- Factors contributing to inflammation
- How does inflammation of the anal sacs manifest in a cat?
- Treatment of the inflammatory process of the paraanal glands
- What can a pet owner do?
Inflammation of the anal sacs in cats is an infectious disease that many pet breeders face. It is typical mainly for purebred animals, which over time have lost the ability to independently empty their anal sacs of secretions. The fluid accumulated in the paraanal glands causes the latter to overflow, causing them to sharply increase in size, which significantly complicates the normal act of defecation in the animal and even prevents it from walking. To prevent this from happening, the cat owner needs to periodically help his pet and carry out a simple procedure for cleaning the animal’s paraanal glands with his hands every few months.
What are paraanal glands?
Anal (paraanal) glands are paired glands located at the anus. They look like small “bags” and secrete a secretion that performs various functions. One of them is recognizing the opposite sex and attracting them for further mating.
Other functions performed by the paraanal glands:
- protection from enemies (scaring away),
- marking the occupied territory,
- maintaining metabolism in the body,
- attracting partners.
During inflammatory processes, the functions of the glands are disrupted. Because of this, the pet experiences serious discomfort. In advanced cases (for example, with the development of an abscess), this problem can lead to serious and irreversible consequences. However, it is possible to avoid them if you know all the most important things about the causes and signs of inflammation.
Essence and purpose
Through the anal sacs, the pet produces a special fluid (secret). Its necessity lies in the self-defense of cats and kittens from various dangers. The discharge has an unpleasant, pungent odor that even hurts a person’s nose. With the help of the secretion secreted by the paraanal glands, it is possible to throw the enemy off the scent and there is an opportunity to hide in a safe shelter. There are other functions of a similar feline structure, according to the Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy, edited by Dyce KM:
- Determining the boundaries of your own territory.
- Ensuring a painless bowel movement process. During defecation, the anal sphincters compress the fluid-filled paraanal glands and a small amount of secretion is released. This mechanism makes it easier for solid stool to pass out.
- Often the male sprays the contents of the anus to attract the attention of the female. Cats can do the same thing.
Common Causes of Inflammation
Inflammation or abscess of the paraanal glands often develops with trauma and mechanical damage to this area (for example, falls from a great height). This leads to dysfunction of the glands, disruption of the outflow of secretions and its subsequent accumulation. All this provokes the development of an inflammatory process involving pathogenic microflora.
Most often, long-haired cats living in apartments face the problem of inflammation of the paraanal glands. This is due to the fact that they lose the natural ability to cleanse the anal sacs (due to the absence of potential enemies and the need to defend themselves from them).
Common causes of inflammation of the paraanal glands:
- dysbacteriosis (for example, due to prolonged use of antibiotic drugs by the pet),
- helminthic infestations,
- eating small bones
- feeding mass market liquid food,
- lack of physical activity,
- injuries to the anus and anal area,
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by frequent constipation.
Older cats are more prone to inflammation and abscess of the anal glands. One of the factors that can affect the development of the inflammatory process is that the pet’s gland channels are too narrow from birth. Veterinarians include cat pregnancy and excess weight (obesity) as additional provoking factors.
Without timely veterinary care, the animal will develop complications. The inflammatory process can quickly develop into an abscess (purulent inflammation), which poses a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of your pet. That is why, when the first signs of a problem appear, you need to contact a veterinary clinic in Moscow as soon as possible.
Predisposing factors and diagnosis
What are the main reasons for the development of such a delicate disease? Poor immune system (chronic infections). The risk of disease is increased in case of poor nutrition, use of low-quality feed by the owners, the disease can develop against the background of complications after castration. Other predisposing factors:
- Almost any acute or chronic gastrointestinal infection.
- Age-related changes in blood vessels, as well as vascular pathologies that develop against the background of the above-mentioned infections and other diseases.
- Intestinal disorders (constipation or diarrhea). If your cat is constantly pushing, then this will not end well.
- All diseases of the rectum.
- Helminthiases.
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture. If a cat is constantly worried because of pain in the anus, rides on its butt on the carpets and constantly licks the perineum, there is reason to suspect paraproctitis. It is especially easy to confirm the diagnosis if the inflamed sinuses are swollen and open, after which a fistula forms.
How is paraproctitis treated in cats? First, the veterinarian will perform mechanical cleaning, squeezing out the accumulated secretion from the gland. Secondly, if there is a fistula canal, the animal is prescribed antibiotics and bandages with antiseptic ointments and liniments are applied. Please note: if your pet has ever had “clogged” para-anal sinuses, then this pathology will haunt him constantly. So take your cat for preventive examinations more often!
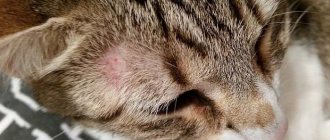
Signs of inflammation and abscess
Signs of inflammation develop gradually. They are accompanied by an increasing painful symptom. Due to pain and itching, the cat constantly licks the area of inflammation (tail and anus). The pet stops playing, spends time in solitude, practically does not move and constantly lies down. However, this is not the only symptom.
