Today, rabies remains one of the most dangerous diseases. This is due to the fact that there is no cure for it, and the frequency of infection is not decreasing. Every year, cases of human rabies are recorded in more than 150 countries around the world. At the same time, about 55 thousand people die every year. These are mainly residents of Asian and African countries, but tragedies occur on other continents as well.
Children are at particular risk for rabies. They are more careless and more often come into contact with animals, not paying attention to threatening symptoms. Almost half of all deaths occur among children under 15 years of age. Every year, more than ten million people are required to be immunized against rabies.
Incubation period for rabies in humans
In most cases, the incubation period for rhabdoviruses ranges from one to 3 months. However, in some cases, this period may be reduced to one week. The maximum incubation period for the rabies virus does not exceed one year.
Due to the fact that the incubation period may be shortened in some patients, vaccine prophylaxis and serotherapy should be performed urgently, immediately after a rabid animal has bitten or salivated an area of the patient’s injured skin.
If possible, the animal that bit the patient should be examined. The animal's condition is monitored for ten days. At the same time, laboratory tests are carried out to identify rhabdoviruses in the animal.
If negative test answers are received and the animal remains healthy within ten days of observation, rabies prophylaxis for the bitten person is stopped.
In this situation, the start of the introduction of anti-rabies vaccines before receiving the results of the study is justified by the fact that a cure for rabies has not yet been developed. The disease is characterized by absolute lethality. All treatment, when symptoms of rabies appear in a person, is reduced only to alleviating his condition until death.
Prevention of rabies in humans, through emergency administration of rabies vaccine, is the only way to prevent the development of this disease and its consequences.
Distribution and pathogenesis
The pathogen is transmitted by bites, after which the first sign may be itching in the bite area. The virus multiplies on the cells of the nervous tissue, and it is transmitted through them, gradually rising to the central nervous system (the spine and then the brain). In addition, the pathogen can be spread through the blood or lymph flow, but this is only an additional method.
When a cell is infected, the virus releases neurotoxins, which cause the symptoms characteristic of rabies. The pathogen affects all nerves, not just the central nervous system; in particular, it affects the nerve ganglia of the salivary glands, which causes severe salivation. At the same time, it penetrates the salivary glands themselves.
The incubation period in cats lasts from 3 days to 3 weeks, and in humans from 10 days to 2 months. The virus is detected in saliva 8-10 days before the first symptoms appear. At the same time, there are cases when the incubation period was reduced to one day for a cat and up to 5 days for a person, or, conversely, extended by several years.
How can you become infected?
Infection with rhabdoviruses occurs after a person is bitten by an infected animal. Also, infection can occur as a result of infected saliva coming into contact with areas of affected skin.
In most cases, urban residents become infected after a dog bite. Cases of infection after cat bites are much less common.
Susceptibility to the rabies virus is high among all warm-blooded animals. Therefore, you can become infected after the bite of any infected animal (bat, rat, squirrel, horse, fox, wolf, etc.).
Based on the causes of rabies, it is divided into urban and natural rabies.
Basic facts about rabies
Rural rabies accounts for 2/3 of all cases. This is due to the fact that residents of rural areas have a higher risk of being bitten by a rabid animal than a city resident.
The most common causes of urban rabies are bites from dogs, bats and cats. Outbreaks of natural rabies are usually associated with attacks by foxes and wolves.
After a bite to the hand, the incidence of rabies is about seventy percent. The maximum probability of infection and rapid development of the disease with a minimum incubation period occurs with bites to the neck and face (the probability of infection is more than 95%).
Rabies is more common in children than in adults. This is because children often play with stray animals and may receive minor bites that they do not report to adults. Bats are particularly dangerous at the moment. In this regard, it is strictly not recommended to try to catch a mouse with your bare hands that has flown into an apartment or onto a balcony.
It should be noted that in states where there are strict restrictions on the import of animals and mandatory vaccinations have been introduced for them, there is practically no rabies. Such preventive measures are common in Japan, Great Britain, etc.
Is rabies transmitted from person to person?
The rabies virus is transmitted to humans only from an infected animal.
Upon contact with a bitten person, transmission of the virus does not occur. There have been isolated cases of infection following a cornea transplant from a person who died of rabies.
In theory, transmission of the virus from a person with terminal rabies to another person is possible. However, to do this, the sick patient must not only bite another person, but also bite through the skin. Or, a large amount of saliva from a patient in the terminal stage of rabies should come into contact with the affected area of the skin (open wounds).
