Pets, despite all the measures taken, can still become infected with serious infections, one of which is staphylococcus in cats. For this to happen, it is not at all necessary for a cat to live on the street or eat in garbage dumps.
To become infected with a staphylococcal infection, contact with a sick animal during a short walk or sniffing the owner’s outdoor shoes will be enough.
Who is staphylococcus?
Cases of staphylococcus disease in domestic cats have recently become more frequent, and this infection is severe in them even with correct and timely treatment. But, despite this, a competent approach from the attending physician and effective treatment methods can overcome the disease and significantly improve the animal’s well-being.
Staphylococcus belongs to pathogenic microorganisms whose structure resembles a bunch of grapes. There is no one specific pathogen that causes staph infection. This definition includes a whole genus of microorganisms that have common characteristics and cause a characteristic type of disease. This microbe was first discovered back in 1881, and to this day, undergoing various changes, it remains able to withstand the effects of the most modern drugs. In the animal's body, staphylococcus affects various organs, in which, under the influence of a pathological process, purulent inflammation occurs. If the disease cannot be stopped, the functioning of important systems deteriorates, often resulting in fatal complications.
The insidious nature of staphylococci lies in the fact that after entering the animal’s body, they may not show their activity and remain in this state for a long time. However, after some shock they can begin to develop sharply and lead to serious violations.
Staphylococci are considered opportunistic microorganisms, since they cause harm to the body only under the influence of a certain factor. According to scientists studying this area of medicine, today many infections, which include those whose etiology is unclear, are caused by these microorganisms.
Predisposing factors
Staphylococcus in cats manifests its activity under the influence of certain factors; they infect the animal, which itself becomes a source of infection and can infect others. The most important reasons that can influence the development of the infectious process in the body of cats are as follows:
- A change in the processes of carbohydrate metabolism that occurs as a result of the development of diabetes or the cat’s poor diet, which contains insufficient amounts of minerals and vitamins.
- Weakened immunity, which decreases after illness, and is also at this level from birth. Most often, cats in this condition are affected by Staphylococcus aureus, which causes severe purulent inflammation that is difficult to treat.
- Hormonal imbalances, which are more common in older cats.
- Cases of intoxication, as a result of which the animal’s body’s defenses are weakened. Usually, after poisoning, the animal’s condition and well-being decreases, which gives rise to the development of a staphylococcal infection.
- A state of acute vitamin deficiency, microorganisms especially react to a lack of B vitamins, as well as carotene and vitamin E.
- The presence of skin pathologies in the form of dermatitis, eczema, lichen, as well as allergies often become the reason for the development of staphylococcal lesions.
The risk of becoming infected with staphylococcus increases many times if the cat is accustomed to outdoor walking. Participation in fights also increases the possibility of infection, as the inevitable breaks in the skin then become inflamed, thereby encouraging the development of infection.
Description of the microorganism
Staphylococcus is a group of bacteria. Currently, several varieties of these microorganisms are distinguished:
The most common type of bacteria is golden. It causes severe inflammation with suppuration.
Translated from ancient Greek, the word “staphylos” means “bunch of grapes”. This is where the name of the microorganism comes from. Staphylococci under a microscope look like spherical clusters of golden color.
Such bacteria are opportunistic microbes. Staphylococcus can stay in a cat’s body for a long time and not cause any damage. At this moment, the bacterium is in an inactive state. But under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors, staphylococcus becomes pathogenic. This leads to painful manifestations. Most often, the emergence of pathogenicity is facilitated by a decrease in immunity.
Which breeds are most susceptible to infection?
Cats of any breed and even outbred cats, which are usually more resistant to any infections, are at risk of becoming infected with staphylococcus and subsequently falling ill. But still, the disease is more often diagnosed in hairless breeds, whose skin is less protected and more easily damaged. Bacteria penetrate through the scratches, and the lack of hair on the skin leads to hypothermia in animals. All this helps to reduce the animal’s resistance to the development of infection.
Long-haired cats, such as Persians, are no less likely to be infected. The nature of this breed is aggressive, and they are more likely than others to get into fights and receive wounds and scratches. The peculiarity of these animals, which have luxurious fur, is that staphylococcal infection is more severe in them.
Can a cat infect a person?
Can a person become infected from a sick cat and what is the likelihood of this possibility - such questions are often asked at an appointment with a veterinarian.
Infection of a person by a cat with staphylococcus is quite acceptable, and this can happen in the following cases:
- contact method;
- nutritional;
- using the airborne method.
