Damage to the genital organ as a result of inflammation in a domestic cat is a frequently diagnosed pathology called balanoposthitis. The pathological process occurs in males against the background of damage to the mucous membrane covering the glans penis and lining the preputial sac from the inside.
The causes of the development of balanoposthitis are, first of all, violations of hygiene rules, infectious diseases, and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the genital organ.
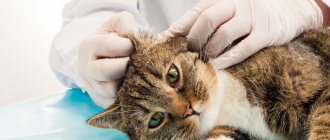
Characteristic signs of balanoposthitis, in which it is immediately necessary to seek help from a veterinary clinic, are severe hyperemia of the penis, the appearance of specific discharge, including purulent discharge. You cannot do without the help of a qualified doctor.
Causes of disease in cats
Balanoposthitis is a pathological inflammatory process localized in the area of the head of the penis in a cat and the foreskin, which performs the protective function of the mucous membranes. In veterinary medicine there is a risk group for the occurrence of balanoposthitis. These are cats that have not undergone castration and often come into contact with other animals, especially females with a history of infections of the reproductive system.
The reasons for the development of inflammation in the area of the glans penis are also:
- Inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area - cystitis and urethritis, damage to the mucous membranes of the urinary canal, inflammation and enlargement of the prostate gland, inflammation of the appendages (testicles).
- Pathologies that do not have an inflammatory nature of origin. This group includes urolithiasis (urolithiasis), often diagnosed in cats, phimosis (characterized by incomplete exposure of the glans penis from the preputial sac), paraphimosis (a pathology characterized by compression of the glans penis by the foreskin at the time of sexual arousal, which leads to problems with blood supply in this place).
- Diseases of an infectious nature. Dangerous sexually transmitted infections transmitted exclusively through sexual contact, as well as pathologies caused by the activation of pathogenic bacterial or fungal microflora.
The development of balanoposthitis in a domestic cat can be caused by mechanical damage to the mucous membranes from foreign objects, malignant or benign neoplasms on the penis or in nearby tissues. Inflammation of the preputial sac and head of the penis can be caused by diseases of the endocrine system (for example, diabetes mellitus), a sharp decrease in the body's defenses, and congenital pathologies - cryptorchidism.
Balanoposthitis develops in males due to a genetic predisposition, allergic reactions to certain detergents used for bathing the animal. Excessive washing of the animal, as well as the use of chlorinated water for these purposes, can provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
Irritation of the mucous membranes and, as a result, inflammation, develop in pets in the area of the external reproductive organs when exposed to chemicals intended to combat ecto- and endoparasites. Less commonly, the cause of balanoposthitis in a cat is a poisonous insect bite or obesity.
Cat, kitten licks eggs after castration
If a kitten or cat licks its eggs after castration, but the animal’s condition is stable, there are no uncharacteristic symptoms - this is normal. After surgery, some time is required for tissue restoration, so the cat will lick the postoperative suture. Animal saliva has antibacterial properties and contains the enzyme lysozyme, so regeneration processes occur faster.
After castration, a kitten or an adult pet may experience stress, so for the first time after the operation they lick their testicles.
If castration is carried out in adulthood, the period of adaptation and hormonal changes in the body occurs more slowly and will take longer than in a kitten.
In case of deterioration of the condition, excessive discharge, suppuration of the suture, wound, fever, swelling of the groin area, immediately contact your veterinarian!
Symptoms and diagnosis of pathology
The severity of signs of the disease is indirectly affected by the age of the pet, the factor that provoked the inflammation, the form and duration of the pathological process. At the initial stages of the development of balanoposthitis, the following symptoms occur:
- severe inflammation (redness) of the prepuce and apex of the genital organ;
- increased attention of the cat to the genitals (frequent licking);
- discharge of exudate from the urethral canal (may be purulent, greenish-yellow);
- unpleasant odor from the animal;
- swelling and swelling of the genital organ;
- decreased sex drive or complete absence of reproductive instincts;
- change in behavior - the pet expresses concern due to painful sensations.
In the absence of timely treatment, the intensity of symptoms increases. Bloody discharge from the urethral canal appears, the animal experiences severe weakness, activity and appetite decrease.
Upon examination, the owner notes the appearance of specific ulcers and lumps on the penis. The inguinal lymph nodes increase in size, which leads to an increase in local and general body temperature. Severe inflammation that has developed in the male genital area leads to problems with urination.
