Just like humans, cats have ceruminous glands that produce “earwax” for lubrication and protection. If there are disturbances in the pet's body or close contact with relatives, the protective properties of the lubricant weaken, pathologies develop, and the cat begins to shake its head and scratch its ears. If the process is not noticed in time and treatment is not started, the cat may become deaf.
We will learn how to identify diseases and what the animal owner should do before the veterinarian arrives.
Pathological signs
Minor rare scratching (2-3 times a day) and head shaking cannot be called odd: all living organisms scratch and shake their heads, cats are no exception. But if the cat begins to itch constantly and at the same time tears his ears with his paws with all his might, you should pay special attention to this. These symptoms are often accompanied by other alarming signs that should alert the pet owner. These are the signs:
- The animal behaves restlessly, gets irritated and nervous for no reason.
- The cat actively shakes its head, tilts it down or to the side.
- When scratching its ears, the pet emits a hiss or an angry purr, and meows pitifully and loudly.
- Scratching left bloody marks inside and around the ears.
- The cat is trying to rub its muzzle and ears on everything around it.
- It is possible that the cat's body temperature may increase.
- The animal does not allow its ears and head to be touched, reacting painfully to any touch.
- The inner surface of the ear becomes red or swollen.
- Various discharges flow from the ear.
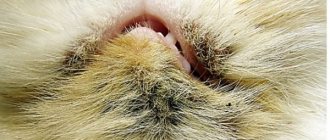
- Brown crusts and ulcers appeared in the ear.
Have you noticed this behavior in your cat? So it's time to see the vet.
© shutterstock
Examining the cat and diagnosing the problem
You can find out why your cat often shakes its head and ears after visiting a veterinary clinic. To make a diagnosis you will need:
- take urine and blood tests to determine deviations in basic indicators;
- undergo a bacteriological examination (bacterial culture), identifying the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- do ultrasound and x-rays necessary to detect internal pathologies, root causes and tumors.
The list of studies is individual and agreed upon locally. In addition to the above, the doctor can perform a biopsy, take a scraping or smear from the damaged area.
Reasons for strange behavior
If a cat's ears itch and it shakes its head, then the reason may be hidden in the most ordinary phenomena. This, for example, could be earwax that has accumulated in large quantities or water that has penetrated into the auricle during water hygiene procedures. Or perhaps a foreign object has gotten into your pet’s ear, or there are fleas.
There are other factors that may explain why a cat shakes its head. These symptoms are caused by specific cat diseases, as well as pathologies common to both humans and cats. Here are the main ones of these ailments:
- inflammation of the ear canal (otitis media);
- presence of tumors;
- hematoma or other head injury;
- fungal infection of the skin of the ears;
- dermatitis;
- allergic reaction;
- ear mites or other parasites that cause scabies.
All these conditions require specialist consultation and immediate treatment.
First, it’s worth taking a closer look at some of the most common diseases of furry pets.
Ear cleaning
The cat has hot ears: what does this mean?
In order to prevent ear diseases and as a hygiene measure, it is necessary to clean cats' ears regularly. You can do this yourself at home, and those who are afraid or do not know how to carry out this procedure can seek help from a veterinary clinic.
The most important thing is to create a calm environment and not scare the cat. It is not necessary to hold it by force, tug and wrap it, it is enough to gently win the pet’s obedience.
Ear cleaning
Use a small piece of cotton wool to wipe the auricle from accumulated wax. Then you can drop a couple of drops of saline solution and massage your ear so that the liquid penetrates as deep as possible into the ear canal. Next, use a cotton swab to clean hard-to-reach places. Ear hygiene should be carried out at least once a month.
Ear mites
A cat constantly scratches its ear and shakes its head if it has parasites. Infection with ear mites occurs from other cats; contact with street animals is especially dangerous.
This mite is not dangerous to humans; it lives and reproduces only in animals, causing ear scabies or otodecosis in them. Adult dogs and cats rarely suffer from scabies, but ear mites are found much more often in puppies and kittens.
The parasite is localized in the ear area or around it. In the animal's ears, you can notice a sticky brown liquid that dries and crusts over the skin of the ear. To diagnose the disease, a scraping is made from the skin in the ear area. The owner himself can notice the tick using a magnifying glass.
