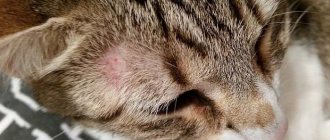
Allergy
Red spots on the ears, and sometimes completely red (sometimes even hot) ears indicate that the cat is suffering from an allergic reaction for some reason. This could be the environment, new food, medication, or flea saliva. To understand the cause of redness, you need to consult a specialist. Fortunately, allergies in animals are treated just as easily as in people, so after visiting the veterinarian, the cat will definitely feel better, and the redness from the ears will go away.
© shutterstock
Types of intolerance in cats
Allergies in pets can be divided into several groups:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Drug allergy.
- Food intolerance.
- Contact dermatitis.
The exact causes of atopic dermatitis are unknown. This disorder results in red spots and hair loss in response to an external irritant, which can be anything. As a rule, this phenomenon is observed in severely weakened elderly animals or small kittens.
Drug allergies are the most common cause of skin changes in the ears. Red spots in a cat's ear appear in response to drops from otitis media or otodecosis (ear mites), taking nutritional supplements, or using flea treatments. This is accompanied by swelling of the epidermis, flaking and itching, which can lead to scratching of the ears and the formation of crusts and erosions.
Food intolerances typically affect the entire body. First, spots form on the face and ears, then move to the pet’s neck, back and stomach. A distinctive feature of this reaction is severe itching of the epidermis, which causes the cat to literally tear out its own fur, so bald patches are always noticeable in the affected areas.
Contact dermatitis develops due to hypersensitivity of the skin to an irritant, which is household chemicals or shampoos for cats. It manifests itself as itching, rash, swelling and redness. Symptoms appear directly in the area of contact with household chemicals. For example, if washing powder gets on your ear, after a while the skin will turn red and itchy.
Ear hematoma
The cat's ear may turn red as a result of the appearance of a so-called auditory hematoma. These problems are very painful for cats and therefore require immediate specialist intervention. Such bruises may appear for the following reasons :
- Ear injury, possibly while playing or due to a bad landing. Vessel rupture can also occur when an animal scratches or shakes its head very hard;
- Infections, allergies, ear mites - everything that provokes violent damage to the organ.
The main symptoms of all ear diseases
If the ear is sore, the animal will show discomfort by scratching or pawing at it, shaking or tilting its head towards the painful area.
Other manifestations of ear disease in cats:
- black or yellowish discharge;
- redness or swelling of the ear or ear canal;
- waxing on or near the ear canal;
- bubbles;
- strong smell;
- hearing loss;
- loss of balance or disorientation.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear in a cat. The disease spreads to all parts of the ear, including the inner ear. Possible causes range from allergies to ear mites and fungal infections. If the cat's ear is red inside and has an unpleasant odor, scratches are visible on the outside, and the cat itself is not behaving as usual, then most likely he has otitis media. The veterinarian will prescribe the necessary medications, and after treatment, the owner will need to keep his pet’s ears clean and regularly wipe them to remove excess earwax. This procedure is also useful for healthy cats, as it is a good prevention of inflammation.
© shutterstock
Treatment methods
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose an allergy. Therapy comes down to eliminating the effect of the irritant and taking antihistamines. In severe forms, it is practiced to treat the affected area with ointments containing corticosteroids. Additionally, the diet is adjusted by adding vitamin supplements and Omega-3.
For lichen, mites or fungal infections, specific treatment is necessary. Drugs are selected based on the results of tests that need to be taken at a veterinary clinic.
Solar dermatitis
As stated earlier, a cat's ear is very sensitive, making it susceptible to sunburn. First of all, this applies to white cats, however, other breeds are not protected from this disease. Dermatitis initially manifests itself through mild redness and some balding of the ear, but may later be accompanied by itching, bleeding, scratching and other symptoms. If measures against solar dermatitis are not taken in time, they can cause another, more serious disease – squamous cell carcinoma.
Clinical signs of the disease
The clinical picture of the disease is often accompanied by anemia, signs of which may include drowsiness, slight weakness, loss of appetite and constant or periodic fever. The nature of such anemia greatly influences the general clinical signs. But in general, cats tolerate low hematocrit much more easily than dogs.
The most dangerous is hemolytic jaundice, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- liver enlargement;
- refusal to eat;
- sudden increase in temperature, fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes and spleen;
- orange cal.
The disease progresses very quickly and it is almost impossible to notice its signs in time. It is difficult to cure this type of jaundice, and the animal often dies.
Obstructive jaundice is characterized by:
- severe diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal enlargement;
- sudden weight loss;
- anorexia;
- darkening of urine.
Most symptoms will depend on what caused the jaundice. But the common symptoms are always yellowing and dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, constipation, nausea and vomiting, and abdominal pain. With jaundice, urine becomes bright orange, and stool becomes completely white.
Yellow staining of mucous membranes is a very dangerous symptom.
