Feline idiopathic cystitis (FCI)
Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) is the most common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms in cats.
This form of disease is very similar to what is called “interstitial cystitis” in humans. Just like in humans, controlling cystitis is quite difficult. Idiopathic cystitis occurs in approximately 60% of cats with bladder disease. In this case, the presence of all clinical signs of cystitis is noted, but the urine is sterile and, as a rule, salt crystals are also not detected.
What is idiopathic cystitis
The development of an inflammatory process and infection of the bladder are all symptoms that identify idiopathic cystitis in cats. Owners often wonder: Do cats get cystitis?
The answer is that it happens, but females are most susceptible to infection, since they have a physiologically very short urethra. The pathology can develop against the background of urolithiasis, aggravating the condition of the furry pet.
For your information! Idiopathic cystitis is a complex form of the disease, the causes of which have not yet been precisely established. It can occur with either pronounced symptoms or without visible manifestations. Most often the animal shows anxiety.
Inflammation of the genitourinary system in animals
Diagnostic measures
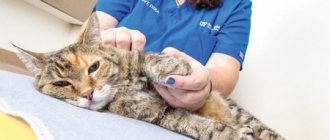
To make a correct diagnosis, your veterinarian will prescribe tests and other diagnostic measures. First of all, the specialist will collect anamnesis, examine the animal and palpate the abdomen in the area of the bladder. You will definitely need to donate blood for a general analysis to check the level of leukocytes and ESR. The veterinarian will also prescribe:
- Blood chemistry. It will allow you to assess the degree of damage to the urinary system.
- General urine analysis. Needed to measure the level of leukocytes and casts, as well as to determine the presence of blood impurities and other inclusions.
A urine test for sensitivity to antibiotics (bacterial culture) and a genital tract smear (in females) may also be required. An ultrasound of the bladder will help determine the stage of the disease, the presence of stones in the bladder or other formations. Sometimes cystoscopy is performed as a diagnostic test.
The main causes of idiopathic cystitis in cats
Stop cystitis for cats: tablets and suspension
The causes of idiopathic cystitis in cats have not yet been precisely proven. The main provoking factor is a stressful situation. Emotional discomfort negatively affects the state of the nervous system. Scientists have proven that this situation leads to changes in the walls of the bladder. A protective layer ceases to form on the walls, which prevents harmful bacteria from penetrating.
Cystitis in cats is a common diagnosis in veterinary clinics.
Provoking factors also include:
- excess everything in the pet, development of obesity;
- several cats living together;
- lack of activity.
Important! Idiopathic cystitis is in no way associated with infection.
Obesity is one of the causes of pathology
Causes of the disease
What is the root cause of the pathology and how to treat it? There are reliable risk factors for feline idiopathic cystitis:
- breed (Persians);
- age (2-6 years);
- castrated animals (not directly, but as a possibility of developing obesity due to physical inactivity and increased appetite);
- stress, conflicts between cats or other pets.
In outdated sources you can find mention of the following etiological factors of damage to the lower urinary tract. These are infections (bacteria), but this has been detected in 1% of cats with urological syndrome and, of course, improvement may be associated with the administration of antibiotics. Although this is not always the case. There are opinions that idiopathic cystitis can be caused by difficult-to-cultivate microorganisms, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, but studies in the 90s and 2000s showed that these bacteria are not the basis of idiopathic cystitis.
Versions of the viral origin of the urological syndrome are put forward; this is supported by the herpes virus, which, after the initial introduction into the cat’s body, remains there forever. And under stress and hypothermia, it can persist and cause vivid manifestations of cystitis.
In cats with obstruction, the crystals may be involved in the formation of “plugs” along the urinary tract. They come in both inorganic origin (inclusions) and protein fractions. Moreover, oxalate inclusions are not found; these are almost always struvite components.
Animals that present to the veterinary clinic with urological syndrome may have lower urinary tract involvement or spastic signs. They are often mistakenly diagnosed as a blockage, although in fact the cause of the obstruction is a spasm, the “blockage” appears as a secondary phenomenon. Inflammation is also often the root cause of idiopathic cystitis. In general, these groups of animals (spasm, inflammation, “plugs”) show the same symptoms of cystitis.