© shutterstock
Preventive measures
To avoid ear problems in the future, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive measures:
- Regular examination and cleaning of pets' ears, especially after returning from a walk. If you start this procedure at a young age, they quickly get used to it;
- exclude contact with stray animals;
- When bathing the cat, avoid getting water into the ears;
- carry out antiparasitic treatment;
- thorough cleaning of sulfur, dirt, foreign objects;
- once a week, instill antibacterial drops, which are freely available in veterinary stores. In this case, you need to drip into two ears at the same time, as they disinfect the cavity, change the smell inside the ear, creating an unfavorable environment for mites and parasites;
- Good nutrition in combination with vitamin therapy helps strengthen the immune system.
Important! At the first symptoms of ear disease in a pet, when the cat tries to scratch behind the ear, also when identifying wounds and crusts, an unpleasant odor and discharge, it is better to immediately seek help.
As a result, the initial stage of the disease can be treated faster and more effectively, and if complications arise, it can only cause great inconvenience to the pet. But making diagnoses and starting treatment on your own is very dangerous. After all, you can use medications for purposes other than their intended purpose, thereby aggravating the treatment process.
Sarcopid mites
If your cat's ears are shaking, this could be a sign that she has another type of mite. Such mites can spread not only in the ear area, but also in other parts of the cat’s body. They cause another feline disease, notoedrosis.
The head is affected first, then the entire body. The skin at the site of infection becomes dry and dense, covered with a crust, and the crust subsequently cracks.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to show the cat to a specialist. He will take a sample from the surface of the skin for analysis. Only the outermost layer from the inflamed area is scraped off; ticks can be seen there.
Both types of ticks provoke severe itching in the animal, forcing them to scratch the skin until it bleeds. Scabies that affects the ears can lead a cat to deafness or meningitis; in especially severe cases, the death of the pet can occur.
Prevention of ear diseases in cats
The best way to prevent the development of ear problems in cats is regular hygienic treatment with special lotions that do not contain alcohol or aggressive components.
It is advisable to accustom a cat to this not always pleasant procedure from an early age, when the kitten is easy to hold. After cleaning the ears, it is important to treat your pet with a treat, he will remember this and will resist less next time.
Cat ears are a special organ with the help of which animals not only pick up the smallest noises, but also orient themselves in space. The auditory function plays such an important role that, with the development of a serious illness, it can turn a healthy, active cat into a chronically ill animal and deprive it of many of the joys of life. Therefore, owners of cats, who are prone to showdowns and fights with their relatives, need to examine their pet daily for abrasions and damage.
Otitis and its varieties
Otitis is an inflammatory process affecting the external, middle or internal auditory canal. There may be several reasons for the development of such a pathology:
- excess wax in the ears;
- colds caused by prolonged exposure to the cold;
- foreign bodies entering the ear;
- infections;
- allergy;
- diseases of internal organs (liver, pancreas);
- fungus;
- complication of notoedorza or otodecosis.
To prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to diagnose the cause of the disease in a specialized laboratory. The veterinarian must take a swab from the cat's ear for analysis.
In addition to ordinary otitis, in cats there is otitis of a bacterial nature, when a secondary bacterial infection is added to the inflammation of the ear.
In this case, the so-called bacterial or secondary otitis develops. It can be recognized by the abundant discharge of pus.
© shutterstock
Otitis of mixed etiology also occurs in animals. This happens when the ear is affected by several types of otitis media at once. In this case, the disease occurs in a particularly severe form and causes serious complications.
Features of treatment depending on diagnostic results
It is important to remember that the specific treatment will depend on the diagnosis given to the animal. Therefore, you should not neglect a thorough examination of your pet and its examination at a veterinary clinic.
Treatment of otodectosis
If your pet is sick with otodectosis, then you should begin treatment immediately, since as the disease progresses, it can lead to membrane rupture, meningitis and inflammation. It is important to note that it is necessary to treat both ears at once. To avoid re-infection, the animal’s bedding and toys are either treated or replaced with new ones. First, the pet's ears are cleaned of pus and other existing contaminants. After this, you should choose a medicine for treatment, there are:
- ear drops (use once a week);
- drops on the withers (use once every three weeks).
The appropriate option will depend on the degree of development of the disease and the condition of the cat. The average course of treatment is one and a half months. To pour the medicine into the ears, use pipettes and syringes without needles. To enhance the effect, massage the auricle with your fingers. Light pressure will help distribute the medicine evenly, which will allow you to quickly get rid of ticks and their larvae.
