When the kidney structures become inflamed, pyelonephritis occurs in cats. The disease has several varieties and is accompanied by severe pain, vomiting, and impaired urine output. The disease is dangerous due to complications such as kidney failure, kidney abscess, and sepsis. Therefore, at the first symptoms, the owner should have the animal examined by a doctor, who will prescribe medications, diet, herbal decoctions and give preventive recommendations. The prognosis depends on the timeliness of treatment.
According to the observations of veterinarians, kidney inflammation is diagnosed in cats 3 times more often than in dogs, and animals older than 7-8 years are at risk.
Pyelonephritis in cats
The name of this disease has Greek roots, and if you decipher it, you can understand that we are talking about the inflammatory process of the renal pelvis, mainly of bacterial origin.
The renal pelvis is a thin-walled sac that acts as a reservoir for urine. When the kidneys are damaged, this organ takes one of the main hits. There are several ways by which the infection enters the kidney:
- Ascending: with it, hostile microflora rises from the underlying urinary tract through the urethra, bladder and ureter;
- Descending or hematogenous: with this route, irritating factors enter the kidney through the bloodstream from other inflammatory foci.
Traditional methods of therapy
To treat this pathology and prevent its development, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants can be used. One of the effective drugs is prepared as follows. You need to take dried dandelion grass and birch leaves in a ratio of 2 to 1, chop and mix well. A large spoonful of raw materials is placed in a deep plate and poured with a glass of boiling water. Leave in a water bath for 30 minutes. Then the mixture is cooled. Strain the mixture to remove any remaining grass and leaves. The resulting liquid is combined with a glass of cold boiled water. Give to the animal 4 times a day warm 30 minutes before feeding. Therapeutic dose – 10 milliliters, prophylactic – 5.
In addition, to eliminate the symptoms of pyelonephritis in cats, infusions and decoctions of juniper berries, birch buds, rose hips, and calendula are used.
However, you should not treat the animal with these remedies yourself. Before use, consult a veterinarian.
Causes
The main causes of pyelonephritis in cats include the following factors:
- damage to the renal pelvis by mechanical irritants - these are kidney sand and stones at various stages of urolithiasis in cats;
- obstruction of the urinary tract and, as a consequence, stagnation of urine;
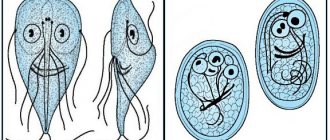
- entry into the kidneys due to various circumstances of opportunistic microorganisms; – they are the most common culprits of pyelonephritis in cats. These are Escherichia coli, Proteus, staphylococci, enterococci.
- negative effects on the kidneys of chemical, toxic (various poisons), physical (cooling, injury), radiation factors.
Causes of the disease
The main provoking factors can be listed:
- Congenital defects associated with the structure of the urinary system.
- Stone formation.
- Exposure to microorganisms (Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, Proteus).
- Cystitis.
- Mechanical damage to the abdominal cavity.
- Urinary retention.
- Exposure to excessively low temperatures and radiation.
- Poisoning with household chemicals (for example, varnish or paint), poisonous plants, poor quality food and other types of toxic substances.
- Side effects from the use of medications, allergic reactions.
If treatment of pyelonephritis in a cat is not carried out promptly and competently, the disease leads to dire consequences. The animal experiences severe renal dysfunction. Therefore, owners need to immediately contact a specialist if their pet shows signs indicating the presence of an illness.
You should not try to treat your pet yourself. Incorrectly selected therapy will only worsen his condition.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in cats
It is not easy for a cat owner to diagnose pyelonephritis. As with other diseases, the most important factor for a favorable outcome is the speed of contacting professionals, a veterinary clinic. Pyelonephritis is an insidious disease, in the initial stages of which it is very difficult to understand whether the cat is sick.
The first signs are a depressed pet, apathy, decreased appetite and lack of mood. Next, the owner should monitor how the cat is urinating. If it occurs with a violation of the frequency and amount of urine excreted, if it is painful for the cat, and is accompanied by a plaintive meow, then in this case it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinary clinic. Veterinarians at the City Veterinary Oncology Center are recognized experts in their profession, including the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases in cats. Pride veterinarians regularly attend conferences, seminars, and master classes with the participation of foreign experts in the field of treatment of kidney diseases in cats. All the most modern methods and treatment regimens for these diseases, including pyelonephritis in cats, are adopted. And the most important thing is that these methods are used with great success and give positive results.
