Description of cat roundworm
Cat roundworms, or toxocaras, have a cream-colored body. The length of an adult female reaches 10 cm, males are shorter - 7 cm. The eggs are round, rough, brown in color, so they are easily attached to the fur of animals.
These parasites develop to their final stage only in the body of cats. They also parasitize other animals, but do not complete their development to adulthood. Rats, mice, chickens, cockroaches, flies, earthworms, and beetles are the main carriers of the larvae. If a cat swallows them, it will become infected with toxocariasis, and the helminths already in the cat’s body will continue to develop into an adult.
When the larvae reach their final host, they are first found in the cat’s intestines, then begin to migrate throughout the body along with the blood, thereby damaging some internal organs: lungs, trachea, liver.
When the larvae reach a size of about 6.5 mm, they settle in the small intestine to go through the 4th stage of maturation and reach maturity.
The female produces several thousand eggs. Just 1 gram of cat feces contains one hundred thousand eggs. Once in the soil, they mature within 3 weeks and become dangerous to animals and humans.
Can a person get infected from a cat?
Scabies mites in cats are contagious, but not dangerous to humans. In rare cases, otodectes cynotis causes otitis externa. Sarcoptic mites or notohedrosis mites can cause itching or other allergic reactions, but they leave human skin on their own within a month - it is too dense for them. Parasites are not able to gnaw tunnels in it and lay eggs. However, scabies in humans manifests itself in the form of severe itching and causes significant discomfort.
Demodex canis lives in the deeper layers of the epidermis of cats and dogs. It dies upon contact with human skin.
Despite the absence of serious complications, it is recommended to use protective gloves when treating your pet and wash your hands thoroughly after each procedure. To kill ticks from personal items (clothing, bedding), you will have to boil them. The area where the sick animal lives is regularly vacuumed, and the floors are washed with a disinfectant.
How does infection occur?
Most often, stray cats become carriers of parasites. Almost all of them are infected with Toxocara. From the cat's body, helminth eggs enter the environment - soil, grass with feces and urine.
If you let a domestic cat out for a walk, the helminth eggs will stick to the fur and paws of the animal. When washing, the cat licks itself, and the helminth eggs are easily swallowed.
Even if the cat is at home all the time, nematodes can get into the apartment along with dust and shoes.
In addition, you can become infected through food that has not been heat-treated. Helminth eggs are found in raw meat.
Toxocariasis affects kittens that are in the womb if she is infected. During pregnancy, helminth larvae enter the placenta through the blood and the kittens become infected. Even if this did not occur during pregnancy, after birth they will enter the kittens' intestines through the mother's milk.
Prevention
Preventing mange in your domestic cat is easy. To do this, you should follow several recommendations.
Safety regulations:
- Limit contact with street animals.
Provide balanced, high-quality nutrition.- Check your pet regularly.
- Carefully care for the cat's tray, bowl, scratching post, and bed.
- Regularly visit a veterinary clinic and carry out antiparasitic treatment with drugs containing selamectin.
- Use shampoos with acaricides as a preventative against scabies.
It is recommended that pets wear collars against ticks and other parasites at all times.
What happens in a cat's body when infected?
After the roundworm egg enters the cat’s digestive system, its shell begins to dissolve and the larva emerges. It enters the bloodstream and begins to migrate throughout the body, lingering in the internal organs: heart, lung, liver, spleen.
These larvae are so adaptable that the animal's immune system cannot fight them. It becomes clogged in the internal organ and begins to gradually destroy it.
Therefore, infected cats develop:
- tissue necrosis;
- abscesses;
- spot bleeding.
Very often, when the larvae are in the lungs and bronchi, during a cough they enter the saliva and, with it, back into the digestive tract: most often into the small intestine. In it they grow to sexually mature adults. They again produce larvae, which are excreted along with feces and fall onto the soil, again infecting other animals.
If the cat's immune system is very weak, the animal becomes infected again. The larvae begin to move through the bloodstream again, finding a new home.