In practice, people with rabies do not pose an epidemiological danger.
The rabies virus is not transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets or kissing.
According to recent studies, an aerogenic transmission mechanism (extremely rare) is only possible when visiting caves with a huge number of bats.
Can you get rabies without a bite?
In addition to a bite, infection can occur after contact with the saliva of a sick animal on open lesions of the skin or mucous membranes. Infection does not occur if the animal’s saliva gets on intact skin, for example, the animal was unable to bite through a thick sleeve of a coat, trousers, etc., but the fabric became saturated with saliva that got on the skin.
Examination of the animal and a course of prevention (injections against rabies to humans) after a bite or salivation of open wounds is mandatory.
In isolated cases, vertical transmission of the virus from a mother bitten by an animal to a child is possible.
Read further: Measles vaccination - when it is done, where, contraindications for vaccination
The most dangerous animal bites
Cases of rabies after a bite in humans are not very common. But even without showing any signs of the disease, you should definitely get a preventive vaccination. After all, absolutely all people who are bitten are at risk of infection.
Few people know, but the danger of bites may depend on several factors, including:
- Locations. The most dangerous are bites on the neck and head. From these places, the rabies virus is able to migrate faster to the brain, as a result of which its incubation period, as well as the first phase of the disease, pass almost at lightning speed.
- Features of the bite. If rabies carriers bite a person on a bare area of the body, then the possibility of becoming infected with the virus is much higher than if bitten through clothing. By the way, the latter is capable of delaying the pathogen.
- Type of animal. Wolf bites are considered the most dangerous to humans.
It should also be noted that in addition to bites, infection with the virus in question can occur in another way. For example, there are known cases of pathogen transmission when a dog licked human skin that had fresh wounds and scratches.
Another way of possible infection is through autopsies on animals or people who have died from rabies.
How does rabies develop?
The rabies virus appears in saliva eight to ten days before the animal shows signs of illness. Therefore, even after being bitten by a seemingly normal, healthy animal, you should urgently treat the wound with laundry soap and consult a doctor for preventative measures.
If possible, the animal should also be taken to a doctor for further observation and examination.
There are two types of rabies virus:
- street (wild variants of the virus common among animals);
- fixed (this type of rabies virus is used to create vaccines).
Both viruses have a similar antigenic nature, therefore, after administration of a vaccine made from a fixed strain, immunity to the wild virus also develops.
Once infected, rhabdovirus spreads along nerve fibers. Hematogenous and lymphogenous spread of the virus is also possible.
The virus is characterized by its tropism for acetylcholine receptors, which contributes to the damage of many groups of neurons, the development of reflex-type hyperexcitability and, subsequently, the formation of paralysis.
The brain of an infected person is affected by swelling, hemorrhage and severe necrotic and degenerative changes. Rabies causes damage to all brain structures. The area of the fourth ventricle is subject to the most severe degenerative changes.
What affects the risk of contracting the rabies virus?
The likelihood of developing the disease directly depends on whether the animal’s saliva contained the virus during salivation or bite. Since approximately 45-50% of dogs with rabies do not shed the virus in their saliva.
For reference. According to statistics, after contact with a rabid animal, from 12 to 30% of people become ill (only patients not vaccinated with rabies vaccine are taken into account).
Despite this, the lack of effective treatment and a 100% mortality rate require a complete treatment and prophylactic complex after contact with an infected animal.
How common is the disease?
The disease is widespread (the only exceptions are Australia, Oceania and Antarctica). Every year, this infection kills about 70 thousand people around the world. Most often, cases of rabies are recorded in Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Signs of rabies in humans
Severe damage to the central nervous system leads to:
- development of convulsive contractions of the respiratory and swallowing muscles;
- a sharp increase in salivation (secretion of saliva and profuse sweating;
- severe disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Further migration of the rabies virus throughout the body is accompanied by its penetration into all organs and the development of multiple organ failure.
The first signs of rabies in humans are the appearance of a scar phenomenon, unclear fears, and depression. Subsequently, the addition of paroxysms of rabies and various phobias is noted.
The scar phenomenon consists of a strong burning sensation, as well as nagging and aching pain at the site of the bite. The pain spreads along the nerve fibers located at the site of the bite. Severe redness and swelling of the scar is also noted.