So, our main assistants for any diseases of pets are the speed of contacting a veterinarian, correct diagnosis, an accurate diagnosis and an optimal treatment regimen.
Features of nutrition during the treatment period
Considering the importance of dietary nutrition during the treatment of kidney diseases, only a doctor can prepare a therapeutic diet. Your veterinarian recommends purchasing certain foods designed specifically for cats with kidney disease. Feed is available in the form of dry and wet rations. They are enriched with useful macro- and microelements, vitamins necessary to restore the animal’s health.
You can do without specialized feed, using natural products to feed the animal, without salt, with a minimum content of phosphorus, sodium and protein. If the owner switches the animal to specialized food during the treatment period, its consumption should continue for life.
The transition to a new diet should be smooth. Abruptly stopping habitual foods and switching to new foods will be very stressful for a weakened animal. In addition to nutrition, it is very important to provide the animal with the correct drinking regime. Water must be boiled or filtered, and it must be changed in the animal’s tray daily.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing pyelonephritis in cats, the professional skills and knowledge of a veterinarian play an important role, as well as modern and accurate laboratory equipment. Both of these factors are directly related to predominantly positive outcomes when visiting the Pride veterinary clinic with pyelonephritis in cats.
Pyelonephritis, like any other diagnosis, is made in a complex manner. The first hint of this disease may be pain in the kidney area upon palpation. This disease causes fever. But to confirm guesses, laboratory diagnostic methods are required, such as biochemical analysis of blood and urine. These diagnostic techniques are carried out using modern and precise devices. In addition, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity may be necessary. For this purpose, the Pride veterinary clinic has professionals who specialize in ultrasound diagnostics.
Diagnosis of kidney problems in cats
Based on clinical symptoms, the owner may suspect that the cat has kidney pain, but only a specialist can determine the type of disease. The veterinarian collects anamnesis and prescribes a general urine test.
If necessary, blood is examined for creatinine and the ratio of serum protein fractions, and an ultrasound is also performed. Bacteriological culture identifies the causative agent of infection, as well as its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment and prevention of pyelonephritis in cats
First of all, the most important thing is a loading dose of antibiotics. This is important because it is necessary to suppress pathogenic microflora, which is responsible for the development of the inflammatory process in the renal pelvis. It is necessary to take into account the presence or absence of kidney stones. If they are present, they should be dissolved and removed from the body. Diuretics are used to remove remnants of kidney stones. And, of course, do not forget about painkillers to avoid painful shock and relieve acute pain in your cat. You should very carefully and clearly follow all the instructions of the veterinarian. Pyelonephritis does not like cleanliness and order, so the cat must be looked after and monitored. The owner needs to be observant and attentive to his pet, and if necessary, contact professionals, veterinarians.
Author of the article: veterinary therapist Elena Sergeevna Avdasheva
Kidney functions
Kidneys are vital paired organs in a cat that are shaped like a bean. The structural units that form kidney tissue and produce urine are called nephrons. Since their number is established during birth and they do not have the ability to recover, any pathological processes in the kidney tissues are very dangerous and irreversible.
Main functions of paired organs:
- removal of excess fluid from the body through the formation of urine;
- filtration of metabolic waste products;
- regulation of blood pressure;
- hormone production;
- maintaining acid levels in the blood;
- normalization of blood electrolyte composition.
Why is pyelonephritis dangerous in cats and how to get rid of it
Pyelonephritis in cats is a serious disease in which the renal pelvis is affected by a bacterial infection. Proper treatment for this problem is necessary, because without it, the animal may develop kidney failure. To prevent this from happening, the owner must know the symptoms of pyelonephritis, which will allow him to seek veterinary help in time and eliminate the risk of complications.
Types of diseases
There are many types of diseases, the result of which is diseased kidneys in a cat. They all have similar symptoms, so diagnosis should be carried out by a veterinarian.
The most common diseases of this nature diagnosed in cats are:
- Nephritis is a number of names of inflammatory diseases that occur in chronic or acute form and occur in animals that have suffered from infectious diseases.