There is frequent urination and severe thirst, sudden weight loss, mental disorders and internal bleeding. In advanced cases, jaundice can result in coma and death. Therefore, it is very important to start treatment in a timely manner. Once a cat's eyeballs, gums, and inside of its ears turn yellow, it dies within a few days.
Sarcoptic mange
Sarcoptosis is a disease caused by microscopic mites of the genus Sarcoptes that parasitize the skin of domestic animals. More common in dogs.
The clinical picture of sarcoptic mange is similar to other diseases: the affected areas dry out and cause itching, subsequently the hair falls off in these areas, and scabs form unattractive ulcers.
In the fight against Sarcoptes ticks, Stronghold drops, which are applied to the animal’s withers, have proven themselves to be effective.
We invite you to read an article about the feline disease sarcoptic mange.
How to rid your pet of the problem?
To relieve redness, you must first determine its cause. If this is an allergy, then antihistamines for cats - Suprastin, Demidrol, Pipolfen - will come to the rescue. If your cat has scabies, use an ointment made from tar and petroleum jelly.
If a cat has red ears inside, then this cannot be normal. The reason for this was one of the diseases described above. It is better to seek help from specialists who will suggest the correct treatment. But if this is not possible, you can try to determine the cause of the disease yourself and try to help the animal. The main thing is not to harm and not to give the cat drugs that can aggravate the situation. The best treatment is prevention. Cat owners should monitor the hygiene of their pets and regularly clean their ear canals. Then such an insidious symptom as redness of the cat’s ears will bypass her.
Causes
Skin pathologies can bother cats temporarily, for example, arising when changing food and spontaneously stopping when returning to a normal diet. But much more often, pets are worried about seasonal diseases associated with increased activity of skin parasites. The most common causes of skin diseases are:
- ectoparasites - fleas, ticks lead to the occurrence of dermatitis, sarcoptic mange, notoedrosis, otodectosis;
- fungal infections cause lichen;
- improper care can cause an allergic reaction, acne, eczema;
- abnormalities in the development of sebaceous glands and hair follicles also cause acne;
- allergies, stress, injuries, kidney diseases, tumors, diabetes mellitus lead to bacterial infections of the skin;
- psychological disorders can cause baldness (alopecia);
- diseases of the internal organs (stomach, liver, kidneys) provoke eczema.
Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome (or hyperadrenocorticism) is an extremely rare disease that develops as a result of excessive amounts of the hormone cortisol in the body. Excess cortisol can occur with the use of large amounts of corticosteroids orally, locally or by injection, with tumors of the adrenal cortex, and also as a result of pituitary gland disease.
The following phenomena are observed in Cushing's syndrome:
- increased thirst and increased urination;
- voracity;
- enlarged abdomen;
- amyotrophy;
- lethargy;
- hair loss;
- thinning of the skin.
In the treatment of this serious disease, as a rule, the drug Trilostane is used, which suppresses the production of cortisol. In some cases, removal of the adrenal gland or pituitary gland may be necessary, as well as radiation therapy to the pituitary tumor.
Read the article on the disease Cushing's syndrome in cats.
Scabies.
A rare disease for cats. Dangerous to humans, like lichen. The causative agent is the scabies mite. It manifests itself as hair loss, itching, rashes with white liquid inside. It is treated by bathing the pet with hexachlorane emulsion or using soap. The following oils have a healing effect: tea tree and sea buckthorn.
The most dangerous skin disease in cats. The causative agent is a skin mite. When bitten, a swollen red spot forms, hair falls out on the face, bloody spots and pimples appear - pressing on which will provoke the outflow of white liquid with a large number of microscopic larvae. Sulfur ointment, veterinary drugs Stronghold and Advocad cope with demodicosis. You can also use human shampoo from the StopDemodex series.
For prevention, provide your pet with a balanced, fortified diet.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections occur in two forms: dry and wet. In the first case, dense formations and crusts appear on the skin. The second form is characterized by the presence of areas of skin with severe hyperemia and moisture, which is accompanied by a rash, ulcers, itching and crusts.
To understand the form of the disease in your pet, you need to not only read the description of the disease, but also carefully study the photo.
We suggest you read: How Savannah cat kittens develop
There can be a huge number of reasons for a bacterial infection:
- allergies accompanied by itching;
- heredity;
- stress;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- presence of shallow wounds;
- diabetes mellitus, tumors, kidney damage, etc.
Treatment is based on the use of antibiotics and local drugs (Miramistin, Levomekol, aluminum and zinc-containing ointments).
Bacterial skin diseases include feline pyoderma.
Tumors and neoplasms
Ear tumors in animals are extremely rare. It is not possible to notice and recognize them in the early stages. Only fairly large tumors can be noticed, and then consultation with a specialist is definitely needed to find out the origin of the tumor. The dangers facing growing tumors include:
- hearing loss,
- vestibular disorder.
Often in such cases the help of a surgeon is required.