Cat diseases dangerous to humans
Veterinarians and experienced felinologists constantly conduct seminars to explain to owners the risks of zooanthroponotic pathologies and the need to prevent infectious diseases contagious to humans, but there are still many myths about the exaggerated danger of cats for humans.
There is a high risk of people developing the following diseases:
- rabies;
- ringworm;
- helminthic infestation.
Separately, it is worth explaining the situation with chlamydia and tuberculosis. Cats, like people, can suffer from this pathology, but the routes of infection differ among species. The structure of the immune system also differs.
Homo sapiens are more susceptible to some infections, cats are more susceptible to others.
For example, tuberculosis occurs more often and in a more severe form in humans, and cats do not tolerate toxoplasmosis well, which is asymptomatic in humans. And only rabies and lichen cause the same pattern of damage in both species.
Rotavirus infection in cats
Diseases in domestic animals caused by viruses occupy a leading place throughout the world. A particular danger is that viral organisms are highly infectious and resistant to environmental factors. In addition, various viruses can mutate, remaining completely inaccessible to the body’s immune system.
One of these viral infections is rotavirus, which causes serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract. When the body is affected by rotavirus infection, dyspeptic disorders occur that negatively affect metabolic processes.
Timely diagnosis of the disease and treatment can prevent serious complications that can develop against the background of a viral disease.
Pathogen information
The virus that provokes the development of infection belongs to the genus of rotaviruses, which took its name from the Latin language, where “rota” means wheel. This is due to the fact that the structure of the virus resembles a round formation with a hub, spokes and a rim.
Rotavirus is an RNA virus and has a diameter of 65 to 78 nm. The capsule is characterized by two layers. Virology distinguishes 9 types of rotaviruses and only 5,6 and 7 are dangerous to animals, but are not transmitted to humans.
RNA viruses are highly resistant to environmental factors due to their three-layer protein shell. Does not have a destructive effect on the lining and gastric juice, as well as digestive enzymes of the intestinal tract.
Replication of pathogenic microorganisms occurs in parts of the small intestine, affecting the villi and cellular structures (enterocytes) of the mucous membrane. As a result, necrosis and changes in the structure of the epithelium occur.
Viral enteritis is characterized by dyspeptic disorders - diarrhea and malabsorption processes.
A toxic substance of protein origin, secreted by the virus during its life activity, disrupts the normal absorption of water and the secretion of substances through chloride channels.
Against the background of developing pathology, a transient type of lactase deficiency occurs, occurring suddenly and lasting about 2-3 weeks.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The incubation period for rotavirus infection is on average up to 5 days. Infectious agents, penetrating into a susceptible organism, cause severe complications. The pet experiences severe pain in the abdominal area, the cat tries not to sit or lie down, and takes a forced position to reduce the pain.
A sign of rotavirus infection is severe vomiting. Eruptions of gastric contents occur so often that they subsequently lead to the appearance of bloody clots in the vomit. Body temperature increases several hours after the onset of the pathological process.
Profuse diarrhea occurs, in which impurities of blood and mucus appear. Small kittens develop catarrh of the gastrointestinal tract.
After the intestinal contents are expelled under the influence of pathological factors, the pet develops an unsuccessful urge to defecate. The animal suffers, cannot find a place for itself, and often falls exhausted straight into its cat litter box. Despite the fact that the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves sharply and strongly, the death of the animal is rarely diagnosed.
The cause of loss of strength may be dehydration, but with timely contact with a veterinarian and adequate therapy, complications can be avoided.
An accurate diagnosis cannot be made without differentiation. Thus, when conducting a general clinical examination, medical history and laboratory tests, it is necessary to exclude parvovirus infection, infectious leukemia, coronavirus and calcivirosis.
In addition to viral infections, similar symptoms may be caused by:
- damage by fungal microorganisms;
- diseases caused by pathogenic bacterial microflora;
- allergic type reactions;
- intoxication of the body with heavy metals or poisons.
The main diagnostic method in a laboratory is the examination of a smear taken from feces using special reactions. Thus, the most informative method is the immunofluorescence reaction, which allows not only to identify the causative agent of the infection, but also to determine the type of virus.