- Renal pyelonephritis, chronic or acute, is a disease in which purulent inflammatory processes occur in the renal pelvis or parenchyma. This disease can infect both organs. It develops as a result of chronic nephritis or bacterial damage to the urinary system.
- Polycystic disease is a hereditary disease in which small cavities with fluid form in the kidney tissue and grow over time. Initially, a small kitten does not show any concern with polycystic disease, because the main symptoms appear much later. Since this disease is incurable, therapy is aimed at prolonging the life of the animal. Cats at risk for this disease include Persian, Himalayan and other exotic breeds.
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the renal tangles, spreading to nearby tissues, which occurs against the background of chronic diseases of internal organs, allergies, liver damage and other negative factors.
- Amyloidosis is the deposition of protein in the kidney tissue, which leads to kidney failure. Most often, Abyssinians and Somali cats suffer from this disease. Treatment is aimed at reducing pain symptoms and slowing down the destructive process. An ultrasound can show that the kidneys have significantly decreased in size.
- Nephrosclerosis is a change in kidney tissue and a decrease in organ size, which leads to a decrease in their functionality. It can occur against the background of a previous infectious disease.
- Hydronephrosis is a circulatory problem in one or both kidneys. It can occur throughout life due to impaired fluid circulation in these organs or be inherited. An ultrasound examination shows an increase in the size of the kidneys, the presence of fluids, tumors and stones in them.
- Chronic renal failure - develops against the background of the above-described cat diseases in the absence of treatment and the presence of severe kidney damage. This disease is one of the main causes of death in older cats, as it leads to complete failure of paired organs.
Reasons for the development of the disease
This disease can develop in cats regardless of gender and age, but most often it is diagnosed in purebred, neutered and old cats. The course of this disease can be expressed in acute and chronic forms.
Reasons for the development of the disease:
- Slowing down the process of urination, stagnation of urine.
- Kidney damage from bacterial infections.
- The appearance of stones in the urinary tract.
- Damage to the body and its individual organs by parasites.
- Reaction to certain drugs and harmful substances.
Regardless of the reasons that caused this disease , it needs urgent treatment, because the more neglected it is, the more difficult it is to fight it.
Causes of pathological processes
There are many reasons for the development of kidney disease in cats, but most often these are shortcomings on the part of the owners associated with improper care or poor living conditions.
Possible causes of kidney disease in cats:
- allergy;
- infectious diseases;
- food or poison poisoning;
- exposure to toxic substances or microbes on the animal’s body;
- injuries;
- parasites;
- age from 8 years;
- genetic predisposition;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- bronchopneumonia;
- the predominance of meat and fish in the diet (exceeding the level of phosphorus and protein);
- weight imbalances up or down;
- lack of fluid intake;
- drug overdose;
- drinking poor-quality tap water;
- excessively salty or sweet foods;
- minimal physical activity;
- hypothermia, drafts;
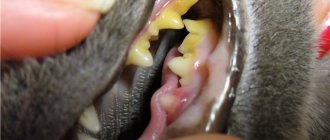
- diseases of the gums and teeth;
- urinary retention.
Due to the fact that kidney diseases are diagnosed in late stages, determining the exact cause of their occurrence is difficult, and in some cases, almost impossible.
How to recognize the disease
If there is no treatment, pyelonephritis can lead to irreparable consequences: the development of renal failure, sepsis and death. For this reason, it is very important to pay attention in time to warning symptoms that may indicate the development of the disease. Having noticed one or more signs of pyelonephritis in a cat, the owner is obliged to take the animal to the veterinarian as soon as possible.
The main symptoms of pyelonephritis in cats:
- The cat is in a feverish state;
- The animal is constantly lethargic and apathetic;
- Increased thirst (polydipsia);
- Vomiting, lack of appetite, diarrhea;
- Increased amount of urine;
- Pain when urinating, indicated by the cat’s plaintive meow;
- When touched on the back or stomach, the cat experiences pain and escapes;
- The color and smell of urine changes;
- The animal's pulse and breathing quicken.
As a rule, with pyelonephritis, the above-described signs are observed in combination, so they can be easily noticed even by an owner who is far from veterinary medicine. But treatment should only be carried out by a specialist. Therefore, at the first symptoms of pyelonephritis, you should contact your veterinarian.
