Gingivitis in cats is an inflammation of the gums that affects one or more teeth. It precedes periodontal disease, a more serious disease that affects not only the gums, but also the ligaments that hold the teeth.
Gingivitis in cats: symptoms and treatment
If left unattended, the tooth becomes loose and falls out. The consequences of gingivitis and subsequent periodontal disease are also putrid odor from the mouth, pain, and the spread of foci of infection in other internal organs of the animal.
What factors contribute to the development of gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the gums, affecting the area around one or more teeth. Gum inflammation is the beginning of a destructive syndrome in the tissues surrounding the bone structure.
The mechanism of action of gingivitis is as follows: first it affects the gums, then the ligaments and bones on which the teeth are attached. According to veterinarians, gingivitis is nothing more than the beginning of a difficult and difficult to treat disease - periodontal disease.
The reasons that provoke the development of gingivitis can be divided into internal (endogenous) and external (exogenous). Internal factors include:
- vitamin deficiency;
- abnormal arrangement of the lower and upper teeth at the moment of closing the jaws (bite);
- hardened plaque;
- caries.
External causes of the disease are considered:
- wounds of the oral cavity caused by tubular bones and other sharp objects;
- radiation received as a result of radiation therapy, x-rays, etc.;
- infections;
- viruses (calcivirus, herpes, etc.);
- exposure to chemical elements.
Gingivitis can occur in any pet, regardless of breed; at risk are animals aged 5 years and older, an unbalanced diet, blood pathologies, and autoimmune diseases.
Prevention of gingivitis
To prevent damage to oral tissues, it is necessary to regularly brush your cat's teeth. The procedure takes only a few minutes, but the benefits are significant. Manipulation allows you to strengthen the enamel, prevent the appearance of carious cavities, stomatitis and periodontitis.
To treat your teeth, you can brush them with Tropiclean paste. This gel is safe because it contains medicinal plants. The drug does not have a pronounced menthol aroma, which is unpleasant for cats. You can brush your teeth and gums with gel once a week. At the veterinary pharmacy you can also buy Radiance and Elgidium pastes, special cleaning powders for animal teeth.
Advice! Your cat should have his own chew toys. They help train your jaws and strengthen your teeth. At a veterinary pharmacy or pet store you can purchase various rubber products for your cat, with which she will willingly spend time.
It is important to eliminate poor nutrition and feeding low-quality cheap food from your cat’s life. To prevent pathological changes, you can give special solid foods with certain components that improve the structure of the gums and teeth. Such food is purchased in specialized pet stores.
Main symptoms
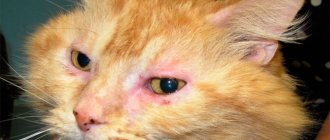
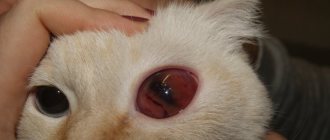
An attentive owner can easily identify signs of gingivitis in his pet. The animal becomes lethargic and apathetic, sometimes showing aggression and irritability. A visual examination of the oral cavity shows red, swollen gums. The characteristic clinical picture of gingivitis is incessant drooling mixed with blood.
A foul odor comes from the animal’s mouth, caused by the decomposition of food debris and the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
The cat feels pain in the gums, due to which it cannot chew or eat. As the disease progresses, he loses a lot of weight and becomes weaker.
If you suspect gingivitis in your four-legged pet, the owner should immediately take the furry cat to the veterinarian. Delay is fraught with the spread of infection throughout the body, damage to the liver, kidneys and other internal organs and systems.
Causes
The inflammatory process can begin due to various reasons:
- Tartar. A hard, yellow plaque formed from food debris is deposited on the enamel of the teeth. Its thick layer is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria.
- Avitaminosis. A cat's diet should include all the necessary vitamins and microelements. The lack of at least one can provoke loosening of soft tissues in the oral cavity.
- Low immunity. Gingivitis can easily be associated with another serious infection in a cat. The body of a sick animal is weakened; it cannot resist the active activity of bacteria.