In addition, a general blood test, blood biochemistry and ultrasound examination are performed. Methods allow us to determine the degree of pathology and prescribe the most adequate treatment
Treatment and prevention of rotavirus infection in cats
Rotavirus enteritis must be treated immediately with the first appearance of characteristic symptoms. The basis of therapy is the restoration of damaged mucosal barriers.
An integrated approach to the treatment of viral infection is aimed at eliminating painful sensations, protecting against secondary microflora, and stimulating the body’s immune forces.
In case of physiological dysfunctions of the body, replacement therapy is indicated.
An important role in the treatment of any viral infections in pets is played by the correct diet, as well as the additional introduction of vitamin and mineral complexes. This will make it possible not only to increase the effectiveness of treatment, but also to free the body from toxic substances more quickly.
The homeopathic drug Gamavit has proven itself well in the treatment of viral infections. It allows you to enhance the effect of the main treatment by normalizing metabolic processes and neutralizing toxic substances.
At the very first signs of rotavirus infection, it is advisable to administer globulins and serums that have an antiviral effect to the cat. Immunomodulators and herbal medicines are used to maintain the body's strength.
There is no specific vaccine against rotavirus infection in cats, so it is extremely important to adhere to preventive measures. As a result of careful attention to the health of your pet, properly selected nutrition, regular antiparasitic treatments and vaccinations, the risk of developing rotavirus is reduced.
It is necessary to regularly carry out preventive examinations with a veterinarian once every 6 months, as well as to treat systemic diseases that gradually undermine the functioning of the entire body.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/ivethelp/rotavirusnaia-infekciia-u-koshek-5d2ee6b18600e100ac7437bf
Danger of scratches
A person can become infected from a cat with a rare form of fever - felinosis. Its causative agents, Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana, enter the body through scratches on the skin and are found in saliva, urine, and on the paws and claws of the animal.
Redness and papules appear on the affected areas. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic; in rare cases, inflammation of the lymph nodes and fever occurs, and sometimes conjunctivitis develops.
If the disease has a mild form, then usually the person’s immune system copes with the infection itself. In case of complications, adequate and timely treatment (erythromycin, tetracycline) leads to rapid recovery.
There will be no re-infection; a person will develop a strong immunity.
It is almost impossible to determine whether a cat is a carrier of Bartonella. Externally, the pathology manifests itself in the form of a slight decrease in activity and enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Hygiene when interacting with a pet
Communication with mustachioed friends brings a lot of joy, so it is difficult for owners to refuse frequent contact with them. But at the same time, any owner should know what a person can get infected from a cat in order to protect themselves and others from health problems.
It is recommended to wash your hands after stroking the cat, and in case of a bite or scratch, disinfect the wound. Loving owners should refrain from kissing their four-legged animals to avoid getting sick themselves and becoming a source of the virus for their pet.
If a cat is vaccinated, is seen by a veterinarian and does not go outside, the risk of contracting something unpleasant from him tends to zero, but does not completely disappear. If you have close contact with animals, be sure to check with a doctor yourself.
All fluffies are very clean. However, it is they who become the source of dangerous pathologies for others, and often this happens due to the owner’s ignorance or due to improper care. If a cat undergoes regular vaccinations, treatments for worms and fleas, and receives the vitamins and microelements necessary for immunity, then the risk of getting sick and infecting people is reduced as much as possible.
The article is for informational purposes only. Contact your veterinarian!
Worm infestation
Young children are most at risk.
Not all types of helminths are dangerous. Diseases that can develop in humans when infected with parasites from a cat:
- toxacarosis (roundworm);
- dipylidia (cucumber tapeworm);
- echinococcosis.
Symptoms of the disease:
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the intestines and stomach;
- rashes on the body;
- loss of appetite, apathy;
- cough and fever.
Infection can occur through saliva or feces of a sick cat.
Signs of parasite infection in pets and humans have a common picture. But the animal usually quickly acquires an unsightly appearance (dull, oily coat) and loses weight.
In order to prevent infection, it is necessary to take preventive measures in a timely manner.