Pyelonephritis can affect not only the kidneys, but also the ureters and urethra. The impetus for the development of the disease is often problems with the immune system and blood supply to the kidneys. Also, pyelonephritis can be accompanied by the appearance of stones in the urinary organs, which injure the membranes of the bladder and kidneys, which contributes to the development of infection. If the cat is not treated, then over time the ureters may become clogged and blood poisoning may develop.
Feeding cats with kidney disease
For all kidney diseases, a therapeutic diet is prescribed. Properly selected food can prolong a cat’s life and improve its quality. Only a doctor prescribes a diet for sick animals - experiments in such a serious matter can lead to a sad outcome.
Veterinarians usually recommend switching the animal to ready-made medicated food. It is difficult to create a menu from natural products that will meet the needs of a sick cat.
Recommended brands of food:
- Eukanuba Renal;
- Clan Vet RENAL;
- Hill's Prescription Diet K/D Feline Renal Health;
- Brid VDC Renal;
- Farmina Vet Life Renal;
- Royal Canin Renal RF23;
- Pro Plan Veterinary Diets Feline UR Urinary;
- Monge Grain Free Vetsolution Renal Feline;
- Purina Veterinary Diets N;
- Sanabelle Urinary.
Read a detailed article about how and what to feed cats with kidney disease.
Diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of pyelonephritis in a cat, the veterinarian will prescribe an examination for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. It is worth noting that some symptoms of pyelonephritis are similar to those of nephrosis, polycystic kidney disease or nephritis. Therefore, the specialist’s task is to exclude these diseases.
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and urinary organs;
- analysis of urine from the bladder and renal pelvis for the presence of bacteria;
- kidney biopsy;
- radiography;
- excretory urography.
Diagnostic methods to confirm the presence of the disease are determined by the veterinarian depending on the complexity of the symptoms and the pet’s individual medical history. Also, the choice of examination method depends on the conditions of the veterinary clinic and the availability of special diagnostic equipment. If the examination reveals stones in the kidneys or bladder, it is necessary to get rid of them, and only then begin treatment. Otherwise, the therapy will not give a positive result.
The prognosis for treatment of pyelonephritis depends on the severity of the disease, the age of the cat and the timeliness of veterinary care.
Causes of kidney diseases:
Often it is not possible to accurately determine the causes of the disease. The most typical are: age, genetic predisposition or congenital anomaly, ecology, infectious and systemic diseases (for example, diabetes), poisoning, trauma, unbalanced nutrition.
All animals over 7 years of age are at risk. They should be examined annually by a veterinarian, have blood tests, urine tests, ultrasounds and blood pressure checked.
Treatment of the disease
Pyelonephritis is a serious disease that is very difficult to cure. In order to get rid of it, you must follow the veterinarian's instructions flawlessly.
Treatment of pyelonephritis involves the following:
- The use of antibiotics to rid the renal pelvis of a bacterial infection that causes pyelonephritis.
- Providing the cat with cozy and comfortable living conditions, protecting it from stress and overwork.
- Adjusting your cat's diet. It should contain fermented milk products and vegetables. All other food is prohibited during the treatment period.
- Use of painkillers.
- Use of antimicrobial drugs.
It is important to note that antibiotics should only be given to a cat as prescribed by a doctor. Only a veterinarian will be able to select the drug and the correct dosage, which will help in treatment and not harm . Typically, for pyelonephritis, the use of antibiotics alternates with antiviral drugs. Droppers or herbal tinctures that have a diuretic effect may also be additionally prescribed.
The antibiotic is selected based on the results of urine tests. Treatment of pyelonephritis is quite long. As a rule, it is about one and a half months. In some cases, it may be necessary to treat the animal in a hospital. In any case, the treatment process should occur under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Prevention of kidney diseases
General preventive measures:
- Proper care and comfortable maintenance of your pet.
- Avoiding hypothermia of the animal.
- Providing a balanced diet for your cat.
- Preventing falls from heights.
- Preventing the animal from walking on its own.
- Vaccination according to the vaccination schedule.
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Water quality control.
- Organization of proper nutrition.
- Regular preventive examinations with a veterinarian.