Types and causes of the disease
Not all cats are susceptible to infection. This may be due to direct and indirect reasons. They relate to the physiological state of the animal, its care and a number of other circumstances. The development of scabies in cats is promoted by:
- decreased immunity;
- unsanitary conditions;
- lack of insecticidal treatment;
- kitten age up to two years;
- genetic predisposition.
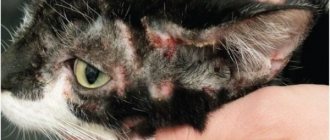
Scabies mites are microscopic organisms; their sizes are measured in fractions of a millimeter. The shape, body length, and structural features depend on the biological species. This determines the type of disease. Various mites cause demodicosis, otodectosis, notoedrosis, and sarcoptic mange. In each case, its own specific symptoms are observed and adequate drug treatment is prescribed.
Demodicosis
The causative agent is the light gray Demodex canis mite. The parasite settles in hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Infection sometimes occurs in the newborn period. Affected areas may be small - up to 2.5 cm (localized form) or spread over most of the body (generalized form). The first one often goes away on its own.
Demodicosis manifests itself in the form of scaly redness or in the form of ulcers and ulcers. The generalized form of the disease often combines both symptoms. In this case, it is very difficult to treat the cat, as complications often arise.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?>
$ads_google = true; ?> } ?>
Otodectosis
The ear mite Otodectes cynotis parasitizes the external and internal parts of the auricle. This type of disease is accompanied by the formation of scabs and scales on the surface of the auditory organ.
A strong putrid odor emanates from the affected area. Ear mange causes your cat to constantly scratch his head and especially his ears.
Notoedrosis
The disease, often called scabies, is caused by the Notoedres scabies mite. It has a round shape and gray color. This type of disease in cats affects the outer side of the ear. A gray liquid with an unpleasant odor accumulates in the affected areas.
Due to the discharge, the fur sticks together, later it begins to fall out and the pet’s head goes bald. In exposed areas, scales accumulate, forming scabs.
Sarcoptic mange
The causative agent of the disease is the yellowish or completely white mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The parasites first settle on the cat's face and then spread to the entire body. The diagnostic sign is the formation of red spots with thin gray lines with a nodule at the end. An inexperienced person may confuse sarcoptic mange with an allergy, since their symptoms are similar in appearance
Sarcoptic mange is dangerous due to bacterial infection and general sepsis.
Signs of infection
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to recognize the presence of toxocariasis in a cat’s body, especially in adult animals. And in kittens they appear most noticeably.
Therefore, cats need to be treated carefully and pay attention to the following symptoms:
- An indicator of helminthic infestation is the quality of the coat. If it is tousled, dull, and the skin is dry, then you can judge toxocariasis.
- Digestive disorders are almost always observed, manifested in the form of diarrhea, bloating, frequent vomiting, and loss of appetite.
- The cat often coughs with its neck stretched out. The eyes look sunken and the third eyelid is visible.
- Toxocara can be seen in feces.
- When infected, the animal's behavior changes. Many of them begin to behave strangely, for example, eating or licking a plastic bag or the excrement of other animals. When the larvae infect a cat's nervous system, it becomes aggressive.
- If toxocariasis occurs in kittens, they grow and develop poorly. If the content of helminths is high, kittens may die.
The disease is diagnosed by testing the animal's feces. It is best to use stool obtained in the morning, as it is more likely to contain eggs.
Symptoms
It is not uncommon for pet breeders to ignore this serious disease for a long time. The thing is that with toxocariasis in cats there are no specific symptoms, especially at the early stage of development of the parasitic infection. However, owners may notice the following signs of the disease:
- excessive aggressiveness;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- digestive disorders (constipation, diarrhea, vomiting);
- sudden deterioration or increase in appetite;
- hair loss, dandruff;
- pallor of the oral mucosa;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- with hypersensitivity to pathogens - urticaria, itching.
Laboratory tests in the blood of an infected animal reveal a decrease in hemoglobin levels and an increase in the number of eosinophils. An accurate diagnosis is made at a veterinary clinic using fecal analysis.
Therapy
You can get rid of parasites by using medications prescribed by your veterinarian. Let's look at the most common of them.