Lack of treatment for the acute form of balanoposthitis inevitably leads to a transition to a chronic course. The severity of painful sensations decreases, as does the amount of purulent exudate released. The pet constantly feels discomfort, especially when urinating. Phimosis develops, causing changes in the scar pattern; the head of the penis cannot be exposed normally during sexual arousal.
The appearance of the first signs of pathology is a reason to immediately seek help from a veterinary clinic. The specialist will conduct a general clinical examination, collect anamnesis and prescribe a number of laboratory tests. A general analysis of blood and urine is indicative, which makes it possible to determine the strength of the inflammatory process. Exudate samples are also taken for further research and identification of the type of pathogen.
Reasons why a cat licks its fur in the absence of parasites
In many cases, a cat constantly licks itself not because of parasites, but for other reasons. The most common of them is stress. Compulsive licking in cats can be compared to the human habit of biting nails. This indicates that the cat is starting to get very nervous. The owner must eliminate the cause of the pet’s emotional distress.
The cat itches, but there are no fleas, it constantly licks itself
Other reasons why a cat constantly licks itself are fungal diseases (lichen), allergies, dermatitis, otitis, and inflammation. The doctor must make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Lichen
Ringworm, or dermatophytosis, is a fungal infection of the skin and fur. The causative agents are fungi of the genus Microsporum or Trichophyton. They affect the roots of actively growing hairs. Characteristic bald patches appear on the head, tail, ears, and paws, and the skin peels off. In the affected areas, the hair can quickly fall out, and the cat begins to go bald.
This disease is very contagious, but is easily treated, does not pose a threat to the life of an animal or a person and does not lead to serious health consequences. Very often, cats with reduced immunity and small kittens get deprived of the disease. The main symptom of lichen is round bald spots covered with scales. If the disease is not treated, then over time the fungi will affect other areas of the coat.
Note! The itching associated with ringworm in cats is usually not severe. If it is accompanied by a skin disease of a bacterial nature, the itching may intensify. Then the cat will constantly itch and lick itself. Scars or scabs may form on the skin.
Ringworm in cats is diagnosed at a veterinary clinic. The doctor makes a hole with a Wood's lamp, takes a scraping from the skin, analyzes wool hairs and inoculates fungi on a nutrient medium. You will also need a blood test to check for infections. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should begin immediately.
For lichen, the course of treatment lasts a long time (about 3 weeks). In severe cases, recovery takes several months. The pet is prescribed medications for internal and external use. The veterinarian can prescribe medications such as microderm, vakderm, fungin, Yam BK ointment, etc. A sick pet must be isolated from other animals and provided with abundant and nutritious food, rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements. Despite the fact that people do not always become infected with shingles from a sick cat, it is necessary to thoroughly clean and disinfect the apartment.
Vaccinations against lichen are made with the Polivac TM or Vakderm-F vaccines. Vaccination is carried out twice with an interval of 2 weeks.
For your information! If the affected hair has stopped growing, it will not be affected by lichen. Therefore, cats often recover suddenly.
Ringworm in a cat
Dermatitis
Dermatitis refers to a whole group of inflammatory skin diseases in cats. Even a calm and affectionate animal becomes aggressive and restless. Reddened areas appear on your pet's skin, and sometimes a rash appears on them. The affected parts of the skin are very itchy and itchy, which is why the cat may often itch, lick, and even gnaw out fur and skin. Sore spots are hot to the touch. The kitten may meow loudly and lick its lips frequently. Then comes the next stage of the disease, when the skin peels off and becomes wrinkled. Purulent lesions may appear.
Causes of dermatitis in cats:
- allergies to food (preservatives and dyes);
- allergies to shampoos and other chemicals;
- infestation with fleas, lice eaters, ticks, worms and other parasites;
- burn or hypothermia;
- a scratch or bite on the skin;
- infection of already damaged skin by bacteria, development of inflammation;
- individual intolerance to certain drugs, especially oxytetracycline.
In most cases, the trigger for dermatitis is an allergy of any origin. Your cat may be allergic to dust, fungus, or food protein. If a cat's fur is brushed too vigorously, the skin may become damaged and dermatitis may occur.