Paroxysms of rabies are called a specific reaction of the patient to the action of any irritants. The patients shudder, stretch their trembling arms forward (the body also goes through a slight trembling) and throw their heads back. The appearance of inspiratory dyspnea (inability to take a full breath) is also characteristic.
The most indicative phobias (fears) with rabies will be the occurrence of hydrophobia (fear of water), aerophobia (fear of air), acousticophobia (fear of various sounds), photophobia (fear of light).
Description
It is unknown where the rabies virus came from. Since ancient times, it has been called hydrophobia, because one of the common signs of advanced infection is the fear of water.
The first scientific works appeared in 332 BC. e. Aristotle also suggested that a person becomes infected with rabies from sick wild animals. The name itself comes from the word demon, since long before the viral nature of the infection was discovered, a sick person was considered possessed by evil spirits. Aulus Cornelius Celsus (an ancient Roman philosopher and physician) called the infection hydrophobia and proved that wild wolves, dogs and foxes are carriers of the disease.
The foundations for the prevention and treatment of the rabies virus in humans were laid by the French microbiologist Louis Pasteur in the 19th century, who, as a result of many years of research, developed an anti-rabies serum that saved more than one thousand lives.
At the very beginning of the last century, scientists were able to establish the viral nature of the disease. And exactly 100 years later, they found out that rabies can be cured even at the stage of the first signs of the disease, which was not the case before. Therefore, this, as everyone previously believed, was a fatal disease, today it is considered curable, but under certain circumstances.
What is rabies
Rabies is a neurotropic (affecting the nervous system) acute viral infection, which can be transmitted to animals and humans. After the virus enters the body, the symptoms quickly increase in intensity, and the infection ends in death in most cases. This is due to the characteristics of the microorganism.
How dangerous is the rabies virus?
- It is resistant to low temperatures and does not react to phenol, Lysol solution, sublimate and chloramine.
- It cannot be killed with a strong antibacterial drug; even viral agents are powerless.
- At the same time, the rabies virus is unstable in the external environment - it dies when boiled after 2 minutes, and under the influence of temperatures above 50 ºC - in just 15. Ultraviolet light also quickly inactivates it.
- The virus moves to the nerve cells of the brain, causing inflammation.
- The microorganism exists on almost all continents and, according to WHO estimates, more than 50 thousand people die from it every year.
The rabies virus can be found not only in African and Asian countries, but also in the post-Soviet space, as it is spread by wild animals.
The first symptoms of rabies in humans
The first signs of rabies in humans can appear as early as a week after the bite, however, more often the incubation period of the virus ends one to three months after the bite.
In patients, the temperature rises (as a rule, low-grade fever is characteristic), the phenomenon of a scar develops, complaints of general malaise, the occurrence of inexplicable anxiety, and depression appear. There are sleep disturbances, possibly both nightmares and insomnia.
Patients also complain of severe dry mouth, poor appetite, headaches, shortness of breath, and tachycardia.
The first stage of rabies lasts from one to three days.
The second stage is accompanied by pronounced excitement. One of the most specific signs of rabies appears - severe hydrophobia. The fear of water is so strong that an attempt to bring a glass of water to the patient’s lips causes a painful spasm of the larynx and an attack of suffocation.
Patients reject water, despite severe dehydration and extreme thirst. Specifically, stretching forward of trembling hands and small twitching of the facial muscles. Such symptoms appear not only when the patient sees water, but also when he hears its sound (an open tap).
Aerophobia is manifested by the development of an attack from a breath of fresh air. In some cases, the attack may be accompanied by pronounced aggressiveness; patients try to attack hospital staff. Periods of aggression and violence are accompanied by pronounced salivation.
There is a sharpening of facial features, sunken eyes, and dilated pupils.
After periods of violence, the patient comes to his senses and is fully aware of what is happening. Also, patients fully remember everything that happened.
After the development of hydrophobia, patients live for several days (rarely more than six days).
The patient's descent into an “ominous tranquility” is a sign of imminent death. The cause of death is paralysis of the cardiac and respiratory muscles.
In isolated cases, variants of silent rabies are possible (usually after an attack by vampire bats). The disease occurs with clinical paralysis without the stage of excitation.
The total duration of rabies is from five to eight days. A longer course of the disease is extremely rare.
Deadly result
A person bitten by an animal can feel safe for a long time. Cases have been described where about a year passed from infection to illness, but most often this period is 1–3 months. The disease begins with the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the bite area (burning, nagging pain, itching, goosebumps), although the wound may already be completely healed. The reason is the multiplication of the virus in the spinal ganglia that innervate the bite area. Bites to the face usually cause olfactory and visual hallucinations. General symptoms - fever, headache, malaise - are accompanied by mental disorders. Apathy and depression are replaced by anxiety, pulse and breathing quicken, and a feeling of tightness in the chest arises.