Other signs characteristic of inflammation of the paraanal glands:
- weakness,
- apathy,
- unpleasant specific odor from the pet’s body (does not disappear after washing),
- poor appetite (in later stages – refusal to eat),
- painful bowel movement,
- discharge from the anal glands.
With an abscess, this condition is accompanied by purulent or bloody discharge. In especially severe cases, body temperature rises. When stroking the affected area, the pet shows aggression and anxiety. Defecation is accompanied by severe pain, so the cat meows loudly on the tray.
Main clinical signs
Pain, soft tissue swelling, hyperemia (redness), hyperthermia (increased local temperature) and discharge of large amounts of pus. This is observed in almost all cases when the paraanal sinuses are inflamed. One of the classic signs is riding on the bottom - this is always due to helminths, but they are not always the cause of such behavior. The inflamed sinuses themselves can reach the size of a good apple (you will see an example in the photo). They often break out, and a large amount of thick, foul-smelling pus flows out of the cavity of the affected organ.
It is important to remember that such symptoms can also indicate more serious pathologies. For example, for anaerobic paraproctitis. It causes serious irritation of all nearby tissues, their pronounced swelling, and cases of necrosis are not uncommon. Pathogenic microorganisms can play an important role in the development of this disease. Viruses, chlamydia, mycoplasma, and gardnerella are especially dangerous (but this is in truly unique cases).
Treatment: main stages and methods
Treatment of inflammation or abscess of the paraanal glands should only be carried out by an experienced veterinarian in Moscow. We strongly do not recommend trying to help your pet at home. This will only worsen an already difficult situation.
The first step in treating inflammation is diagnosing the animal's condition. The veterinarian examines the affected area, interviews the owner (about the severity of symptoms, the degree of their manifestation, etc.), after which he assesses the cat’s condition and prescribes treatment.
Cleaning
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner (at the first stage of the inflammatory process), then treatment will be limited to cleaning the paraanal glands. This procedure does not require special conditions, so it can be performed in the clinic or at home, but only by a professional veterinarian.
Before cleansing the glands of accumulated secretion and secretion, it is necessary to palpate them. This will allow you to determine the consistency of the contents and select a cleaning method. If the secretion is liquid, then the external method is used, if it is dense, the method of rectal sanitation is used.
After cleaning is completed, the affected area is thoroughly treated using an antiseptic solution. To prevent further inflammation (preventive measure), an anti-inflammatory suppository is inserted inside.
Washing
Unlike external cleaning, washing the paraanal glands cannot be done at home. It is carried out only in a veterinary clinic, since it is prescribed in difficult situations (for example, when a fistula forms).
Before washing the abscess, the glands are cleared of accumulated secretions, then an injection is given with local anesthesia. Next, the specialist injects an antiseptic solution into the anus using a catheter (an alternative is a syringe without a needle).
Washing is carried out not once, but several times. This is necessary so that the liquid flowing back (antiseptic solution) becomes completely transparent. This condition indicates that there is no secretion or purulent discharge left.
After washing, the pet is given an anti-inflammatory suppository, and the damaged area is carefully treated with antiseptic ointment. If the cat's condition is of concern, the specialist will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Removal
Unfortunately, washing does not always give a positive result. In particularly severe situations (for example, with a developed abscess), the veterinarian resorts to an extreme method of treatment - surgical removal of the paraanal glands.
The surgery is performed using general anesthesia. The surgeon makes two incisions in the area where the glands are located, and then removes them along with the ducts. Then he puts stitches and treats with an antiseptic solution.
After surgery, your cat will need home care. In order for it to fully recover, it is necessary to regularly treat the area with regenerating agents (solutions, ointments), give vitamins and antibiotics for 7-10 days.
Warning
It is worth remembering that you need to be very careful when cleaning your cat’s anal glands at home. Treatment of inflammation can also be carried out in veterinary clinics, especially if there is no experience or desire to do this. Problems can await not only squeamish owners - the process itself often causes difficulties:
- under the influence of fear and pain, the animal can seriously injure the owner, who did not secure it firmly enough;
- There are many vessels and nerve endings intertwined around the anus; inept actions can injure them, which will lead to a deterioration in the pet’s health.
If you still need to carry out the procedure yourself, you should first learn from a specialist, ask questions, clarify the technique and procedure.
The frequency of cleaning is individual in each case. For some animals, it is enough to do this once, while others have to cleanse the glands regularly.
It is very important to pay attention to your pet's behavioral habits. If there is increased attention to the back of the body, it is worth checking it for symptoms of inflammation of the glands. On average, sick animals need to clean their anal sacs once every six months, while healthy animals cope with this on their own.
Recovery after treatment
After cleaning, rinsing or removing the anal glands, your cat requires special care. This will allow her body to recover faster and avoid unwanted consequences. The first thing that is necessary is to ensure the pet's comfort. Set up a bed for him in a warm place without drafts or blowing.
Maintain a therapeutic diet for 10-14 days. Eliminate solid food completely and provide constant access to fresh drinking water. Avoid excess carbohydrates in your animal's diet. It must be completely balanced so that the cat quickly recovers from a severe inflammatory process.
Treatment of anal discharge
Regardless of the causes of anal discharge in cats, a doctor should first of all deal with them.
