Eyes are an indicator of a cat's health. The vital organ reacts sensitively to any external and internal stimuli. Before you get a pet, you need to know what pathologies can manifest in cats throughout their lives. First of all, pay attention to the condition of the eyes. They are covered externally by the upper, lower and third eyelids. The prevalence and type of disease, intensity, and the length of time that passes before the immune response appears influence the development of dysfunction of all organs. What eye diseases do cats have? We will talk about this in our article.
Eye diseases in cats: an overview
Why do my cat's eyes hurt?
The causes of the disease may be due to external factors, breed and predisposition to any ophthalmological disease. At any age, the disease requires treatment. Otherwise, the animal may become completely blind: cell decay and protein decomposition begin.
Possible causes of the disease
- Metabolic disease.
- Problems with intraocular fluid.
- Injuries, concussions, blows, bruises of varying degrees.
- Congenital pathology, if infectious diseases were transmitted to the kitten during birth.
- Old age. With age, metabolism slows down and the eye organ becomes less protected from external influences.
Extreme sports people and mixed breeds are most susceptible to eye diseases
Extreme sports people and mestizos are the most susceptible to diseases. Less commonly, eye pathology is observed in the “British” and “Scots”. Isolated cases occur in outbred cats. The main point, from the point of view of differentiating eye diseases, is the factors that determine the presence or absence of infection:
- Conditions of detention.
- Preventive measures.
- Stress levels matter most to cats.
- The presence of a source of the pathogen and its concentration in the environment.
- Concomitant diseases that cause predisposition to the infectious process.
Taking these factors into account, we can conclude that in inadequate conditions of detention in the absence of preventive measures, when the animal is in a stressful state, there are greater risks of eye infectious diseases.
Stress can cause eye problems in cats
What causes the functioning of the vestibular apparatus to be disrupted, what are the symptoms?
The most common clinical symptoms of vestibular disease include: sudden falls of the animal on a completely level place, an unexplained body roll in one direction or another, a clear and constant curvature of the neck, as well as nystagmus - a rapid and involuntary oscillatory movement of the eyeballs. If the cause of the disease is serious, a “sagging” muzzle may be observed. This is explained by the fact that the facial nerves (and, accordingly, muscles) are closely connected with the hearing organs.
The causes of this pathology can be extremely diverse, ranging in severity from spontaneously resolving to fatal. Very often the disease develops against the background of advanced meningococcal infection; its cause can be any inflammatory disease. Also in veterinary practice, there are often cases of vestibular syndrome occurring against the background of the willful use by animal owners of certain “human” antibiotics that are toxic to cats.
Remember!
Giving your cat gentamicin, as well as any drugs from the tetracycline group, is strictly prohibited! Perhaps you will cure the infection, but after such “therapy” your pet may well remain disabled.
Types and classification of eye diseases
Eye diseases in cats are a broad and multifaceted group of diseases. Pathologies are conventionally divided into two types:
- Non-inflammatory (non-infectious) diseases.
- Inflammatory (infectious) diseases.
Table. Common eye diseases in cats
| Non-communicable diseases | Infectious diseases |
| Cataract | Keratitis |
| Mechanical damage | Glaucoma |
| Drooping of the upper eyelid | Panophthalmitis |
| Retinal disorder | Conjunctivitis |
| Eversion and non-closure of eyelids | Inflammation and ulcer of the cornea |
| Foreign body entry | Neoplasms of the conjunctiva |
The list of inflammatory eye diseases in cats includes types of keratitis: superficial, superficial vascular, deep and purulent. Some cat breeds have a fold on their cheeks that injures the cornea of the eye. Then breed keratitis occurs, which must be prevented and treated.
Video - Eye diseases in cats
Infectious diseases
Most of the troubles for cats are caused by infectious diseases that occur in severe forms. A very important and distinctive point of all infectious eye diseases is the incubation period from the moment of infection by the pathogen until the manifestation of symptoms noticeable to cat owners and veterinarians.
Viruses are capable of mass distribution between animals and can be transmitted by airborne droplets from an infected to a healthy organism. Based on the nature of the pathogens that cause eye diseases, there are several types of microorganisms:
- Viral.
- Fungal.
- Protozoans.
- Bacterial.
Most of the troubles for cats are caused by infectious diseases that are severe.
The most important are the viral and bacterial group of infections.
Clinical symptoms of inflammatory processes
The vast majority of diseases begin with exactly the same signs, when the cat’s condition worsens sharply:
- In the acute phase, an increased temperature is observed.
- Increased loss of fluid in the body.
- Complete lack of appetite.