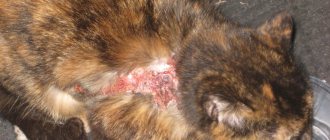
- Injury. Cats often get damaged gums when they eat sharp fish bones and too hard dry food. The resulting injury becomes infected and the inflammatory process begins.
- Lack of care. Few pet owners regularly brush their pet's teeth. This is especially harmful for older cats, when lack of care leads to an active increase in plaque on the teeth.
In cats that eat exclusively soft foods, gum inflammation is much more common. This happens due to the fact that natural abrasive particles do not enter the animal’s oral cavity, allowing them to involuntarily remove stones from their teeth.
Plaque on teeth
Therefore, gingivitis is more often treated in cats that do not eat hard food.
Treatment methods
Severe forms of gingivitis are treated comprehensively. If the pathology was diagnosed at the initial stage, then brushing your teeth will be quite enough. Experts warn: toothpastes intended for humans should not be used.
The concentration of some components in cleaning products is very high and negatively affects the health of the fluffy. In addition, cats do not like the menthol aroma that is present in most formulations.
To clean plaque, a special brush is used, which can be purchased at any veterinary pharmacy. If this is not possible, a regular toothbrush intended for children 3-5 years old will do. The bristles of these brushes are very soft and safe.
Miramistin, Chlorhexidine and other special disinfectant solutions are used to treat the oral cavity. After treatment, the gums are lubricated with “Zubastic” or “Dentavedin” ointments.
In the later stages, medication and sanitation in a veterinary clinic are indicated. The cavity is cleaned using an ultrasonic scaler.
The drug Interferon is effective in the fight against gingivitis. It stops the development of pathology, preventing its transition to severe stages. In addition, the product has a powerful immunostimulating effect.
The drug is well absorbed by animals and belongs to the category of harmless, not causing side effects, including allergies. Despite this, only a veterinarian can prescribe it and set the dosage and duration of treatment.
To treat advanced forms of gingivitis, antibiotics (Lincomycin, Clindamycin, Stomorgyl, Convenia) and immunosuppressants (Prednisolone, Azathioprine, corticosteroids) are used.
Tooth removal is indicated only in the most severe cases, since a toothless cat becomes disabled. But if the veterinarian makes such a decision, it means that there is no other way to eliminate the cause of the disease and the direct source of pathogenic microflora.
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Diagnosis of the disease
Of course, only a veterinary clinic employee can make a diagnosis. It is unacceptable to treat a cat on your own. If your cat has several symptoms and is worried, you should take him to a veterinarian.
During the examination, the doctor will examine the infectious oral cavity and take a smear to identify the form of the disease. In severe cases of the disease, additional blood and urine tests may be required. In rare cases, the animal is sent for dental x-rays.
What to do at home
The owner must provide his pet with the most comfortable living conditions and strictly follow the veterinarian’s instructions. You should not self-medicate, as this can aggravate the situation and cause irreparable harm to the cat’s health.
You can alleviate the suffering of a fluffy by using a soda solution or decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a disinfectant and antimicrobial effect. However, traditional methods cannot replace traditional treatment and are used as additional measures.
A decoction of chamomile, oregano, and strawberry leaves has worked well. You need to boil 1 teaspoon of the dried plant, pour a glass of boiling water, and cook over low heat for 10 minutes. Then strain the broth, cool and use to wipe the animal’s mouth.
During gingivitis, a cat usually refuses to eat, since even a small, barely chewed piece causes her pain. However, to defeat pathology, the body needs strength. Your four-legged pet should be fed with special soft food intended for weakened cats, pureed meat and vegetables, meat or chicken broth.
Features of nutrition during treatment
The predominance of dry and carbohydrate food is one of the causes of gingivitis, so during the treatment period the pet’s usual diet is adjusted:
Important! The basis of nutrition is soft puree food.