If the disease has already occurred, you should immediately seek medical help. In its most severe form, a person experiences echinococcosis, which without proper treatment can cause internal bleeding. With proper and timely treatment, complete recovery occurs.
Medicines in the treatment of helminthic infestations
In order to determine the need to use medications, you must first consult a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis. Doctors will prescribe a series of tests that will help diagnose the type of helminthiasis. This will make it possible to select the most effective and safe medications. Self-medication in this case is completely unjustified, since anthelmintic medications are mostly very toxic and, if used incorrectly, cause serious harm.
In the treatment of helminthic infestations in humans, a variety of medications are used, which differ in their composition, spectrum of action, as well as the presence of side effects and contraindications.
Thus, levamisole can be used in the correction of ascariasis. To achieve a therapeutic effect, it is enough to take a single dose of 150 mg of the active substance once in the evening, the children's dosage is 2.5 mg per kilogram of body weight. Levamisole can provoke a variety of side effects, among which the most common are problems in the digestive tract, represented by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, etc. The drug has few contraindications, including individual intolerance, pregnancy and breastfeeding, agranulocytosis and children under fourteen years of age. This medication is also available under the trade name Dekaris.
One of the most popular medications for helminthic lesions is Pirantel. It copes with ascariasis and enterobiasis. It is usually prescribed to take 10 mg per kilogram of body weight. Pyrantel has few contraindications; it is not used only during pregnancy and in case of excessive sensitivity to its components. Also, the medicine can cause a minimal number of side effects, which disappear soon after therapy. They may include nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, diarrhea and stomach discomfort (pain).
Only a doctor can choose the appropriate medicine. And it should be used only in accordance with the instructions.
In parallel with the treatment of people, it is imperative to deworm the pet. Various drugs are used for this, but before using them it is better to consult a veterinarian. Doctors most often prescribe Drontal to their tailed patients, and they usually recommend giving small kittens Milbemax, etc. Practicing veterinarians strongly advise using such medications once every six months - for preventive purposes. This will help prevent transmission of the disease from cats to humans.
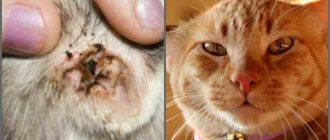
Ringworm
This is a highly contagious disease. Domestic cats are at risk of catching it from stray animals. A person can become infected simply by petting a sick pet.
The pathogens - Microsporon, Trichophyton - are anthropozoonotic, that is, common to both.
When affected by this fungal infection, redness, peeling, and purulent lesions usually form on the skin of the hands, head and face. Without timely treatment, the affected area grows and hair loss occurs.
A person can bring the fungus into the house on their shoes or hands if they pet a sick street cat.
It is often difficult to determine who the primary and secondary sources of infestation are in a home. Cats, due to their healthy immunity, sometimes act as carriers of ringworm without contracting it themselves.
This fungal infection requires long and persistent treatment. At the first signs of infection, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to immediately identify the pathogen and begin active therapy. The prognosis is favorable, lichen is completely cured. To prevent infection of pets and people, preventive measures must be followed.
Therapy, caring for sick animals
Once rotavirus has been diagnosed, treatment should begin immediately. Let us emphasize once again that specific therapy simply does not exist, and therefore everything is limited to alleviating the animal’s condition through intravenous infusion of compounds that relieve signs of intoxication and dehydration. When the animal’s condition improves, you can begin “normal” feeding. The diet should include only easily digestible foods that will not put too much strain on the cat’s digestive system.
Rabies
This is one of the most terrible diseases in the world, as it is incurable. The only way to protect yourself is to regularly vaccinate domestic and stray animals.
The rabies virus is contained in the saliva of a sick animal. It is transmitted by a bite or contact with scratches and microcracks in the skin.
The disease in humans occurs in two forms. Can be paralytic and violent. If you suspect infection, you must immediately contact a medical facility and undergo a course of vaccinations. Success depends on timely treatment - immediately after the bite.
There are three forms in cats - atypical, violent and hidden.