The effect of medicinal drops is quite irritating, so the cat may react to the administration of the drug quite aggressively, which is the norm.
Help with abscess
An abscess should be opened by a veterinarian. The specialist will not only treat the resulting hole with antimicrobial agents, but also, if necessary, install drainage. The latter is necessary in order to prevent the re-accumulation of pus and completely heal the wound. In some cases, the animal is additionally prescribed antibiotics to help fight inflammation.
Removing wax plugs
Sulfur plugs are removed by pre-soaking them. For these purposes, saline solution and hydrogen peroxide are used. But a much more effective option are special lotions that can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy. They allow you to gradually soften the resulting plug. There is a high probability that after several procedures the cat will independently free itself from the formation that is interfering with it during the next shaking of its head. Do not use cotton swabs to remove the wax plug, as this will push it further and harm the animal.
Treatment of otitis media
In case of otitis, treating the ears with a special solution also plays an important role. There are antiseptic and drying lotions, as well as agents that dissolve sulfur. The appropriate option will depend on the type of otitis media. In this case, the selected solution is poured into the affected ear and the shell is massaged. In the initial stages of otitis, treatment is carried out up to twice a week. For severe illnesses, the solution is used up to four times.
Table: common medications for the treatment of ear diseases in cats
| Name | Indications for use | Packaging | Approximate cost |
| Amit |
| 20 ml | 165 rub. |
| Bars ear drops | Otodectosis | 20 ml | 180 rub. |
| Bars lotion |
| 20 ml | 130 rub. |
| Dekta | For the treatment of ear scabies complicated by otitis media | 6 ml | 110 rub. |
| Ectodes | Prevention and treatment of ear scabies (otodectosis) | 10 ml | 55 rub. |
| Otoferonol | Prevention and treatment of otitis not of tick-borne etiology | 5 ml | 85 rub. |
| Otoferonol Plus | Anti-mite, anti-inflammatory, disinfectant | 5 ml | 90 rub. |
| Otodepin |
| 10 ml | 45 rub. |
| Serco ear drops |
| 5 ml | 53 rub. |
| Otokan | Treatment of tick-borne otitis complicated by bacterial and fungal infection | 10 ml | 48 rub. |
Photo gallery: veterinary products for the treatment of ear pathologies
Amit is an antiparasitic agent, it is used to destroy demodectic and sarcoptic mites Bars - ear drops that have acaricidal, as well as mild anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects Bars ear cleaning lotion facilitates the removal of earwax, dirt and inflammatory exudate from the auricle and ear canal of dogs and cats Dekta - a complex acaricidal drug for external use Otodepin - ear drops intended for regular hygienic treatment of the ears of pets Otoferonol - an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drug intended for the treatment of otodectosis in cats and dogs
How to help your pet
Options for providing assistance to the injured animal are selected after establishing the exact cause of the pathological condition.
Removing wax plugs at home
The cat begins to shake its head if it is bothered by wax plugs. You can clean your pet's ears yourself. Saline solution or hydrogen peroxide will help in this situation. The selected product is instilled into the ear canal, 2-3 drops three times a day. The treatment course lasts 7 days . Subsequently, the animal usually successfully copes with this problem on its own.
If the cat is unable to remove the plug, the owner himself can remove it using a cotton-tipped swab or a piece of gauze. As a last resort, it is recommended to contact a veterinary clinic.
Surgical intervention
This type of treatment will have to be used if a tumor or foreign object is discovered in the cat that cannot be removed in any other way.
Surgery may also be recommended in cases of chronic otitis media, which results in narrowing of the ear canal.
Feline dermatitis
Has your cat started shaking his head all the time? Perhaps he has dermatitis. The disease is treated as follows:
- Remove the crust with a piece of cotton wool or gauze using hydrogen peroxide.
- Lubricate weeping ulcers with preparations with astringent properties (“Silver nitrate” 2%).
- Place drops containing novocaine into the ear canal. This will help relieve attacks of itching.
Continue treatment until symptoms disappear completely.
Fungal infections
If the fungus has entered the cat's ears, he begins to actively shake his head. In this situation you need to act like this:
- Every day, clean the ears with Chlorhexidine (0.05% solution).