- exclude cereals and dry food with a high content of starch, sugar, flour;
- three times a day they feed soft food with a high protein content - broth, pureed vegetables, meat puree;
- exclude snacks, since after eating the cavity is treated with gels and sprays;
- enrich the diet with vitamins A and C;
- probiotic complexes help improve immunity.
The basis of nutrition is soft puree food
Possible complications
Even mild forms of gingivitis, if not treated correctly, can result in the development of plasmacytic-lymphocytic gingivitis - an ulcerative lesion of the oral mucosa. The danger of the disease is that ulcers form not only on the gums and around the teeth, but also in the larynx and esophagus.
Since the animal cannot eat normally and swallows food whole, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic processes, and intestinal blockage cannot be ruled out.
If left untreated, gingivitis progresses to periodontal disease, characterized by tooth decay and loss. The pathology is characterized by severe pain, festering wounds, and ulcers in the oral cavity. In the future, complete destruction of individual parts of the oral cavity can be observed, and in severe cases, jaw fractures.
In addition, advanced gingivitis creates a threat of infection of the body with toxins that arise during the life of pathogenic microorganisms. The body becomes severely poisoned and sepsis develops. Blood poisoning is accompanied by irreversible pathologies of internal organs.
Diagnosis of gingivitis in cats
If inflammation and redness of a cat's gums are detected, there is a possibility of developing gingivitis. Only a veterinarian can make a diagnosis after conducting an examination and laboratory tests.
The doctor examines the animal’s mouth for inflammation and visually expressed symptoms. To confirm the suspected disease and assess the severity, it is necessary to undergo appropriate tests. Usually a tissue biopsy, x-ray, and sample taking for histology are prescribed.
The virus that provoked plasmacytic-lymphocytic gingivitis can be identified by scraping from the mouth.
Symptomatic diet and procedures
Changing gum color is always a cause for concern. Even a banal change of teeth in a kitten should not go unnoticed by the breeder.
And pathological conditions require mandatory consultation with a veterinarian; in some cases, a visit to the veterinary clinic can be very urgent.
For the speedy recovery of the animal, it is very important to strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations. Any medications should be administered only in the recommended dosage and not exceed it.
If your cat's gums are red due to oral diseases, then folk remedies can help. It is recommended to irrigate the mouth with decoctions of sage or oak bark after each meal. The procedure is performed using a syringe without a needle. You need to tilt the cat's head down so that it does not swallow the contents of the syringe.
To ensure that oral diseases bother your cat as little as possible, you need to regularly clean the mouth and teeth of plaque and tartar. To do this, use a soft toothbrush.
In case of diseases of the internal organs, it is necessary to normalize the cat’s daily menu, exclude harmful foods from it and supplement the diet with vitamins.
It is necessary to ensure that your cat always has fresh drinking water. The food in the bowl must also be extremely fresh.
If a cat has suffered swelling from an insect bite or a blow, or severe poisoning, then you should carefully monitor the animal’s further behavior. If symptoms of damage to internal organs or the oral cavity appear, you should contact your veterinarian again.
Stages
Periodontal disease develops gradually and is divided into 4 stages, namely:
- Stage 1 . The easiest is the first stage of periodontal disease in a cat, which is treated relatively quickly. Redness and swelling of the gums appear, as well as tartar and bad breath. No structural changes are visible on the x-ray.
- Stage 2. At this stage of periodontal disease, X-rays already reveal a deficiency of bone mass, which is approximately 1/4 of the total volume.
- Stage 3 . Here, serious structural changes in the oral cavity are already visible, and the deficiency of bone mass is more than 1/2 of the total volume.
- Stage 4 . This is the most terrible and dangerous stage of periodontal disease. Purulent processes begin to develop and an abscess appears. The bone tissue is destroyed, and the changes are clearly visible on the x-ray.
Note. There is also a disease called periodontitis, many people confuse it with periodontal disease. In fact, severity and symptoms vary. Periodontitis is more dangerous and requires urgent professional intervention.