Symptoms of rabies in a cat:
- unusual animal behavior;
- refusal of food and water;
- vomiting and diarrhea;
- hydrophobia and photophobia;
- desire for isolation;
- rapid intensification of all signs;
- muscle paralysis.
The rabis virus infects the mammalian brain and causes inflammation, which rapidly develops, affecting the entire nervous system. Death usually occurs from paralysis of the respiratory system.
No attempt is made to treat a sick animal; it is immediately euthanized, and the body is subject to cremation.
Can a cat become infected with rotavirus from a person?
Rotavirus infection in cats affects the gastrointestinal tract, mainly the small intestine, and is therefore also called rotavirus enteritis.
The causative agent of rotavirus infection
An RNA virus from the rotavirus family. “Loves” mainly the epithelium of the stomach and small intestine. This means that it will multiply and, accordingly, affect precisely these organs.
Epizootology
The spreader of the infection is a sick cat. The disease is mainly transmitted through nutritional means, contact and household contact, and cases of airborne dust transmission are not uncommon. Mostly, kittens that are bottle-fed and living in nurseries get sick - this is the highest risk. The incubation period for rotavirus infection ranges from 15 hours to 5 days.
How does rotavirus enteritis develop and occur in cats?
The favorite and only place where rotavirus feels comfortable and has the ability to reproduce is the epithelial cells of the stomach and small intestine.
Enterocytes at the tips of the intestinal villi are predominantly affected, which leads to disruption of water metabolism, absorption of nutrients and inflammation of the intestinal wall. A cascade of reactions is launched, forming a kind of vicious circle.
Fermentation and putrefaction processes occur in the intestines, nutrients are not absorbed, water is absorbed back, causing dehydration.
Clinical picture of rotavirus enteritis in cats
The onset of the disease is acute. The kitten is characterized by severe anxiety - it rushes about and screams. Palpation of the abdomen is sharply painful. High fever up to 40 degrees. A little later, vomiting and an imperative urge to defecate appear, and dehydration develops.
The stool is liquid, mixed with mucus and blood. In some cases, some individuals may experience catarrhal symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract. The duration of the disease is 3-10 days. The course is mostly benign.
Lethal outcome is rare and depends on concomitant pathologies.
Diagnosis of rotavirus infection in cats
Most often, electron microscopy of stool or other virological and serological methods are used.
Treatment of rotavirus infection in cats
Treatment is symptomatic. Rehydration and vitamin therapy is carried out. Drugs are administered intravenously to maintain cardiac activity and correct immunity. All activities must be carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Feline cryptococcosis
Feline cryptococcosis is a type of fungal disease that affects the skin, respiratory system, brain, and sometimes the central nervous system. Infection most often occurs through airborne droplets, when fungal spores are inhaled.
Feline immunodeficiency virus
Feline immunodeficiency virus is a disease that affects the lymphatic system of an animal and causes immunodeficiency syndrome. In most cases, at the initial stage the disease is asymptomatic and only lasts for a long time (sometimes up to several.
Reovirus infection of cats
Reovirus infection belongs to the respiratory category. It occurs in all types of animals, but cats are most commonly affected. The causative agent of the disease is Reovirus. There are three serotypes of reovirus. The clinical picture depends on the type of virus.
Rotavirus in cats is a genus of Rotavirus viruses from the reovirus family that causes rotavirus infections, also known as “intestinal” or “stomach flu” (not related to the real influenza virus), in cats, other animals and humans. Rotavirus attacks the walls of the small intestine, disrupting its function.
Rotavirus: where from
• Consumption of food and water contaminated with fecal particles from infected animals and people
• Inhalation of fecal particles from infected animals
Rotavirus is ubiquitous and affects almost all mammals, including livestock, cats, dogs and humans.
Moreover, there are several different strains of viruses, each of which “specializes” in its own type of mammal. However, in rare cases, cross-infection or mutation of one strain occurs under the influence of another.
Thus, a cat can become infected with rotavirus from a person, and a person can become infected with a cat, but this does not happen often.