Preventive measures
The main rule that will help avoid the occurrence of pyelonephritis in a cat is timely treatment of any diseases. Infection of the renal pelvis can be caused by gynecological, colds, as well as problems with the animal’s genitourinary system. Therefore, it is very important to contact a veterinarian at the first signs of illness. In addition, an important condition for preventing pyelonephritis is keeping the cat warm and dry. You should regularly take the animal for a walk and provide it with a balanced diet, which will contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals for the normal functioning of the body.
By bringing a cat into the house, the owner obliges himself to take care of it. The main manifestation of care is attention to your pet, thanks to which you can notice the disease in the early stages and quickly get rid of it without consequences for the small furry creature.
Symptoms
As a rule, kidney disease in cats in the early stages is asymptomatic, which complicates diagnosis and aggravates the animal’s condition. And when significant damage occurs in the kidney tissues, causing loss of organ function, obvious symptoms become noticeable.
Kidney disease in cats in the later stages occurs with the following symptoms:
- increased thirst;
- dehydration of the body;
- frequent or infrequent urination, as well as its absence;
- painful urination;
- laboratory tests reveal increased levels of protein in the urine;
- blood in the urine, darkening of it;
- bad odor from the mouth, the presence of inflammation, ulcers and cracks in the oral cavity;
- lack of activity, weakness, drowsiness;
- pale gums;
- refusal of food;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- retinal detachment;
- The cat's desire to sleep on cold surfaces.
Reasons for the development of pyelonephritis, their classification.
The direct causes of the development of pyelonephritis are:
- cat/cat colds;
- reduction of the body's own defenses;
- pyogenic processes in internal organs or tissues;
- any inflammatory mechanisms in the urinary system: prostatitis in cats, cystitis, purulent inflammation of the uterus in cats (pyometra).
There are also a number of circumstances that create conditions for the development of purulent pathologies in the kidneys:
- stagnation of urine;
- mechanical irritation of the renal tubules with sand and sand stones;
- disturbances in urination against the background of abnormalities in the functioning of the entire urinary system;
- poisoning with poisons that are excreted by the kidneys;
- breakdown of urine directly in the kidneys;
- the introduction into the kidneys of opportunistic bacteria, which under certain conditions multiply, causing inflammation in the kidneys - enterococci, E. coli, staphylococci, etc.
According to their source, pyelonephritis is divided into:
According to the method of manifestation:
Possible complications
Kidney diseases should be treated as soon as an accurate diagnosis is made. If the acute stage of renal pathology is not treated in a timely manner, it quickly turns into a chronic form with constant relapses.
Disorders of the urinary system organs lead to complications for the entire body. The immune system is weakened, constant stagnation of urine creates a favorable environment for the rapid development of infectious diseases.
There is a high probability of developing renal failure due to untreated diseases. It leads to a critical decrease in calcium in the body, anemia occurs, bone tissue loses its mineral elements and becomes fragile. Any careless movement or jump from a height can cause fractures.
Against the background of kidney failure, the organ loses the ability to produce the hormone responsible for the production of blood cells - red blood cells. Kidney failure, which develops against the background of untreated kidney disease in cats, can cause death.
Clinical manifestation of kidney inflammation.
Acute manifestations of the disease or exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis in cats are accompanied by:
- increase in general body temperature and fever;
- deviations in the process of urination: pain (the cat meows), increased urge, and increased volume of urine excreted;
- outwardly the cat looks depressed, refuses food, but is very thirsty;
- renal colic;
- the ESR index in the blood increases, the level of leukocytes increases;
- with uremia (exudation of toxic protein products into the blood) - there will be vomiting;
- abnormalities in laboratory urine tests - the environment is alkaline, there is protein, renal epithelial and bacterial cells are detected;
- with a long course of pyelonephritis, all the phenomena of kidney failure develop.
Pyelonephritis in cats (treatment) should only be handled by a veterinarian, because an incorrect algorithm or incorrectly selected medications will lead to the transition of the acute form to the chronic form, and then to renal failure.
- When a cat has pyelonephritis, it is imperative to follow a diet that will contain lactic acid and vegetable ingredients.
- For pain, it is important to use painkillers.
- During treatment, the cat should not be exposed to any stress and should be calm and clean.