Most often, infection occurs during a bite, since even a small damage on the human skin left by the teeth of a sick animal will be enough for this. Infection is also possible if hygiene rules are not followed, since pathogenic microbes remain on the hands after playing with the cat or after cleaning its litter box.
It has been noted that most cases of infection from sick animals occur in the elderly and children. It is for this reason that in order to protect yourself and your loved ones from the possibility of infection with staphylococcus, it is necessary not only to wash your hands thoroughly, but also to be able to identify the disease at the initial stage by its first signs.
Risk group
Each individual cat has increased sensitivity or, conversely, resistance to Staphylococcus. If an animal with weak resistance is easily affected by a microorganism, then an impressive dose will be required to infect a strong organism with pathogenic staphylococcus. Individuals suffering from:
- diabetes;
- immunodeficiency;
- hormonal imbalances;
- impaired liver and kidney function;
- allergies;
- scabies mite damage;
- inability to resist at the genetic level.
Poor nutrition and deficiency of vitamins A, E, group B seriously reduce the body's ability to protect against the genus Micrococcacea.
INTERESTING!
With staphylococcosis, a strong immune response is developed at the level of phagocytosis and blood protein systems. However, staphylococcus successfully suppresses the body's immunological responses.
Diagnostics
If you suspect an infection or the development of an infection in cats, you must meet with a veterinarian and carry out the prescribed tests.
Since staphylococcal infection has a number of similar symptoms to other diseases, diagnosis includes the following:
- analysis of blood samples for bacterial culture;
- microscopic examination of scrapings from areas of skin with lesions;
- study of smears of discharge from the genital tract.
As a rule, a general blood test is not carried out in this case due to its lack of information, for the reason that changes in the blood from exposure to staphylococcus can only be detected in the stage of sepsis.
Sowing bacteria
, which includes both external clinical signs and laboratory results.
When detecting staphylococcosis, a blood test is not indicative, because active persistence can be observed exclusively in sepsis.
Studies of exudate taken from the ears, ulcers, and erosions are also not indicative. This is due to the fact that the material is in close contact with foreign microbial flora: observing the bacteria will take a lot of time. The optimal biomaterial for research is vaginal discharge or prepuce.
It is possible to speak unambiguously about staphylococcosis in the case when the Staphylococcus strain has pronounced coagulase-positive or hemolytic properties.
Clinical manifestations
Manifestations of the disease can be seen with the naked eye, therefore, with careful attention to your pet, staphylococcal infection is detected already at its initial stage. The main symptoms are:
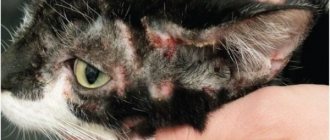
- Dermatitis that lasts a long time and is difficult to treat. Often, as a result of severe dermatitis, a complication develops in the form of pyoderma with a purulent inflammation of the skin. The pathology begins with small erosive areas with severe itching, which, in the absence of timely treatment, turns into weeping dermatitis.
- The appearance of individual areas of baldness. Typically, such areas of the skin are accompanied by an unpleasant odor with the release of exudant fluid. This is more often observed in older cats and those who are obese. In the absence of timely treatment, the damage spreads to the tissue located in the subcutaneous layer. Its tissues are rapidly destroyed with the formation of inflamed boils in their place.
With the activity of staphylococcus and with the further development of the infection, along with damage to the skin, other, no less pronounced symptoms may be observed. Most often, a sick animal experiences severe weakness, fever, loss of appetite and severe thirst.
Symptoms and ways of infection with toxocara. How to take a blood test for toxocariasis?
Toxocara are multicellular parasites belonging to the type of roundworms. The final hosts of these helminths are representatives of the canine and feline families (less often cows), but human infection is not excluded.
More than 90% of those infected are children under 5 years of age.
What kind of disease
Toxocariasis is a helminthiasis characterized by a long course, problems with diagnosis and serious consequences due to the localization of the parasite.
The disease is caused by the following pathogens:
- Toxocara canis (definitive host - dog, wolf);
- Toxocara cati (definitive host - cat);
- Toxocara vitulorum (definitive host - cow).
In the Russian Federation, the most common type of pathogen is the first one. The disease is widespread due to the specific maturation of Toxocara eggs - in the ground. The animal is infected through contact with the environment, soil.
In the body of a dog (cat), the larvae penetrate through the mucous membranes into the bloodstream and settle in the tissues and organs, affecting them. Once in the respiratory tract, the larvae are partially expelled with saliva and through coughing/sneezing, and partially swallowed and enter the intestines, where they develop into adults.