Important! Dermatitis is dangerous because it often becomes chronic. Symptoms will come and go, and your cat's health will worsen. Deep, non-healing wounds may occur on the skin. Sometimes the cat licks itself and rubs the skin until it bleeds.
If you suspect dermatitis in a cat, you should not hesitate to contact a veterinarian. Only a doctor can find out the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment. First of all, you need to get rid of the allergen that triggered the development of dermatitis. To do this, you will have to replace food, shampoo and other household items. The veterinarian will help you choose the appropriate food.
Dermatitis in a cat
Endocrine system disorders
Excessive licking may be a sign of endocrine dysfunction in cats. The veterinarian performs many diagnostic tests to find out what exactly is causing these symptoms. Knowing the cause and mechanism of development of hormonal imbalance, the doctor will prescribe suitable treatment for your pet.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammation of the middle ear in cats, often leading to dangerous complications. Pets suffer from otitis media much more often than people. If the cat begins to scratch its ear frequently and intensely and shakes its head, otitis may be suspected. The skin on the inside of the ear appears irritated, red and swollen. Treatment must be started immediately, otherwise purulent otitis may develop.
For your information! In the purulent form of the disease, a thick, dark brown liquid with an unpleasant odor is released from the ear. This disease causes severe pain to the cat. In severe cases, inflammation of the facial nerve may occur, then the pet's ear, eyelid or lip sag. Further inflammation affects the vestibular apparatus and brain. Because of this, the cat may die or remain disabled.
Otitis media in cats can be caused by parasites (especially fleas and ticks), bacteria, fungi, allergies, trauma, and foreign bodies in the ear. Hypothermia can also cause otitis media. Therefore, if the cat is cold or caught in the rain, it must be warmed up and kept in a warm room. Water that gets into the ears is very dangerous for your pet.
Diagnosis and treatment of otitis should only be carried out by a veterinarian. He will prescribe a course of treatment from a variety of drugs. Taking good care of a sick pet will keep it alive and healthy.
Otitis in a cat
Skin diseases
In addition to dermatitis of various origins, there are many other skin diseases of cats. Parasites can cause diseases such as demodicosis, scabies, and eczema. Ringworm and eosinophilic granuloma are especially widespread.
Dermatomycoses are a group of fungal diseases that affect the fur and skin of cats. Ringworm is a type of dermatomycosis. Treatment must be strictly under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Eosinophilic granuloma affects the lips and oral cavity. The disease manifests itself in the form of redness, swelling and hair loss at the site of the lesion. Pain and itching are rare, but the cat may lick the sore area frequently. The veterinarian diagnoses the disease and prescribes treatment. Eosinophilic granuloma is treated for a long time, but successfully and has a favorable outcome.
Skin diseases take a long time to cure
Important! Sometimes it happens that a cat licks its belly until it becomes bald. The reasons for this lie in severe stress, a fungal infection or skin parasites. If a cat licks itself a lot and begins to go bald, you need to take it to the veterinary clinic.
Bald patch on paw due to lichen
Prevention of hematuria, blood in the urine of a cat
- To prevent blood from appearing in your cat’s urine, the following measures must be observed:
- Feed your pet only high-quality food.
- Sterilization can be carried out .
- Minimize your cats' outdoor activities.
- Don't let them fall.
A spayed or neutered cat is not as susceptible to this disease. Many people are afraid to castrate, fearing that the individual will change its behavior in the future. But this is not true. The animal will remain with the same character.
Also pay attention to the cat’s jumps; if possible, it is better to reduce their number. When it falls , diseases not only related to the amount of blood in the urine will appear.
The presence of various clots in the excretory fluid is a sign of serious illnesses that need to be treated. Show your cat to a veterinarian, conduct the necessary examination and follow all his instructions.
Discharge from endometritis
This disease can have both an acute and chronic course. The second form of the disease does not affect the pet’s well-being. The cat mates with males, but in most cases pregnancy does not occur. If fertilization does occur, the cubs often die in the womb or almost immediately after birth. An acute inflammatory process in the inner mucous membrane of the uterus is a serious illness. Bloody discharge in cats with this pathology is accompanied by loss of appetite and general weakness. If you do not provide medical assistance to the animal in time, it may die.
Feline skin diseases
Itchy skin is difficult to diagnose because the owner does not always see when his pet is itching. Itchy skin can be caused by various reasons, including psychogenic ones.