- A preference for antibiotic therapy is required. The most commonly prescribed drugs are fluoroquinolones (eg, ciprofloxacin) or sulfonamides (sulfaethidol). The use of other groups is unjustified, especially when the animal is admitted to the clinic in such conditions that there is no time to select antibacterial agents. Usually, a double dosage is given within a week, a 14-day break, and a repeat at the usual dosage for up to 2 weeks. This helps prevent the transformation of the acute form into a chronic one.
- Diuretics may be prescribed to speed up kidney filtration.
- For purulent pyelonephritis, corticosteroids are used.
- If uremia is detected, droppers with glucose and potassium chloride are placed.
- To boost immunity, immunostimulants are prescribed to increase the body’s antibacterial resistance.
With timely detection of the disease and correctly prescribed treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable, and complete recovery is possible.
When the case is advanced, the acute disease becomes chronic with repeated exacerbations and attenuations. With a very long presence in the body, pyelonephritis will certainly develop into kidney failure.
Treatment
It should be repeated that this pathology is not completely eliminated. The kidneys return to a state of maximum functionality, to the extent possible for a particular degree of damage. You will have to monitor your kidney function for life, at regular intervals determined by your doctor, taking the necessary tests. Treatment will directly depend on the course - acute or chronic.
Procedure for treating acute renal failure
- Identifying and eliminating the root cause.
- Removing the animal from a state of dehydration.
- Elimination of hemolysis.
- Removing intoxication.
- Hemodialysis (in especially severe cases).
- Recovery diet.
Treatment procedure for chronic renal failure
- Maintenance diet and appetite stimulation.
- Normalization of blood pressure and compensation of heart failure.
- Restoration of water-salt balance, acid-base and mineral.
- Elimination of signs of anemia.
- Fortification.
- Hemodialysis.
List of medications used
Below is a list of the most commonly used medications for kidney failure. Only a veterinarian can combine medications and draw up therapeutic treatment regimens from them! It is strictly forbidden to try to self-medicate your pet!
Antibiotics
To eliminate the primary factors of kidney failure (pyelonephritis), fluoroquinolone antibiotics are prescribed, which do not put additional stress on the kidneys:
- enrofloxacin: intramuscularly 5 mg/kg cat body weight for 5 days. In rare cases, you can extend the course to 7-10 days;
- ciprofloxacin: 5-15 mg/kg body weight for up to 5 days.
Hormonal drugs
The use of glucocorticoids helps suppress immune reactions that provoke glomerulonephritis, increase diuresis (while suppressing antidiuretic hormone), relieve swelling directly in the renal tissues, and also increase appetite in cats.
- In the acute course of the disease, it is best to start with: dexamethasone: 0.2 mg/kg intramuscularly or intravenously until the general condition stabilizes and the water balance is normalized.
- methylprednisolone: 3 mg/kg intravenously once daily for 4-5 days;
Diuretics
They are prescribed in any case: furosemide (considered best for renal failure): 0.1 ml/kg twice daily into the muscle. Monitor the effect. In its absence, the permissible increase in dosage is 2-3-4 times.
Potassium-containing drugs
The loss of potassium is replenished with special potassium-containing drugs, but always under laboratory control of its content in the blood: panangin (asparkam). Application: orally, 1 tablet/10 kg of weight up to 3 times a day until the condition stabilizes.
Laxatives
Laxatives for stool retention and prolonged constipation:
- lactulose (Duphalac), lactusan: orally 0.5 ml/kg until stool normalization. Can be taken until the end of the entire treatment therapy, because is not addictive;
- bifidum 791 BAG - live bacteria that improve intestinal digestion and speed up bowel movements: 1 dose per 1 cat orally with a small amount of chilled boiled water throughout the entire course of treatment.
Rehydration and nutrient solutions
Intravenous or subcutaneous drips with rehydrating and nutrient solutions that restore salt and mineral metabolism, as well as eliminate dehydration:
- Ringer-Locke solution + glucose 40%: 500 ml + 50 ml;
- trisol: calculated 7% of total body weight once;
- rehydration mixture of glucose solution 40% + vitamin C 5% + saline: 15-55 ml/kg by slow dropper, depending on the severity of dehydration.
Antiemetic therapy
- metoclopramide: 0.5-0.7 mg/10 kg body weight subcutaneously or intramuscularly as vomiting occurs, but not longer than 5 days;
- ondansetron: 0.5 mg/kg into muscle symptomatically.