In the human body, toxocara are present only in the form of larvae and do not develop into adults; they enter the bloodstream through the small intestine and affect all organ systems.
A person can become infected with toxocariasis through contact with a sick animal, as well as through dirt (soil) that contained mature worm eggs. A transplacental method of infection is also possible, in which the child becomes infected from the mother during the period of intrauterine development. A person is not capable of infecting other people, since he is an intermediate host of pathogens. The disease is diagnosed using a test for toxocariasis.
Signs of the disease
The disease is not expressed symptomatically in itself. However, the larvae of parasites infect internal organs, disrupting their functioning, which leads to serious disruptions in their functioning and severe symptoms.
Signs of toxocariasis vary depending on the form of the disease:
- acute (lasts up to 3 months, symptoms are pronounced: fever, allergies, inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- chronic (lethargy, allergic skin reactions, loss of appetite);
- latent (characterized by the absence of symptoms).
Specific symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the greatest accumulation of larvae:
- neurological (localization: brain; symptoms: migraines, photophobia, vomiting, convulsions, unstable emotional state);
- ophthalmological (localization: eyes; symptoms: loss of vision, swelling of the eyelids, strabismus);
- visceral (multiple organ).
Visceral toxocariasis depending on the organ systems affected by helminths:
- digestive (flatulence, stool upset, taste of bile, weight loss, nausea after eating);
- respiratory (cough, asthma);
- cardiovascular (symmetrical leg swelling, bluish skin).
In children, the disease manifests itself in the form of the same symptoms.
If a doctor or yourself identifies the above signs, it is recommended to take a blood test for toxocariasis.
Other manifestations
The causative agent of staphylococcal infection in cats can cause damage not only to the skin, but also have a detrimental effect on other organs. Symptoms of staphylococcus in a cat are as follows:
- First of all, the disease affects the organs of the reproductive system. In females, inflammation, which initially occurs in the vagina, soon spreads to the uterine cavity with the development of endometritis. In cats, inflammation of the foreskin occurs with purulent discharge.
- Damage to the hearing organs occurs with the development of chronic otitis, in which the animal experiences pain, shakes its head and does not allow its ears to be touched.
- The development of purulent conjunctivitis, when not only the eyes swell and fester, but vision can also sharply decrease.
- Often, a complication of staphylococcal infection is kidney damage, accompanied by pain when urinating with cloudy urine.
- If the infection affects the liver, the animal may experience yellowing of the mucous membranes.
Note! Any of these symptoms should alert the cat owner, since even if such manifestations are not a symptom of staphylococcus infection, then they are definitely an indicator of trouble in her body.
Proper care for a recovering pet
Recovery and prognosis also depend on the underlying cause. Always follow your veterinarian's instructions and take your cat to see him at least once a week for the duration of treatment. So, antibiotic therapy usually lasts at least six weeks. It is imperative to inject the entire course of drugs, since otherwise the pathogen will not be completely destroyed and a relapse of the disease will develop. Even when the signs of infection subside, under no circumstances should you stop giving the medicine to your animal! Do not forget to also regularly treat areas of inflammation on the surface of the skin, as compliance with this rule helps speed up the healing process.
Lesions of the genital area
The most reliable sign of staphylococcal infection is obvious changes in the condition of the mucous membranes covering the genitals. Cats with this diagnosis most often suffer from purulent vaginitis, which easily takes a more serious form in the form of endometritis. In this case, exudate is noticed from her genital tract.
Cats often experience inflammation of the foreskin, also characterized by purulent discharge. If the inflammatory process spreads to the preputial sac of the genital organ, then the animal experiences severe swelling, difficulty and pain when urinating, i.e. postitis. When conducting a microscopic examination of purulent fluid, a large number of staphylococci with various strains are found in it.
Complications
The future fate of the pet is largely influenced by the timeliness of the treatment, especially in the case of Staphylococcus aureus in a cat. Incorrectly administered therapy or its absence in advanced cases very often leads to the development of sepsis, with signs of blood poisoning. During the examination, you can detect a large number of bacteria constantly circulating in the blood plasma. As a result of the activity of these microorganisms, toxins accumulate in the blood and do not have time to be eliminated from the body. Such changes affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system, disturbances in which often result in septic shock and death of animals.
The enemy under the microscope
A microorganism in the shape of a ball with lush golden-lemon clusters -
It is a member of the genus Micrococcacea, which is divided into three species: golden (aureus), epidermidis (epidermidis), saprophytic (saprophyticus).
To date, scientists have identified 10 more species from this genus, which are not yet included in the official classification.