Typically, the virus infects young (children) mammals, as well as older individuals and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Rotavirus in cats: symptoms
• Anxiety or depression
• Diarrhea (sometimes bloody)
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/mozhet-li-kot-zarazitsja-ot-cheloveka-rotavirusom
Other diseases
In addition to the most common, there are other anthropozoonotic diseases; cases of these infections are much less common.
Toxoplasmosis
It is also provoked by protozoa - Toxoplasma.
It poses the greatest threat to pregnant women; it can lead to the development of fetal pathologies and miscarriage.
The symptoms resemble the onset of acute respiratory viral infection, enlargement of the lymph nodes occurs, fever and conjunctivitis occur. Infection occurs during an acute illness of the animal through feces, if they have been in the litter tray for a long time (3-5 days) and through mucous discharge from the nose.
In the chronic form of the disease, the cat is not contagious to humans. Pets are infected with Toxoplasma through raw meat. The disease requires immediate treatment, the prognosis for the person is favorable.
The acute form of the disease is a common cause of death in small kittens and young animals.
Scabies
The causative agent of the disease is the scabies mite. Signs in a cat are revealed during an external examination. Areas of flaky skin and bald patches appear on the body.
It is extremely rare for a person to become infected. But if itching, rash and peeling of the skin appear, you should immediately consult a doctor; timely therapy can quickly cope with the disease.
Salmonellosis
Cases of infection from a pet are extremely rare.
The general symptoms of the disease are fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting. This is a serious disease, but it can be successfully treated with timely consultation with a doctor. Cats are usually infected by eating raw meat.
Aujeszky's disease
This disease of mammals is characterized by damage to the central nervous system. Its symptoms in pets are drooling, loss of coordination of movements, outbursts of aggression, itching of the skin.
Animals become infected through infected meat and often die. The disease is transmitted to humans by airborne droplets and manifests itself in itchy skin and increased body temperature.
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Tularemia
This severe bacterial disease is transmitted by insects that usually parasitize the corpses of rodents, and in the warm season - by blood-sucking insects.
A person can become infected from a pet through any household contact. The disease in mammals develops rapidly, and the infectious period is also short. The lymph nodes, respiratory system and spleen are affected.
It is rare and there is no vaccine.
At the first signs of infection, active therapy should be started immediately under the supervision of a physician.
Toxoplasmosis: sources of infection
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease. Toxoplasma multiplies in the cat's body, and the eggs are excreted in excrement, and can remain viable for many years.
Toxoplasma is found everywhere - in children's sandboxes, soil, water, meat, vegetables, even on the soles of shoes. The cat itself can become infected when it swallows a sick mouse, licks a paw soiled in the ground, or smells the excrement of stray animals. When Toxoplasma enters a cat’s body, the bacteria are conditionally divided into two groups.
One group begins active reproduction in the small intestine. Cysts then form and are excreted in the feces. Signs of infection are not always obvious, so the owner may get sick while cleaning the litter box. But only if the tray has not been cleaned for three days - the cysts need to mature. Cysts continue to be released for three weeks after infection, and once excreted, they no longer pose a threat.
Toxoplasma from another group begins to invade tissues and spread throughout the body. To understand whether pregnant women can have contact with animals, you need to consider in detail the symptoms of toxoplasmosis in cats and the treatment required for the animal.
How can you tell if your cat has toxoplasmosis?
When you first become infected with toxoplasmosis, several weeks may pass before cysts are excreted in your feces. Signs of the disease are very minor: scant tear discharge, rhinitis, diarrhea or vomiting. And after a couple of days, not a trace remains of the malaise - the disease transforms into a latent, and over time, into a chronic form. If the cat is healthy, then the immune system prevents toxoplasma from actively multiplying. Now the animal ceases to be a source of infection, unless it becomes infected again.
If the pet is not in good health, then the disease becomes acute or subacute; this form of the disease is extremely dangerous for humans.
Treatment of a cat for toxoplasmosis
There is no 100% guarantee that your pet will be cured. You can only try to transfer the disease from acute to chronic form. Therapy continues for a relatively long period of time: from several weeks to a year.