Mebendazole
This drug is available in powder form and has a slightly yellowish tint. It has no smell or taste. Can be used once. Usually added to food with a dosage calculation of 0.015 g per 1 kg of cat’s body weight.
Febentel
An effective medicine, produced in the form of a white powder that is tasteless and odorless. It is added to the cat’s favorite food once a day.
Treatment lasts 3 days. Dose – 0.01 g per 1 kg of animal weight.
Fenbendazole
This is a low-toxic and effective powder product, odorless and tasteless. Add to cat food once a day. Dose – 0.25 g per 1 kg of body weight. The recommended duration of use is 5 days.
Piperazine salt
It is slightly toxic. Dose – 0.2 g per 1 kg of animal. It is added to food that the cat will happily eat.
Drontal
A medicine produced in tablets. 1 tablet is designed for 4 kg of animal. Treatment with this medicine is carried out once: it is crushed and added to the cat’s food.
Treatment at home
The first thing to do is isolate the sick pet to prevent the disease from spreading and infecting other pets. The choice of medications depends on the shape and type of scabies mite and the degree of infection.
Typically, cats are prescribed a comprehensive treatment aimed at eliminating parasites, as well as restoring their general condition.
Complex treatment may include the following:
- antiparasitic drugs;
- injections of the ivermectin series (Novomec, Ivemex, Ivermectin);
- external insecticidal agents and solutions: Stomazan, Butox, Neostomazan, Mitroshin solution, etc.;
- symptomatic remedies;
- antiparasitic, anti-inflammatory ointments, for example, Amitrazine;
- emulsions, gels, special shampoos;
- immunostrengthening drugs (Immunoparasitan);
- immunomodulators;
- mineral and vitamin supplements.
Diagnosis of scabies
If you suspect your cat has scabies, it is important to seek veterinary help promptly. The clinic will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Diagnostics includes an external examination of the animal and taking skin scrapings for microscopic analysis. This procedure is repeated two or three times to confirm the output. Based on the results, the doctor makes a conclusion about the cause of the problem. Often, a mite infestation can be confused with dermatitis, an allergic reaction, ringworm, or eczema. Therefore, a laboratory test is mandatory in the diagnostic system.
The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of the disease and the condition of the pet itself. The average treatment period for scabies ranges from one to four weeks. Medical care for a pet consists of injections, ointments, solutions, drops, and hygiene products with a therapeutic effect (shampoos, soaps). To eliminate scabies in cats, acaricides, antibiotics, antihistamines, antiseptics, and immunomodulators are used. To prevent the cat from licking the ointment applied to the surface of the skin, it is necessary to use a protective cap.
The causative agent of toxocariasis
Toxocara cati or Toxocara mystax is a species of roundworm belonging to the family Toxocaridae. It causes the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of representatives of the cat family. In most cases, adult forms of this helminth parasitize the lumen of the small intestine, thereby causing the disease toxocariasis. In rare cases, when Toxocara enters the animal's body massively, the disease can lead to death.
Males of Toxocara reach a length of 5-10 cm, females are much larger - from 9 to 18 cm. The body is predominantly light yellow in color. The head end has clearly defined formations - “lateral wings”.
Cat Toxocara eggs are round in shape and have a thick shell. Their size is about 85 microns. The embryonic phase lasts from 10 to 15 days.
Neurological form
When Toxocara larvae infect the brain, a neurological form of toxocariasis develops. In this case, the membrane and tissues of the brain, as well as the central nervous system, are affected. A person begins to experience difficulties with thinking, recognizing objects, and motor skills.
The clinical picture of the neurological form of toxocariasis consists of the following symptoms:
- seizures similar to an epileptic attack;
- syncope;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- gait changes;
- balance disorders;
- photophobia;
- intolerance to loud sounds;
- sharp reaction to touch;
- intense throbbing or pressing headache;
- nausea with bouts of vomiting;
- muscle hypotonicity (up to complete cessation of functioning and absolute immobilization);
- causeless aggression, affective states;
- inability to independently cope with a stressful situation.
In rare cases, it is possible to develop combined toxocariasis, when a person suffers from several forms of pathology at once. However, science has isolated isolated cases of such deviation.