The insidiousness of staphylococcus lies in its secrecy. It can exist peacefully in the body for a long time until something provokes its aggressive attack. This does not have to be a serious illness; it is enough for the pet to survive stress or a common cold. More often, animals are affected by Staphylococcus aureus, which requires painstaking and lengthy treatment.
The ability to produce coagulase, an enzyme that causes blood clotting, divides staphylococci into coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative.
Treatment
Treatment of staphylococcal infections requires complex therapy that lasts a long time. First of all, a sick cat is prescribed a drug that actively affects the very cause of the disease. Thus, with the help of ASP, which is a polyvalent antistaphylococcal toxoid, bacteria are actively destroyed. Antibiotics and antibacterial external preparations complement complex therapy.
Most often prescribed for this purpose:
- Azithromycin;
- Amikacin;
- Baytril;
- Cyflox.
With the help of Streptocide or Sulfacyl ointment, as well as Manefid, wound healing and antiviral effects are exerted on damaged areas of the skin, resulting in faster recovery. The use of Antistaphylococcal bacteriophage destroys any strains of staphylococci. In case of severe dehydration and intoxication of the animal's body, droppers with saline solution are indicated.
Different Approaches to Healing
They approach the fight comprehensively. The owner should aim for long-term treatment; it will not be possible to defeat the disease in 2-3 days. Various types of therapy are used in veterinary practice:
- antimicrobial;
- symptomatic;
- pathogenetic;
- specific immunotherapy;
- nonspecific immunotherapy;
- antibiotics;
- bacteriophage
Specific immunotherapy can be active or passive. Passive is appropriate to use in the early stages of the disease and for minor lesions. When the disease becomes severe, active immunotherapy is used, which is based on the drug ASP, produced specifically for animals. Nonspecific immunotherapy involves stimulating the cellular component of immunity.
Traditionally, when treating staph, veterinarians prescribe antibiotics. Before this, the sensitivity of staphylococcus to the drug must be determined. Enroxil, Baytril, Cyflox are effective in the fight against staphylococcosis.
Bacteriophage is a lifesaver in the fight against staphylococcus. This is a molecular nanomechanism that nature created. It is imperceptibly introduced into the bacterium; the process can be compared to an injection.
The bacteriophage penetrates the shell and fills the bacterium with its genetic material, after which it begins to actively multiply inside. As soon as the bacterium is completely damaged, its gradual restructuring begins to meet the needs of the bacteriophage. Finally, the young phage cells completely break down the bacterial membrane.
Fermented preparations, such as lysozyme, are used to wash ulcers, erosions, the vagina, and the prepuce cavity. Drying and cauterizing drugs are used, which reduce the amount of contagion.
Treatment at home
You cannot treat a sick animal with a staphylococcal infection yourself at home, as this can lead to its death in the shortest possible time. The development of a pathological process in the absence of professional medical care from a veterinarian very quickly leads to septic shock, which is fraught with irreversible processes that threaten death.
Any warning signs consistent with a staph infection should promptly contact your veterinarian. It is allowed to treat an animal at home, but only with the help of the prescriptions made by a specialist.
Consequences of staphylococcus for cats
A serious consequence of staphylococcus infection for cats can be considered weeping dermatitis, which is difficult to treat with medications and brings a lot of suffering to the animal. Further progression of this disease contributes to a more widespread spread of pathology on the animal’s body, not excluding its head and muzzle. Kittens from dehydration caused by this disease in most cases do not survive and die in the first week of illness.
As a result of the development of Staphylococcus aureus, animals undergo changes in a variety of organs. Staphylococcus in a cat's ears leads to chronic forms of otitis and purulent conjunctivitis.
You can find symptoms that indicate Staphylococcus aureus in your cat's nose, with an erosive surface forming around the nose and mouth.
Adult cats are also often unable to get a staphylococcal infection as a result of infection of the body with pathogenic microbes. Their large accumulation leads to poisoning of the body with toxins released by microorganisms as a result of their existence. The development of septic shock is the main cause of death in animals of any age.
Prevention
It is much easier to prevent cats from becoming infected with staphylococcus by taking effective preventive measures than to then treat them for a long time and persistently for this serious disease, often accompanied by complications. To do this, it is important to prevent your pet from coming into contact with street stray dogs and cats. It is important to fill his diet with necessary microelements and vitamins, but it is better to protect the cat from excess carbohydrates in the diet. It is important to prevent the development of chronic diseases in cats, and in case of any diseases, take care of their elimination. Particular attention should be paid to antiparasitic treatment - the presence of fleas can cause increased activity of staphylococcus and lead to more severe skin lesions.