Itching is accompanied by the following types of skin reactions in cats:
Scratching on the head and neck;
Bilateral symmetrical alopecia;
Eosinophilic granulomatous complex.
One type of skin pathological reaction is feline miliary dermatitis, which has multiple causes. The disease manifests itself as opening papules located on the back of the pelvic limbs, lower back, back and neck. After opening, the papules dry out, a crust appears on them, the skin peels off, and scabs form.
There is itching throughout this entire process. This disease can be caused by pathologies associated with malnutrition, infections, idiopathic diseases, allergies and parasites, for example, the cheyletiellosis mite.
Feline cheyletiellosis develops slowly; cats lick off most of the scales containing mites. Symptoms include severe itching and skin peeling. Ticks and their eggs must be found by combing out with a comb or sticky tape. But this diagnosis is relevant only for half of the cases. An alternative is to have a specialist take skin scrapings and examine the material using light microscopes.
Feline superficial pyoderma is secondary in nature, is quite rare, and develops in parallel with other diseases that are accompanied by itching: notoedrosis, atopy, flea dermatitis, various allergies and others.
What to do if you can’t see a doctor. Blood in a cat's urine
What to do if you can’t see a doctor and blood is found in your cat’s urine? Now everyone has mobile phones, you can always dial our veterinary center and consult on any issue.
- As first aid, you can follow this algorithm:
- Move the animal to a warm and clean room without touching it.
- As a pain reliever, inject an intramuscular drug with an analgesic effect. No-shpa or baralgin will do.
- Replace solid writing with liquid.
- Free access to water.
- Give the animal decoctions of herbs that remove toxins from the body.
Do not give your animal antibiotics without your doctor's knowledge!
How to treat an animal whose cat has blood in its urine
Treatment directly depends on what diagnosis was made. The algorithm for taking medications is prescribed by a veterinary specialist. It may include the following components: antibiotics, diet, injections, vitamins, removal of kidney stones, painkillers and others.
Symptoms of the disease
The severity of symptoms depends on the cause of the lesion, the duration of the disease, the age of the cat and concomitant diseases.
Manifestations of the initial stage of balanoposthitis:
The pet often licks the problematic part of the body.
- inflammation of the foreskin and glans;
- frequent licking of the cat's genital area;
- purulent discharge of varying intensity of yellow or green color on the penis;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- swollen, edematous penis and affected area;
- decrease and absence of sexual instincts;
- restless behavior;
- discomfort, soreness of the genitals.
Balanoposthitis in animals
Balanoposthitis in animals is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the penis and prepuce in males, resulting from traumatic damage to the organ and the penetration of pathogenic microflora (staphylococci, yeast-like fungi).
The disease occurs against the background of trichomoniasis, blistering rash of viral/microbial origin, campylobacteriosis.
The disease is caused by the development of bacteria in the tissues of the reproductive organs.
This is facilitated by the accumulation of smegma (secretions consisting of sebum, dead epithelium, moisture), unsanitary keeping of animals, and trauma to the penis due to inaccurate coitus.
Treatment of symmetrical alopecia
For this disease, corticosteroids are used. There is a possibility that skin itching will persist for some time after treatment.
Feline eosionophilic granulomatous complex (FGC) manifests itself in three clinical disorders: gradual skin changes, plaque formation, and granulomas.
Eosionophilic plaques are multiple or single red lesions, oval and round in shape. They occur predominantly in the armpits and interdigital areas, on the abdominal skin and inner thighs.
A related disease is flea allergic dermatitis (FAD). This is a hypersensitive reaction of special Ctenocephalidesfelis fleas to salivary antigens. This type of dermatitis can appear in pets regardless of breed, age and gender. Accompanied by both moderate and severe itching. The disease can be identified by detecting fleas or their feces on the cat’s body, which is quite difficult to do, since she often licks herself.
Treatment of miliary dermatitis
Since this disease is multifactorial, the doctor needs to completely collect anamnesis, study the history of symptoms, contact with animals, diet and living conditions of the cat, as well as inquire about previous treatments and treatments and their results. In addition, a check for the presence of fleas, a cytological examination, and scrapings are carried out. Treatment is mainly through antibiotics. If the itching continues to be present and the disease recurs, additional examinations are carried out for the presence of allergies. It is also necessary to prevent infection of people who have been in contact with a sick animal.