- Give the animal the antifungal drug “Ketoconazole” for internal use, dose – 5 mg per 1 kg of cat’s weight. Take twice daily.
- Otibiovin drops will have an effective effect. They need to be instilled several times a day into the pet’s ear.
© shutterstock
Fleas
If there are fleas, you need to start treatment immediately. The following steps will help get rid of parasites:
- The ear needs to be treated with a special preparation against parasites.
- After some time, clean the auricle from dead insects with a piece of cotton wool soaked in hydrogen peroxide.
- The entire cat should be thoroughly washed with flea detergent.
If necessary, the procedure must be repeated.
Ear scabies mites
This attack is treated with special antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs:
- in the form of ear drops, ointment preparations (“Tactic” or “Amit”);
- in the form of injections (“Otodecnin”);
- Hydrogen peroxide and a soft tampon are used to remove purulent plaque in the ear.
Both ears must be treated at once, even if symptoms are found in only one.
How is notoedrosis treated?
Parasites must be combated with ointments and special detergents: tar, sulfur sediment, green soap.
In case of a particularly severe form of infection, use “Hyposulfite” and “Benzyl benzoate” to treat the affected areas.
If purulent formations appear, antibiotic treatment must be added.
© shutterstock
Otitis
Inflammation of the ear canal can be cured using a whole range of measures:
- if there is purulent discharge, it is removed with hydrogen peroxide and a piece of cotton wool;
- drops are instilled against otitis (Aurikan, Surolan, Oridermil, Oritsin, Bars);
- Novocaine is used to relieve pain (it is injected at the base of the animal’s ear);
- For allergic otitis, antihistamines are used.
For otitis media of a bacterial nature, the cat is treated with Otonazole, Mastiet, and Otibiovin. These are preparations for topical use.
Allergy in a cat
Animals, like people, also have allergies. Often such a reaction occurs to certain types of food or household chemicals. An allergy can be suspected if the cat shakes its ears, and at the same time its ears are clean . Treating such an ailment is simple: they use the same means that treat allergies in people (antihistamines for oral and local use).
Why does a cat scratch its ears?
If your pet begins to behave restlessly, constantly scratch itself and shake its head, the reason for this may be the animal’s predisposition to problems with hearing organs.
This category includes:
- Anomalies in shell structure.
- Anatomical structure of the organ associated with the characteristics of the pet’s breed.
- Congenital narrowing of the auditory canal.
Problems can arise from injury during brushing, or from excessive wax production. Blockage of the ear canal occurs if the cat has polyps, granulomas or other tumors in the ears.
The primary factors for ear diseases include:
- Presence of mites in the ears.
- Entry of a foreign object.
- Allergic manifestations.
- Failure in the functionality of keratinization processes.
- Hyper or hypoplasia of the sulfur and sebaceous glands.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Damage to shells.
Supporting secondary factors:
- Disturbances in the balance of ear microflora.
- Penetration of fungal infection.
- Inflammation of the meatus followed by otitis media and fibrosis.
- Poor hygiene and improper cleaning.
Hygiene problems
If the breeder does not clean the pet's ears, then dirt accumulates in the animal's shells. This acts as a favorable soil for the production of pathogenic microorganisms.
Severe scratching may indicate the appearance of wax plugs.
This happens due to malfunction of the glands and increased secretion.
Sometimes this is related to the cat's breed . But improper aggressive cleaning of the passage can also provoke an abundance of sulfur.
In this case, no special treatment is required; you can remove the plug yourself by softening it with saline solution. If it is deep and cannot be treated, then to prevent damage to the ears it is necessary to show your pet to a veterinarian.
Diseases that cause itching
Ear scratching can be dangerous. Cats scratch their ears due to dermatitis, seborrhea, and otitis media.
Otitis
Characterized by tissue inflammation affecting the middle and inner ear. The disease can be the result of a cold, allergies, foreign body penetration, mites, infections, fungus, excess sulfur in the passages, liver and pancreas diseases.
With secondary otitis, a bacterial environment occurs, which is accompanied by purulent discharge and an increase in the pet’s temperature.
Dermatitis
May be superficial, purulent or oozing. Its symptoms, from ordinary scratching to purulent non-healing wounds, will depend on this.
Dermatitis can occur independently or be a consequence of otitis media, parasitic infection, or allergies. Pathology must be treated after identifying the cause of the disease .