Methods of protection against toxoplasmosis
To protect a pregnant woman from infection, you can ask relatives to clean the tray every day and treat it with a 10% ammonia solution; do not give your pet raw meat; Attach a bell to the collar to prevent the cat from catching birds and mice. It is necessary to maintain the pet’s immunity at a high level, feed it enough, take care of cleanliness and hygiene, and visit the veterinarian every year.
Doctors strongly recommend limiting a pregnant woman’s interaction with a cat, but only if the pregnant woman has not previously suffered from toxoplasmosis.
If toxoplasma is present in her body in a dormant state, then all concerns can be discarded. Acquired immunity will become a reliable barrier to infection and will not allow it to pass through the placenta. In this case, pregnancy and a cat in the house will set the mood for harmony and calm. The situation becomes much more serious if the woman has not previously had toxoplasmosis, then there is a risk of infection and all contact with cats must be stopped.
Preventive measures
A person can easily prevent any anthropozoonotic diseases by following simple rules.
Deworming
Your pet must be dewormed promptly, at least once every three months. This simple procedure is carried out independently. The cat must be given a special tablet or suspension and the threat of infection with many unpleasant diseases caused by parasites will be prevented.
Annual vaccination
It is one of the main methods of combating anthropozoonotic diseases:
- Pets must be vaccinated against rabies annually. In many public veterinary clinics, Nabivak-rabis injections are given free of charge. This disease, terrible not only for cats, but also for people, has now been practically eradicated from the world. Sometimes its local foci flare up, the causative agents of which are wild animals - foxes, rodents. Universal vaccination helped to cope with the disease. People who work with animals year-round can also get a rabies vaccination once a year.
- Vaccinating your cat against common feline viral infections is also necessary. Although they are not dangerous to humans, they indirectly help maintain their health. After all, if an animal is weakened, it will easily catch a disease that is dangerous to humans.
- Ringworm can also be prevented with special vaccinations. They are not mandatory until they are proven to be 100% effective.
Treatment for external parasites
Cats, especially those walking outside, must be treated with special antiparasitic agents twice a year. They are available in the form of collars, drops, lotions, and shampoos.
After all, many external parasites are causative agents of unpleasant diseases that are equally dangerous for both cats and humans.
Worms that live in a cat's body
Do not think that a cat can only get parasites from food. If this were so, then a good heat treatment of the food before giving it to the animal would be sufficient to protect the pet from disease. However, infection can even occur from insects that fly in through open vents or windows during the warm season.
The following types of worms can be found in the body of cats:
Nematodes (roundworms). They have an elongated body and can grow up to 10 cm in length. In excrement they look like white moving threads. Since their bodies are very thin, it is almost impossible to detect them with the naked eye in the early stages. These parasites live in the stomach and intestines of the cat. The most common representative of this group is Toxocara, which is the causative agent of toxocariasis. Hookworm, another representative of the same group, can enter the body even after an ordinary walk on contaminated soil, on the surface of which eggs were contained, as well as from water, after hunting insects or mice. Since nematodes live in the digestive system, they cause a gradual loss of weight in the cat.
Nematodes (roundworms)
Cestodes (flatworms). They have a flattened body shape, so they resemble a small ribbon. The second name for this group is tapeworms. The head is embedded in the epithelial tissue of the host, and segments with eggs mature on the body, which break off and come out with excrement. In addition to the intestines, these parasites settle in the nervous system, causing deep damage.
Flatworms
Trematodes. Their body is so small that a person cannot see the parasite with the naked eye. They invade all the internal organs of the cat, causing various diseases. Often large lesions are present in the liver, causing great suffering to the animal.
Trematode worms
Preventive action
Following simple rules will help prevent infection of cats and humans:
- To reduce the risk of Bartonella entering the human body, it is necessary to trim your cat's claws in a timely manner. And never play with her with bare hands, avoid scratches and bites. If an injury occurs, the affected area should be thoroughly washed with soap and disinfected.
- If the cat is on a natural diet and receives raw meat, then it is necessary to be especially careful in its selection, storage and processing. The diet should be purchased only from trusted sources; the meat is thoroughly washed and frozen in freezers for at least three days. Before feeding the pet, it is washed again. It is also advisable to pour boiling water over it.