- Lethargy and apathy.
When specific signs of pathology appear, it is most likely that there is a certain infection in the eyes. The precursors of eye diseases are the following:
- Eyelash growth inward.
- Inversions and inversions of the eyelid.
- Squinting and photophobia.
- The third eyelid extends half the eye or more.
- Swelling, redness, or clouding of the fundus of the eye.
- Lacrimation, other discharge and discharge from the eyes.
Entropion of a cat's eyelid
Symptoms are clearly visible on white fur, even if the eyes are treated with a solution. Only in the development of the process can clinical signs characteristic of each individual isolated disease be observed. If eye diseases are not treated in a timely manner, the animal’s condition worsens.
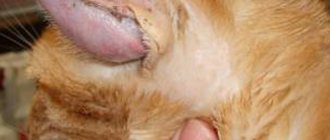
The most common eye diseases in cats: photos
Glaucoma
Intraocular pressure increases. Poor drainage of eye fluid appears. The result is damage to the optic nerve and complete loss of vision. There are primary and secondary glaucoma. Primary begins unexpectedly due to disruption and improper outflow:
- The pupils dilate.
- No reaction to light.
- The cat begins to squint.
- Eyeballs are sunken.
- Redness of blood vessels in the whites of the eyes.
- The front of the eyes takes on a dark shade.
Glaucoma in a cat
Cataract
A fairly common occurrence in cats is when the lens of the eye becomes clouded. The lens is a natural, clean lens. Light passes through a clear lens without refraction. The image reaches the retina and is then processed by the brain.
If the natural lens becomes cloudy, the brain cells will not be able to process the image correctly. Bright, shiny eyes indicate the absence of disease. But they, like people, get sick, grow old, and lose their sight. The main symptoms of cataracts are clouding of the eye and a cloudy appearance.
Cataracts are quite common in cats.
Keratitis
Accompanied by an inflammatory process. The cornea of the eye is damaged under the influence of internal and external unfavorable factors. It occurs both as the main disease and as a concomitant with other inflammatory processes. Any impact on the cornea may cause keratitis in a cat.
Keratitis
Conjunctivitis
The membrane of the eye becomes inflamed, the process of inflammation from the inner surface spreads to the eyeball. Conjunctivitis can be acute, purulent, catarrhal. Depending on the diagnosis and form of the disease, treatment is prescribed. Primary conjunctivitis manifests itself as an independent disease. The secondary type accompanies other diseases that appear in cats.
Conjunctivitis and uveitis in a cat
Diagnostics
Often, to a professional veterinarian, ataxia is obvious upon initial examination. But to fully understand the situation, it is necessary to collect all the anamnesis data. Have there been any injuries (even several years ago), how and what does the cat eat, what severe infections has it suffered? If possible, how her mother’s pregnancy progressed. Examination of the ears with an otoscope is mandatory.
X-rays, ultrasound, or even an MRI will be needed to confirm the diagnosis and identify or rule out tumors, hemorrhage, or swelling of the brain. In some cases, if a brain or spinal cord infection is suspected, a cerebrospinal fluid test may be necessary.
Only a physiological examination and study of the animal’s medical history can help in diagnosing disorders of the vestibular apparatus. Along with examining the cat's inner ear, it is also necessary to conduct a full range of neurological examinations. A blood test will assess the overall health of your pet.
Perhaps it will help find out the cause of the vestibular disorder. It is recommended to conduct a complete blood test, including biochemical and sugar content. It would be nice to have the results of a urine test (general and Nechiporenko) to determine the normal functioning of the liver and kidneys, to rule out the toxic nature of the disorder.
If the disease cannot be diagnosed even after these tests, then a spinal tap, MRI, or x-ray of the skull may be required. If the results of these tests are negative, then central vestibular disorder can be safely excluded from the list of possible causes of the disease, despite the similarity in the manifestation of symptoms.
However, since we are talking about vestibular syndrome, it is very important to determine what type of vestibular disorder your pet suffers from. And all this is definitely a prerequisite for a pet treatment program.
How to treat eye diseases at home?
When treating the eyes, medicinal solutions, drops and ointments are used. First, the eye is washed with furatsilin or weak manganese solution. Then drops are instilled and antibiotic ointment is applied. In particularly severe cases, surgery is performed. To select a treatment method and medications, it is best to consult a veterinarian.
Medicinal solutions, drops and ointments are used to treat the eyes.
Treatment of cataracts in cats
To see the symptoms, you just need to look into your pet's eyes. If a small white spot appears instead of a pupil, most likely the first symptom of cataract has appeared. Regardless of age, it is necessary to periodically examine the cat.