Seborrhea
It begins when the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted. A large amount of dandruff appears on the animal's fur. Problems with the glands may be congenital.
With dry seborrhea, there are no symptoms other than itching and dandruff; the weeping form of the disease leads to the loss of tufts of hair and the appearance of inflamed areas.
Hormonal disorders, problems with the thyroid gland, scabies, allergies, and dermatitis can cause pathology.
Parasitic lesion
Outdoors, your pet can become infected with fleas or ticks. Fleas live exclusively on animals and feed on their blood. Since insects are carriers of many diseases, during a bite they can transmit an infection to the cat.
When infected, small kittens develop anemia and allergic reactions. The animal may stop eating and lose a lot of weight.
Fleas live in a cat's fur. You can fight them at home using appropriate means. After treatment, your pet needs to be dewormed 2 weeks later.
Otodecosis (ear mite infestation) can affect one or both ears.
Scabies, caused by a parasite, causes the animal to scratch the shells until blood appears.
The pet becomes restless and nervous, he sleeps poorly, and refuses to eat. A sticky secretion is released from the ear canal, gluing the pile, which gives the cat a sickly appearance.
The tick itself is difficult to detect, but you can see its waste products and dark brown crusts in the depths of the passages.
The disease is contagious, so at the first manifestations it is necessary to take your pet to the veterinarian.
Infectious causes
Inflammation of the ears can spread throughout the entire auditory system: the disease can affect the concha, ear canal, middle and inner ear.
Inflammation can begin after untreated scabies, with improper care of the cat, or an allergic reaction to household chemicals or food.
The clinical picture in this case will depend on the degree, cause and location of the disease. Infectious pathology is accompanied by fever, apathy, refusal to eat, poor coordination of movements, and irritability.
In addition to scratching, the cat will constantly tilt its head towards the affected ear. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable, otherwise the animal may become deaf, and if the infection enters the brain, it will die.
What else causes itching?
A cat may scratch its ears when a foreign object gets into the ear canal. You should not take it out yourself - this can damage the eardrum.
The cat experiences itching and discomfort when tumors appear in the ears (tumors, polyps, hematomas). You cannot treat them yourself .
In the case of a hematoma, surgery and pumping out of the contents are often required. If a tumor occurs, the doctor diagnoses the disease and makes prognoses, choosing treatment.
The sooner surgery is performed, the greater the chance of a favorable outcome and preservation of the patient’s hearing.
Problems with the ears can occur after water procedures if the breeder did not use a special cap and water got into the auricle. Fluid stagnation causes inflammation, which can subsequently develop into a severe form of otitis.
Problem for small kittens
A kitten's anxiety can be due to any of the reasons listed above, but most often the problem is associated with otodectosis. Ear scabies occurs when infested with mites.
These parasites cannot be seen with the naked eye, which complicates the diagnosis and treatment process. Mites produce in the ear canal and shell.
Due to the pain, the kitten may meow pitifully and shake its head. If there is purulent discharge, you should immediately take your pet to the veterinarian, otherwise meningitis and death are possible.
When to see a doctor
For any cat, scratching its ears is a normal process, which is a hygienic procedure that helps the animal get rid of dirt and foreign bodies. But when it becomes permanent, and the pet experiences great discomfort and anxiety, it is necessary to show it to a doctor. Only by identifying the reasons for this behavior can effective treatment methods be selected.
If a cat has otitis media, measures taken to get rid of ear mites can lead to serious consequences, including complete hearing loss. A visit to the clinic should not be postponed if:
- Ear scratching causes anxiety, causing the cat to shake its head in irritation.
- The animal becomes nervous.
- The cat scratches its ears vigorously more than 10 times a day.
- Small wounds appeared on the surface of the ears.
Detection of one or more of the listed symptoms is a serious reason to visit a doctor.
Why does a cat scratch behind its ear until it bleeds?
After hunting fun in nature, dirt and remnants of “prey” remain . This leads to an unpleasant odor. By licking itself, a cat not only removes foreign objects (dirt, food, etc.) from its fur, but also smells.
First of all, the cat washes its face and ears. But sometimes an animal literally “tears” its own ears: it constantly pulls them with its front and hind paws, shakes its head, and rubs its ears hard against various objects in the house.
If a cat scratches behind the ear until it bleeds, it means that the itching and/or pain is very strong. You need to contact your veterinarian immediately.
