cope with stress, for which she is given sedatives. The herbal preparation “Cat Bayun” has proven itself well. The composition includes mint, meadowsweet, sweet clover, motherwort, valerian root, St. John's wort, etc.
As for probiotics, normoflorins are mainly used. They effectively destroy pathogenic microorganisms and saturate the intestines with beneficial bacteria, renewing the biosynthesis of vitamins B1, B2 and K. In addition, probiotics promote the formation of acetic and lactic acids, which promote good absorption of vitamins, iron, and fats.
Do not underestimate the seriousness of dysbiosis. If left untreated, cats may develop gastritis, pancreatitis, gastroenteritis, allergies, hepatitis, and respiratory diseases along with the death of microflora. If treatment was carried out promptly and competently, the prognosis is usually favorable.
How to carry out the initial diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis
The normal intestinal microflora is subjected to detrimental effects, after which some of the bacteria die. The “vacant space” is quickly filled with bacteria and E. coli that are atypical for the body.
Symptoms may arise and pass spontaneously:
- Depression, apathy.
- Decreased/increased appetite or lack thereof.
- Loose stools, sometimes mixed with blood.
- Dehydration, unhealthy coat appearance.
- Possibly abdominal bloating and flatulence.
The difficulty of diagnosis is that symptoms may indicate a number of other or concurrent diseases. Dysbacteriosis in a cat after antibiotics, especially if several courses or a broad-spectrum drug were used, is guaranteed to develop, so treatment is prescribed in combination with prophylactic agents.
Normally, a cat’s intestines are filled with lacto- and sour-lactic bacteria, so if you suspect dysbiosis, switch the animal to a light diet with plenty of natural dairy products. At the same time, give vitamins, enzymes, and immunostimulants, which are available for purchase in regular pet stores. If the animal feels better, you are dealing with dysbiosis. However, you still need to see a veterinarian, usually, even at an early stage; in parallel with the death of microflora, gastritis, hepatitis, gastroenteritis, and allergies can develop.
Important! The use of probiotics without preliminary tests is at least useless. Millions of bacteria live in the intestines of an animal, and it is simply impossible to “guess” which ones are missing.
What to do at home
The owner is required to strictly comply with the veterinarian's instructions. All medications and their dosage are prescribed by a clinic specialist. Self-medication can aggravate the situation and have a detrimental effect on health.
The pet must be provided with good living conditions and protected from drafts. The cat's immune system is weakened, which means there is a high risk of contracting a viral disease or infection.
To relieve your four-legged pet from the accumulation of gases, you can give cumin or dill oil - 3-5 drops per day. If your cat suffers from constipation, castor oil will help.
To improve appetite, a decoction of dill, basil, yarrow, and coriander is given. Herbs are mixed in equal proportions, poured with hot water, infused and filtered. A cat needs 10 drops per day.
Traditional methods allow you to get rid of the symptoms of dysbiosis, but should not replace traditional treatment.
The role of normal intestinal microflora
The main task of beneficial microflora is as follows:
- normalize metabolic processes in the body;
- trigger the immune defense mechanism in a kitten that has just been born;
- produce necessary vitamins.
In the body of a newborn kitten, beneficial microflora is formed, characteristic of the environment in which the pet lives. Her condition will depend on the body’s defense system and overall health.
The microflora does not remain constant; it is influenced by various factors: age, living conditions, etc.
As the disease develops, an imbalance occurs, which negatively affects health. Infections are resisted by the intestines and the lactic acid bacteria living in it. For this reason, when the disease develops, the entire body is at risk.
In animals that have recently been born, the disease is much less common compared to adults, because kittens retain the immunity received from their mother.
Prevention
Dysbacteriosis can be prevented; it is enough to follow the simplest preventive measures known to every pet owner:
- Careful food selection. The use of economy-class food does not contribute to the health of pets. They provoke deviations in the gastrointestinal tract and allergic manifestations.
- Avoid feeding your cat food from “your table.” The diet should be balanced in fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
- Controlling cat food. Often the impetus for the development of dysbiosis is an accidentally swallowed fragment of sausage casing and other synthetic materials.
- It is advisable to use bottled water rather than raw water.
- Antibiotics are taken only as prescribed by a veterinarian. An experienced doctor will never prescribe them unless necessary. After use, restorative therapy (pro- and prebiotics) is carried out.
- Timely treatment of animals from parasites (once every three months). This applies not only to outdoor cats, but also to pets.
As for artificially bred breeds that naturally have a tendency to dysbiosis, it is advisable to give preparations with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli at least twice a year.
According to veterinarians, courses of probiotics will not harm even healthy animals, regardless of age. They will prevent dysbiosis, improve metabolism and strengthen the body as a whole.
Diagnostic methods
After treatment with antibiotics, the probability of developing dysbiosis is 100%.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the veterinary clinic prescribes a number of diagnostic measures:
- stool and urine analysis;
- taking a smear to determine whether there are worms;
- blood chemistry;
- assessment of the condition of the liver and pancreas.
Based on the results obtained, the veterinarian will tell you what to do next and prescribe the appropriate therapy.