Medical and surgical treatment methods are used. The medicinal method used is tissue therapy according to V.P. Filatov with the introduction of aloe extract, antibiotics, and vitamin preparations. Retrobulbar blocks are performed according to V.V. Aurorov so that the substances get behind the eyeball.
On a note! Conservative methods do not always lead to a positive effect. It is possible to slow down the development of cataracts in cats, but it is not always possible to completely cure them. The only effective method of getting rid of cataracts is surgery.
Medical and surgical treatment methods are used to treat cataracts.
Help for eyes with conjunctivitis
It is better not to torture the cat, but to immediately take it to a veterinary clinic. The disease appears as a result of an allergic reaction or a viral, less often bacterial, infection. Effective eye care for conjunctivitis:
- Before instillation, the eyes are washed with 0.05% Chlorhexidine (for external use) using a gauze pad or cotton pad.
- Eye drops for cats and dogs “Tsiprovet” are instilled into the inner corner of the affected eye - two drops each.
- After five minutes, Tobrex eye drops are instilled - two drops each.
- After another five minutes, Actipol is dripped.
- Tetracycline one percent eye ointment is used at night. Apply along the edges of the affected eyelid.
The instillation procedure is carried out six times a day for five days. If conjunctivitis does not go away, treatment continues for the next 5-9 days, reducing the dose to four times a day. During illness, especially in the cold season, it is not recommended to let your cat go outside.
Conjunctivitis is treated with drops
Help with eye pain and purulent inflammation
Purulent inflammation and lacrimation is a pathological condition when, due to the penetration of a viral infection, the eyes stick together. There are a large number of varieties of purulent inflammation. One of the most common is panophthalmitis - serious damage to the entire eye.
First aid consists of treating the eyes with Furacilin. The antibiotic “Azenil” is given orally in the form of a suspension (the powder is diluted with 9 ml of water). The medicine is used for a week. If the kitten is small, it is enough to dilute a quarter teaspoon of the suspension with one teaspoon of distilled, mineral or boiled water. Stir thoroughly until smooth.
In addition to oral administration of Azenil, the antibiotic eye ointment Terramycin or syntomycin eye ointment is used. Gently apply a cotton swab to the affected eye two to three times a day.
Drops effectively help with inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drops “Barrier” are instilled two drops 2-3 times a day for a week.
This is what panophthalmitis looks like in cats
Causes
There are a large number of reasons that can lead to the development of nystagmus in dogs. Most of them are associated with central nervous system disorders and related diseases. In some works devoted to this problem, one can find such a definition as “a disorder of the balancing system,” that is, a disruption of the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and the part of the brain responsible for maintaining proper balance of the head and body.
Also possible causes of the development of nystagmus in dogs can be, for example, hypothyroidism, traumatic injuries (for example, due to a car accident), various tumors, thiamine deficiency, viral infections (for example, carnivore distemper), and, as a result, inflammation, heart attacks, hemorrhage in the heart, exposure to poisons and toxins (for example, lead).
Degenerative processes in the retina of the eye
Cats over five years of age may experience degenerative processes that affect the organ of vision. In case of dystrophy, atrophy, or detachment of the retina in especially severe cases, microsurgical operations are performed on the eyeball to restore vision and improve the health of the pet.
Cats over five years of age may have degenerative processes affecting the eyes.
Trauma or foreign object in the eye
If a kitten's eyes protrude from their sockets, this indicates that the eyes are poorly protected and are at additional risk of injury. Most often occurs in the summer when dry grass appears. Especially often, young pets with damage to the visual organ are brought to see an ophthalmologist. Eye injuries vary in severity:
- Bumps and bruises.
- Concussion injuries.
- Burns of various types.
- Internal and external wounds on the cornea of the eye.
- Penetration of foreign bodies and blunt objects into the eye.
If your eyes hurt due to a mechanical injury, you will need immediate help from your doctor. As first aid, the eyes are washed with clean water at room temperature or with special ophthalmic antiseptics. It is necessary to monitor the tear flow so that the liquid flows to the nose. A light bandage using sterile gauze is applied to the injured eye. It is slightly moistened with water or an ophthalmic septic tank.
Only a veterinarian can adequately help an animal.
Some household chemicals and home renovation products can cause eye burns. By blocking access to repair work sites, your cat can be protected from various burn injuries. Regarding eye injuries, it is impossible to give advice for all situations. Hidden injuries sometimes occur when animals are contused. Only a surgeon can assess the severity. It is important to follow all subsequent doctor's recommendations.