Scratching on the head and neck can range in severity from minor scratches and redness to scabbed, erosive or ulcerated lesions. The reasons for this may be psychogenic and autoimmune disruptions in the pet’s body, allergies, dermatomycosis, parasites (demodicosis, notoedrosis and otodectosis mites).
Tinea mycosis, caused by a specific fungus, affects animals after contact with other creatures or objects contaminated by the fungus or its spores. Both cats and their owners are susceptible to infection.
Demodicosis, caused by a mite of the genus Demodex, occurs in the tissues adjacent to the sebaceous glands and contributes to the appearance of local lesions on the limbs, head, neck and muzzle.
Otodectes is a contagious pathology also caused by a special mite Otodectes cynotis. Usually appears after contact with other animals. As a rule, it is accompanied by itching, inflammation of the ear, and accumulation of thick dark secretions in the ears. Papules covered with crusts may form on other parts of the body.
Notoedres (also known as scabies) is a contagious disease that develops due to infestation of the Notoedres mite. Accompanied by very severe itching. The lesions are papules that are covered with crusts, usually located on the neck and head, sometimes on other parts of the body, including the surfaces of the paws that have been in contact with scratches.
Treatment of scratching and related diseases
First of all, an anamnesis of the disease is collected, the living conditions of the animal, its diet, behavior and habits are studied. Next, skin scrapings and hair samples are taken. If the test result is positive, the sick cat is treated with antifungal agents. Symptoms are then treated. If secondary infections are detected, additional treatment is prescribed. Itching is relieved with corticosteroids and antihistamines.
With symmetrical alopecia, the animal loses hair in parallel on both sides of its body. The skin is usually not damaged, but there is severe itching accompanied by hair loss. It is necessary to exclude the presence of fleas and check the sanitary condition of the cat’s home, as well as a thorough study of its diet.
Therapeutic measures
How is balanoposthitis treated in a cat? In order to prescribe adequate and effective therapy, it is extremely important to immediately identify the root cause of the disease. In particular, if a bacterial etiology of inflammation is suspected, a scraping is taken from the foreskin and sown on a nutrient medium. A culture of the microorganism is grown, from which a drug suitable for its destruction is selected. If inflammation is caused by frequent washing, stop washing the genital area with soap and treat the affected “regions” with emollients.
How is a blood test collected? Blood in a cat's urine
When you see blood in a cat’s urine, it urgently needs to be collected, but not everyone knows how to do this. In order to collect cat urine for analysis you need to prepare an empty tray, gloves and a special container. Next, follow this algorithm of actions:
- Wash your cat's litter box thoroughly and run hot water over it.
- Remove all the filler from it.
- If the animal does not want to urinate in such a “toilet,” then purchase pebbles.
- After the animal has done its job, put on gloves and pour the liquid into a special container.
- The jar must be taken to the center in the next couple of hours.
Blood in a cat's urine. How is blood in an animal's urine diagnosed?
If your cat is peeing blood , an experienced and qualified veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination to make the diagnosis as accurately as possible. Diagnostics includes the following categories:
- General analysis of cat excretory fluid. With its help, the presence of blood and other impurities is determined.
- Sensitivity and culture. It turns out what infection was the causative agent of the disease, and only then antibiotics are determined.
- Genital smear. It is examined only if there is a suspicion of vaginitis.
- General blood analysis. The level of infection of the animal's immune system is determined.
- Biochemical analysis. With its help, kidney function is checked.
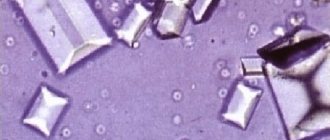
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity. Detects kidney stones.
- Cystoscopy. A bladder examination is performed.
- Analysis of stones, if they were found. As a result, a special diet and medications are prescribed.
Take care of your pet at home. Blood found in cat's urine
Your cat fell , he began to bleed blood in his urine, you turned to a specialist, he prescribed treatment for the animal. You must follow it unquestioningly, but also take care of your sick pet at home. Provide him with peace, do not tug, do not allow children near the cat, and do not touch your pet again.
Remove all solid food from food. Leave only liquid gruels and mixtures. Strictly adhere to the diet prescribed by your veterinarian.
Do not self-medicate under any circumstances
! This will only harm the cat.