Reduced pressure
Reducing blood pressure is achieved with ACE inhibitors:
- enalapril: the dosage is selected individually for each sick animal. The target (maximum) effective dose is 0.5 mg/kg of the cat’s body weight – you cannot give it all at once, so as not to provoke a sharp drop in blood pressure and collapse. You need to start with 1/8-1/9 of the target dose to give the body time to get used to the hypotensive effect. Increase the dose gradually until the condition normalizes. Maintenance dose: ½ part of the target dose;
- Ramipril (inactive prodrug): 0.125 mg/kg body weight once daily.
For the cardiovascular system
Cardiogenic drugs to support the state of the cardiovascular system:
- cocarboxylase: 1-1.5 ml per cat (5 mg/kg) once or twice a day intramuscularly (sometimes done subcutaneously or intravenously);
- Riboxin: 0.1-0.2 g/10 kg intramuscularly or intravenously;
- sulfocamphocaine: 0.1 ml/kg body weight subcutaneously until the condition normalizes.
Detoxification products
- enterosgel: 20 g/10 kg of pet’s weight once a day;
- liarsine: 0.5-2 ml per animal 1-2 times a day for 10-14 days;
- plasmapheresis (removal of toxins from the bloodstream by purifying blood plasma using protein-saline solutions);
- sirepar: 1.5-3 ml every day until signs of intoxication subside;
- Lespenefril (to remove nitrogenous substances from the blood): ½ tsp. per animal with a small amount of water inside 1 time/day for a month.
To eliminate anemia
Maintaining the hematopoietic process to eliminate anemia is achieved with hematopoietic drugs:
- Recormon: 25-50 IU/kg 1-3 times a week until the hematocrit level reaches 30%. The drug is taken continuously if it is not possible to achieve the desired level;
- ursoferran: once in a dose of up to 0.5 ml per animal into the muscle or subcutaneously;
- hemobalance: for a cat weighing up to 5 kg - 0.25 ml, over 5 kg - 0.5 ml intravenously or intramuscularly 1-3 times a week for a course of 7-10 injections.
Hemostatic drugs
In acute renal failure, it is necessary to use hemostatic agents to prevent gastrointestinal bleeding;
- dicinone: 0.5 ml up to two times a day for 5-7 days;
- Vikasol: 1-2 mg/kg once a day. Average course: 3-5 days.
- aminocaproic acid: 8-10 mg/kg orally (by mouth).
With complete lack of appetite
A nutrient mixture is prepared, which is given hourly in 5 ml doses using a syringe without a needle or a small rubber bulb. Mixture composition: 100 ml milk and water, 1 tsp. starch, 2 tsp. sugar - bring to a boil. Then a whole raw chicken egg and 1 crushed mezim tablet are added to the cooled solution. As appetite appears, the time interval decreases and the amount of mixture increases.
To support the gastrointestinal tract
With kidney failure, the production of gastrin (the hormone that activates digestion) is inhibited, which causes a lot of stomach acid to form in the stomach. In this case, urea in the stomach turns into ammonia, irritates the gastric mucosa and can provoke a peptic ulcer. To maintain the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and protect the gastric mucosa, the following is prescribed:
- ranitidine: 2 mg/kg by slow intravenous injection or 3.5 mg/kg orally twice daily at regular intervals;
- famotidine: 0.5-1 mg/kg intravenously or subcutaneously up to twice a day.
Features of treatment
Treatment of kidney diseases is carried out comprehensively, and only a specialist can deal with it. Treatment involves performing certain tasks and processes:
- Establish the cause (make the correct diagnosis).
- Stop the inflammatory process (antibiotics).
- For edema, diuretics are prescribed.
- Provide the cat with a dry, clean place.
- In case of intoxication - administration of hemodez.
- Diet.
- Prescription of vitamins.
Prevention
Important and necessary in the fight against kidney disease in cats is not only proper treatment, but also strict implementation of preventive measures:
- in cases of stomach poisoning or colds in an animal, be sure to consult a doctor and treat them until complete recovery, strictly following all the veterinarian’s recommendations;
- cat food must be fresh, high-quality, balanced;
- protect the animal from hypothermia and lying for a long time on wet and cold ground;
- Follow all hygiene rules when caring for your ward.
Remember that disease is easier to prevent than to treat.