How to treat a combed area
The veterinarian should tell you what to do to eliminate the itching. Often, self-medication or delayed consultation with a doctor leads to serious problems.
At home, the most primitive activities are allowed. You can take a cotton swab, hydrogen peroxide, and treat the affected area.
Instead of peroxide, an alcohol solution or brilliant green is also used. You cannot apply ointments to your ears, use traditional medicine methods, or perform other manipulations yourself.
Symptomatic treatment
Physiological tremor does not require treatment.
To understand that a cat is shaking its head because it is in pain, it is important to observe it. The following signs should alert you:
- the animal not only shakes its head, but also actively itches (to the point of wounds and abrasions);
- pus or ichor flows from the ears;
- the cat does not lay its head on a certain side;
- the animal's appetite decreases or completely disappears;
- there is a shaky gait, movements are not coordinated;
- the cat meows loudly and pitifully or, on the contrary, becomes lethargic and tries to hide from prying eyes.
In case of pathological jerking of the head, the diagnosis must be made by a doctor. To do this, he will examine the cat's ears and take blood tests. If no external signs of pathology are found, the veterinarian will perform an ultrasound or computed tomography. After making the correct diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe the appropriate treatment:
- For the treatment of otodectosis, antiparasitic ear drops may be sufficient; for the treatment of otitis, antibiotics will have to be used.
- It is also best to entrust the removal of foreign bodies from the ear to a veterinarian. After the procedure, the specialist will treat the ear with antibiotics and prescribe drops that will help avoid infection.
- Antifungal therapy involves treatment with chlorhexedine (rinsing the ears with a solution) and treating the ears with Otibiovin drops. Veterinarians also prescribe internal administration of Ketokenozol. But it must be given to your pet strictly in the dosage recommended by the veterinarian.
- Dermatitis is treated with hydrogen peroxide and treatment with ointments that have astringent properties, for example, 2 percent silver nitrate. Dropping a few drops of novocaine into the ears will help relieve itching.
- If neoplasms occur, the issue of surgery is decided. Most often, the ear and hearing can be preserved when growths and tumors are removed.
- Neurological disorders and failure of one or another organ require specific treatment, which can only be offered by an experienced veterinarian.
- Multiple organ diseases and liver failure require treatment of the underlying disease. When recovery occurs, the tremor will go away.
Therapy methods
Treatment depends on what problem is causing the itching. This could be dermatitis, fungus, ear mites, otitis media and other pathologies.
Dermatitis should be treated with drops containing novocaine. Using a swab dipped in hydrogen peroxide, the crusts are carefully removed, and the ulcers are treated with an astringent ointment.
Fungal infections are treated with antifungal agents.
Ear mites are removed by mechanical cleaning of the ear canals. A swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide is used. Additionally, medicinal drops and ointments are used. In case of advanced disease, injections with antibiotics are prescribed.
Therapy for otitis media is selected depending on the disease. First of all, you need to treat the ears with a cotton swab with peroxide.
Immediately after these manipulations, treatment procedures using the following drugs begin:
- Leopard;
- Otoferonol premium gold;
- Aurikan;
- Oricin;
- Surolan;
- Ordermil.
Tick-borne otitis media is treated comprehensively. Drugs prescribed:
- Anandin;
- Tsipam;
- Decor.
Antimycotic agents are also used:
- Clotrimazole ointment;
- shampoos Nizoral, Sebazol.
The products are applied to the inside of the ear. They cannot be washed off, otherwise there will be no therapeutic effect.
For fungal and yeast forms of otitis, it is necessary to strengthen the animal’s immunity.
The bacterial variety of pathology often leads to the development of diseases that are difficult to treat.
Local medications are prescribed:
- Otonazole;
- Otibiovin;
- Mastitis.
Advanced forms of the disease are treated with novocaine blockades with antibiotics. After the course of treatment, preventive treatment is carried out. This way it is possible to prevent relapses .
An allergy is diagnosed when a pet scratches its ear, but there is no discharge. In this case, local and systemic antihistamines are used.
Special drops are used against fleas; they are applied to the withers. If the animal is often outdoors, then an anti-flea collar is used.
Detected hematomas, formations, and polyps are removed surgically. Identified foreign bodies are removed immediately. The animal's ears are treated with antiseptic drugs.