Prevention of eye diseases in cats
To prevent your cat’s eyes from hurting and always remaining healthy, not watery or festering, preventive maintenance is carried out. Proper care begins with nutrition. It is necessary to monitor what food your cat eats and how balanced the diet is. The main prohibition is that cats should not be given sweets.
You should pay attention to the appearance of the eyes. It should look like this:
- The conjunctiva is pale pink.
- There are no additional expirations.
- Healthy eyeball, without inflammation.
- The eyes are dry, the cornea is shiny and moist.
- The eyelids are of normal size, not enlarged and without swelling.
How to treat a cat's eyes?
If the cat is not sick, the eyes are healthy and clean, you can get by with a minimal set of eye care products. For prevention purposes, special lotions and saline solutions are used. It is not recommended to use tea, especially bagged tea. Tea leaves can lead to eye inflammation. Instead of tea, it is safer to use herbal infusions. But it should be noted that allergic reactions sometimes occur to some types of herbs.
The eye wash should be at room temperature or lukewarm. The eyes are washed from once a day (at night) to three times in the morning, afternoon and evening. If discharge appears and does not stop within three to five days, it is better to immediately contact a veterinarian. Self-medication can sometimes make the situation worse.
Some cat breeds have short nasal passages and tear ducts due to their skull structure. Tears do not fall into the nose, but accumulate in the eyes. For this reason, very often, throughout the day, tears accumulate, and the cat seems to be crying. The situation is not critical, but the eyes need to be treated every day. It is better to systematically carry out prevention and proper care than to subsequently treat eye diseases.
Cats need to be vaccinated
What does nystagmus mean?
I would like to note right away that if a cat owner discovers such a strange state of the eyes in his pet, when the pupil rotates as if wound up and the cat looks into emptiness, this does not bode well. This kind of phenomenon is not the norm. These rhythmic oscillatory eye movements (usually movements occur in the horizontal plane) indicate serious brain damage.
Where does nystagmus come from?
Nystagmus is an alarming symptom
Let's look at the anatomy. The eyes play a very important role, and it is impossible to imagine maintaining body balance in space without clear vision. After all, there is a close connection between the eyes and other organs of the vestibular apparatus. Thus, it can be argued that the eyes for our brain are sensors that transmit readings to the brain, and it already analyzes it and makes decisions on what to do next. But,
when a cat begins to have nystagmus, this indicates damage to the brain as the main center.
Types of nystagmus
I would like to immediately note that such a disorder can be either acquired or congenital. The latter is typical for representatives of the Siamese breed. Kittens with nystagmus are often born there.
As for acquired nystagmus, the cause may be:
- injury,
- severe stress,
- transferred disease.
And if congenital nystagmus is not treated, then acquired nystagmus can and should be fought. However, not with the symptom of spinning eyes itself, but with its root cause.
Nystagmus can also be pendulum - in this case, the speed of eye movement is the same in all directions. And also clonic - in this case, we can distinguish the slow and fast phases of pupil movement.
Daily care for your pet's eyes
Pet stores have a wide selection of pet eye care products. Most often, special preparations “Ophthalmosan”, “Diamond Eyes” or a regular domestically produced eye cleaning lotion that contains succinic acid are used. They are not designed for treatment, but they help well with mild inflammation and allergic reactions. They are mainly used for eye cleansing, removal of secretions and daily treatment.
The eyes are cleaned and instilled according to the instructions, wiped with a cotton swab with movements towards the inner corner of the eye. The products are used regularly without special prescriptions, clarifications or instructions from a doctor.
- Dirt and dry discharge in the eyes are first carefully removed mechanically with clean fingers.
- Place two drops of lotion in the inner corner, where there is more discharge, or in the lower eyelid.
- Use a cotton pad to wipe the eyes towards the nose, simultaneously removing any remaining moisture.
If it doesn’t work the first time, the procedure is repeated. Your pet's eyes should be monitored regularly to avoid inflammation and wrinkles under the eyes. Inflammatory processes are especially common in smooth breed cats.
Video - How to put drops in a cat's eyes?
What is anisocoria?
Normally, both pupils of a pet turn into narrow vertical slits in daylight or in a well-lit room. If you notice different pupils on your cat, you should bring it to a window or table lamp. A condition in which one eye does not respond to light and remains wide and round is medically called unilateral mydriasis.
In a darkened room, another pathology may be detected when one of the pupils does not dilate, but remains constricted. This deviation is called unilateral myiasis. Both disorders in medical science are united by the same term “anisocoria” and are considered dangerous signs.