But many pet owners do not want to resort to the services of veterinary clinics. Of course, if the owner is absolutely confident in his abilities and is fully aware of the situation that is happening to his cat, more independent treatment is allowed. However, beginners should listen to the opinion of doctors so as not to put their cat at risk.
Sometimes ridding a cat of anal discharge is not so easy. If the abundance of secretion does not decrease and lasts for several days, an examination should be performed. Here you must thoroughly wash and disinfect your hands. Next, you need to squeeze the area adjacent to the animal’s sphincter with two fingers. If at the same time a thick and viscous secretion occurs, it makes sense to think about the presence of certain disorders in the animal’s body.
To avoid worsening the situation, a whole range of measures should be taken to help correct the cat’s condition. Initially, you should arm yourself with special medical gloves. After smearing your finger with Vaseline, you need to insert it into the source of the cat’s discharge.
Carrying out manipulations according to the instructions will lead to an improvement in the pet’s condition within 2-3 days.
However, this procedure cannot be performed without special skills and a full understanding of what is happening. The best thing is to trust the professionals at the veterinary clinic, who will professionally take care of the animal’s health.
© shutterstock
If the disease is advanced, doctors can prescribe complex treatment for the discharge. Both procedures and medications will be used here. Antibiotics are especially often recommended. If your cat is bleeding from the anus, this may be a reason for surgery. However, this is an extreme measure that is carried out quite rarely. Often less radical methods of treatment are sufficient, even if it involves bleeding.
After the cat’s condition improves, you should consult a doctor about preventing discharge. This will avoid relapses and improve the cat’s overall condition. Only compliance with the doctor's instructions can prevent the worsening of chronic diseases and the recurrence of inflammatory processes. He can give advice related to:
- cat care;
- food;
- routine examinations of the animal.
It's a shame when your beloved pet gets sick. Especially when the kitten has discharge from his butt. However, the main goal, in this case, should be a directed and productive fight against the disease.
Timely measures can not only alleviate the cat’s condition, but also quickly save it from a dangerous disease.
Therefore, most owners try to make every effort to create favorable conditions for their beloved animal to recover.
Prevention of inflammation of the paraanal glands
Inflammation and abscess of the paraanal glands are a serious blow to your cat's health. However, it is possible to avoid it. The main thing is to follow simple recommendations for prevention from experienced veterinarians.
Adviсe:
- Your pet should lead an active lifestyle (in accordance with its age). If you don't have much time, special toys and exercise equipment for cats will help with this.
- If your animal's anal glands are often clogged, consult a specialist and discuss the issue of removing them.
- Try to avoid cheap liquid food and do not give your pet small bones, as well as foods that can cause gastrointestinal injury.
- At the first signs of inflammation, consult a doctor. Don't forget about regular preventive examinations.
- Carry out anthelmintic treatment once every 6-12 months. This completely eliminates the possibility of developing parasitic diseases.
Inflammation or abscess of the paraanal glands is dangerous to the health and life of the cat. A seemingly insignificant problem can lead to dangerous consequences, including death. That is why we strongly recommend that you follow preventive measures, and if the first signs of inflammation appear, contact your veterinarian immediately!
Paraproctitis in cats
There is a widespread opinion that if a cat “rides” on its butt, then it is probably tormented by worms. True, this isn’t about your beloved and beloved pet, is it? You do not forget about regular anthelmintic measures (tablets, sweet suspensions or drops on the withers), as well as vaccinations against infections and treatment for fleas and other “bloodsuckers”. Then what is the reason? And the reason for such unusual and even unworthy behavior of your noble/high-ranking pet is that his anal glands (sinuses) are probably inflamed.
Pathological processes
While white discharge from under the tail is more or less understandable in pregnant cats, for other animals it should be a cause for concern. They may indicate one of the following infections:
- Vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina). At first, the discharge is almost invisible, since the cat often licks its butt, which is one of the characteristic symptoms of the disease. As inflammation develops, watery excreta is observed, which over time turns into white and mucous. Vaginitis develops against the background of endocrine disorders with the participation of pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococcus, streptococcus). Untimely treatment can cause cystitis, pyometra or endometritis.
- Chronic endometritis. Inflammation of the endometrial mucous membrane of the uterus, resulting in scanty white spotting. Usually the cat feels good, estrus occurs as usual, but pregnancy does not occur. But even if conception occurs, the fetuses simply die in the womb or are born too weakened. Chronic endometritis can develop into hydrometra (accumulations of fluid in the uterus, which is secreted in drops, whitish or colorless excrement of mucous consistency) and even purulent endometritis.
- Acute endometritis. The disease can be accompanied by discharge of any color, consistency and smell. The cat becomes apathetic, does not allow its belly to be touched, and the external genitalia become inflamed. Delayed treatment or lack thereof leads to the death of the animal.
- Pyometra. A purulent accumulation in the uterine cavity, which most often occurs in unsterilized cats after reaching 5 years of age. Its causes may be hormonal disorders, sexually transmitted infections, taking drugs that suppress sexual activity, or childbirth with complications. The discharge may be whitish, reddish or brown. Lack of treatment leads to death.