- You should not give your pet food that shows signs of infection or is spoiled.
- Do not allow pets to come into contact with stray or wild animals.
Protecting pregnant women from sick cats
It is especially dangerous for pregnant women to come into contact with sick pets.
Following simple rules will help reduce the risk of infection:
- Do not eat raw foods;
- it is necessary to take a monthly test for toxoplasmosis;
- during pregnancy you should not get new pets;
- When caring for pets, you should be careful and follow the rules of hygiene;
- Boost your immune system every day through a healthy lifestyle and healthy diet.
Disinfection and personal hygiene
The most important preventive measures to prevent infections with any anthropozoonotic human diseases is daily cleaning of premises using disinfectants.
If one or more pets live in the house, you must:
- Regularly carry out wet cleaning of premises
- Every day, remove feces from the cat litter box, throw away contaminated litter, and thoroughly wash and disinfect the litter box itself.
- Cat houses, beds, bedding, toys, scratching posts and upholstered furniture in the house should be regularly treated with a steam generator or washed at high temperatures.
- After playing with animals, feeding, or cleaning, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap. If necessary, treat with disinfectants.
Prevention
Knowing that cat worms are transmitted to humans, many owners begin to follow simple rules to prevent infection. What to do to avoid getting infected again?
It is necessary to wash your hands thoroughly after contact with an animal or its things; Don't kiss the cat; Do not share food from your plate with an animal; Carefully and promptly treat surfaces with which the animal frequently interacts; Periodically wash or process all your pet’s things – bowls, beds, shelters, toys; When an infection occurs from a cat, it is very important to treat the pet in a timely manner; Replace or treat with antiseptics all the things that the cat used, otherwise the parasites may be transferred to the animal again; You can also treat all surfaces on which the animal likes to lie with antiseptics; Be sure to replace the tray, as this is what can infect again.
In the future, it is important to apply preventive measures in relation to the cat - periodic preventive anthelminthization, limiting the animal’s contact with potentially infected individuals, limiting its access to the street, and eating only thermally processed meat, fish and poultry. The owner should also limit his contacts with potentially infected animals (for example, do not pet stray cats)
It is not known whether a pet can become infected through the hands of its owner, but theoretically there is such a possibility. After all, after contact with an infected animal, a person can transfer worm eggs from his hands to the fur of his healthy pet.
If the cat is sick
At the first signs of the disease:
- The pet must be isolated from other animals and people.
- Urgently contact a veterinary clinic to diagnose the disease.
- Follow all prescriptions and recommendations of the veterinarian.
- Carry out complete disinfection of residential premises.
The most suitable products for treating hard and soft surfaces are Verocid, Virkon, Tetralin, Laina, any chlorine-containing cleaning preparations, Chlorhexidine for treating hands and animals.
Echinococcus
A rarer type of cat worms in the form of tapeworms can affect any organs, but are usually localized in the liver area. An animal becomes infected by eating inseminated meat or by catching a carrier – a small rodent. Dangerous parasites are not often transmitted from cats to humans, causing serious damage to internal organs, including the brain.
Echinococcosis develops when worm eggs enter the human body through contact with the fur or tray of an animal. Active reproduction of helminths begins in the intestines, and then migrates throughout the body. Having settled in one of the organs, a colony of parasites interferes with blood circulation, which is fraught with tissue necrosis. In cases of extreme infection, surgery may be prescribed. If the disease is ignored, death is possible.
Ways of infection by parasites
Helminths reproduce by laying eggs. When they come out with the excrement of an infected animal, they can persist for some time outside the host’s body, in the external environment. The cat licks itself, so parasites can end up on its face, fur, and paws. Therefore, the most common way of infecting a person with helminths from a cat is through contact.
By kissing and stroking a cat, a person can pick up parasite eggs if he does not wash his hands.
It is very easy to become infected with worms through the feces of a domestic cat. You should clean the tray as often as possible while wearing rubber gloves. A cat's litter box is the most dangerous place to become infected, since helminth eggs are released in feces.
Also read the article about worms in cats.