Article on the topic
Prevention of rabies. What to do if you are bitten by a dog? This period lasts about four days, then specific encephalitis develops. The patient exhibits violence, aggressiveness, muscle spasms, epileptic seizures and paralysis are observed. Bright light, loud sound, touch and even a light breath can provoke an attack in the form of paroxysms of rage, between which consciousness clears up. Symptoms of encephalitis are soon joined by signs of impaired brainstem function, including impaired swallowing (dysphagia). Drooling combined with dysphagia leads to foaming at the mouth. But the most striking clinical symptom of rabies is hydrophobia (hydrophobia): when trying to drink, painful involuntary contractions of the swallowing muscles, diaphragm and auxiliary respiratory muscles occur.
When convulsions and attacks of hydrophobia stop, those around them mistake this condition for an improvement in the patient’s condition. But in reality it is a sign of imminent death. It occurs after 12–20 hours from paralysis of the heart or respiratory center. The total duration of the disease is 5–8 days, rarely slightly longer.
Diagnosis of rabies in humans
To make a diagnosis of rabies, a medical history (animal bite) is extremely important. If possible, the animal should be captured and examined.
The specific symptoms of the disease are also taken into account. Diagnosis of rabies is divided into intravital and postmortem.
Test for rabies in humans
Intravital is carried out by carrying out:
- virological examination of biological material (saliva, cerebrospinal fluid);
- PCR, ELISA, RIF;
- study of corneal imprints.
For post-mortem diagnosis, electron microscopy of frozen brain tissue, immunohistochemical examination of the brain, as well as MFA or PFA are used.
All work with the rabies virus is carried out only in specialized laboratories in compliance with the strictest safety measures and protocols for working with especially dangerous infections.
Read further: What is the polio vaccine, what are the consequences and reactions to the vaccine
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to correctly and quickly identify the diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the following nuances:
- detection of the site of an animal bite or scratch on a person;
- presence of signs characteristic of rabies;
- laboratory tests of the eye shell, in which the virus can be identified by an imprint of the surface of the eye shell.
To eliminate the risk of rabies infection, it is necessary to carry out vaccination on time, which prevents infection in 98% of cases, since this problem is very serious and leads to irreversible consequences - death.
Unfortunately, final confirmation of the diagnosis can only be after the death of the patient. This is carried out using the following means:
- histological examination for the presence of Babes-Negri bodies in the body. The cerebral cortex, cerebellum and amnon horn are examined;
- biological puncture. Brain cells of experimental rodents that receive a dose of intracerebral infection are being studied;
- immunofluorescence test. Nerve tissue, salivary glands and brain cells are examined for the presence of the rabies virus.
Treatment of rabies in humans
There is no cure. All treatment comes down to creating the most gentle conditions for the patient and alleviating his condition until death. After death, the body undergoes mandatory cremation.
Attempts have been made to treat with rabies gamma globulins, but there is no data on their effectiveness.
To date, only six cases of rabies survival have been reported. The most famous patient is Gina Gies, who was treated according to the Milwaukee Protocol.
This is an experimental treatment developed by Dr. Rodney Willoughby. Therapy consists of putting the patient into an induced coma (to protect the central nervous system until the body produces antibodies to the virus) and using antiviral drugs.
The patient spent seven days in a coma. In total, the treatment took 31 days. Subsequent studies showed that her brain was not damaged. Mental and cognitive functions were completely preserved.
How can a person avoid infection?
Rabies is a disease that is easier to prevent than to treat.
To avoid infection, you must:
- vaccinate pets in a timely manner;
- keep an eye on your pet during a walk, do not allow contact with wild and stray animals;
- catch stray dogs;
- do not touch street cats;
- do not hand feed squirrels in the park;
- When traveling to other countries, check the level of rabies and, if necessary, get vaccinated.
Prevention and vaccination against rabies in humans
After animal bites, you must immediately thoroughly wash the wound with laundry soap and running water, treat it with alcohol and iodine. It is strictly forbidden to cauterize or excise the wound, as this contributes to the spread of the virus.
After treatment in the hospital, the wound is sprinkled with powder containing anti-rabies gamma globulins.
They no longer give 40 rabies injections in the stomach. This method is outdated.
A person should be vaccinated against rabies no later than two weeks from the moment of the bite. After the specified period, it is practically ineffective.
Rabies vaccination schedule
At the moment, the following rabies vaccination schedule for humans is used: 1 milliliter of vaccine five times on the day of the bite. The drug is injected into the shoulder or thigh. Next, the rabies vaccine is administered on the third, seventh, fourteenth, twenty-eighth (or thirtieth) and ninetieth day after the bite.
The injection is given on the 28th or 30th day, depending on the vaccine manufacturer.
In case of severe bites or late treatment (10 days from the moment of the bite), anti-rabies gamma globulins are administered in addition to the vaccine.
Preventive vaccinations are recommended for people working with animals, hunters, researchers, veterinarians, etc. The rabies vaccine is valid for about a year. Therefore, for patients bitten by an animal within a year after a full course of vaccinations, vaccination is indicated only on the day of the bite + on the third and seventh days.
Preventive vaccinations are carried out upon application, as well as on the seventh and thirtieth day. A year later, the first revaccination is indicated (one administration), with further administration of the vaccine every three years (single administration of the vaccine).
Compatibility of rabies vaccination in humans and alcohol
Alcoholic beverages should not be drunk for six months after rabies vaccination and throughout the entire course of vaccination.
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of developing adverse reactions to the rabies vaccine.
The use of glucocorticosteroid drugs and immunosuppressants is also contraindicated.
Is it possible to wet the rabies vaccine?
The instructions for vaccines do not contain information about the prohibition of getting the vaccine wet. However, it is not recommended to actively rub the grafting site while swimming. Also, it is advisable to refrain from visiting the sauna (overheating is contraindicated).
During the course of preventive vaccination, overheating, hypothermia or excessive physical activity should be avoided.
Features of a viral disease
Until 2005, this disease was considered fatal to humans. There was no reliable evidence of a cure for this disease after the onset of symptoms at that time. Today, a free rabies vaccination, given immediately after possible infection, effectively prevents further spread of the virus.
In 2005, the first case of complete recovery of a person from this disease at the stage of manifestation of its symptoms was recorded. Thus, by 2012, 5 out of 37 people were cured by vaccination.
Historia morbi: what everyone should know
The disease, which in most cases ends in death, occurs in all warm-blooded animals. It is easily transmitted to a person who has been in contact with an animal whose saliva contains a dangerous virus. The causative agent is Rabies lyssavirus, which quickly attacks the peripheral nervous system of the infected creature. It can die only when heated to 100 degrees. With the opposite effect – freezing – its activity remains for up to 2 years.
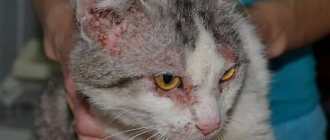
Do cats get rabies and do they have this dangerous disease that manifests itself in the form of encephalitis? Alas, pets are not immune from infection - especially if they have recently come into contact with carriers of the infection: foxes, rats and other rodents, raccoons, wolves, already infected stray cats - and have been bitten by them.
Interesting fact
The dangerous rhabdovirus has seven genotypes. Most animals infected with it will die within a few weeks of Rabies lyssavirus entering the bloodstream through saliva. In some mammals (for example, one species of mongoose), the virus “dormants” for several years, which allows them to infect their fellows and people for a long time.
How can a cat become infected with rabies and is the owner able to recognize it in an animal?
Any stray can infect a pet. If you live in a private house and know that there are foxes or ferrets in the neighborhood, it is not advisable to let your cat out for a walk unattended. The danger also comes from rats from the basements of city houses - do not allow the cat to play with such prey or try to eat it. Otherwise, the consequences are the same - the painful death of a pet, which you will not be able to help.
You can once again learn about the main sources of disease and danger of rabies in cats from the video:
If your cat is salivating, is lethargic and lethargic, or, conversely, attacks all family members and tries to bite you, refuses to eat and suffers from frequent vomiting, most likely, a dangerous virus has already entered the pet’s body and disrupted its functioning.
Can a domestic cat get rabies? Alas, living within the four walls of a city apartment will not protect your pet if you let him out for a walk every day and do not keep track of what animals your four-legged friend comes into contact with.
Outbreaks of viral activity are recorded annually even in large cities. Do not think that this disease is found only in villages or settlements located in close proximity to wild animal habitats - the threat exists, and you can avoid it only by protecting your pet in advance.