Diverticula (pockets) on the bladder can remain after urachus, either as pathological phenomena due to overdistension of the bladder, or after urinary obstruction.
Cystitis in cats often occurs as a result of hypothermia. Walking in cold weather (especially in the rain) or sleeping on concrete or tiles can lead to bladder inflammation. This is especially true for animals with reduced immunity. If a cat has ever had cystitis, he should avoid drafts and hypothermia, since under these circumstances the disease is likely to return. Other causes of inflammation in the urinary tract include:
- Infectious diseases. The inflammatory process occurs as a result of the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the bladder itself or neighboring organs (kidneys, urethra, ureters), from where the infection spreads. Often the disease occurs even against the background of a cold due to weakened immunity and the growth of pathogenic microflora. That is why it is important to promptly treat any illnesses that occur in your pet.
- Urolithiasis disease. If there are stones or sand in the kidneys or bladder, they injure the walls of the organs, causing inflammation.
- Fungal diseases. Spores of microscopic fungi spread through the bloodstream, causing inflammation in various organs, including the excretory system.
- Metabolic disease. This problem occurs as a result of the cat’s poor nutrition and insufficient consumption of clean water. It is important to monitor your pet’s diet and feed it high-quality food in small portions.
Bladder injuries (including those received during castration) and severe stress (caused by sterilization, vaccination, being in a confined space, jealousy of another pet, etc.) can also lead to the inflammatory process. Keeping a cat under stress for a long time negatively affects the body as a whole and can cause cystitis. There is an assumption that it is the pet’s depressive mood that provokes idiopathic cystitis in cats.
The disease more often affects males than females, and females than males due to the anatomical structure of the urinary tract. The pathology occurs quickly, is acute, and only at this stage the treatment is short-term and successful.
Urologist about cystitis: Do not buy expensive drugs, not all of them treat cystitis, I did research and found the most effective and cheapest remedy!
- Hypothermia. But it’s not the frost that’s dangerous for pets, it’s drafts and prolonged stays on the concrete floor. Cats exposed to cold rain often develop cystitis. Small animals, almost devoid of fur, are especially vulnerable; their owners are forced to clothe them.
- Genital infections. Males most often suffer from uncontrolled matings with sick bitches.
- Precipitation of uric acid salts. Cystitis can provoke urolithiasis. Neutered cats suffer the most. Urothiliasis is difficult to distinguish from inflammation of the urinary tract; the diseases often occur simultaneously.
- The key cause of feline idiopathic cystitis is the use of economy-class food. They contain defective proteins, the disposal of which produces uric acid, which is difficult to dissolve in water. The resulting grains of sand clog the urethra or urinary tract, urine stagnates, which creates conditions for the proliferation of microbes.
Signs of the disease
The difficulty of diagnosing the pathology lies in the lack of specific signs. Symptoms of the disease are similar to many urological disorders. Pathogenesis can manifest itself as follows:
- frequent urination;
- in the process of excreting urine, the animal behaves restlessly, as it experiences pain;
- the cat may start urinating in the wrong place;
- traces of blood are visible in the urine;
- the pet refuses to eat;
- wool quality decreases;
- the animal becomes timid and nervous.
Cystitis in a cat: symptoms and treatment at home
The same symptoms appear with urinary tract infections and urolithiasis. The disease is diagnosed by excluding similar pathologies. Idiopathic cystitis is characterized by a rapid onset and acute course.
Note! The duration of exacerbation can be up to seven days. If the pathology goes away without treatment, it will recur after a certain period.
Symptoms of the pathology will appear after 7 days
Types of cystitis in four-legged pets
There is no single correct treatment regimen for idiopathic cystitis, since the basis of any treatment is always the elimination of the root cause. But in the case of urological syndrome, this is almost impossible to do.
What they do:
- bladder lavage;
- prescription of antispasmodics;
- give anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs and glucocorticoids, but there are risks: nephrotoxicity, azotemia, infectious complications);
- Amitriptyline is prescribed (relief of stress, depression, but there are risks of blockage and AUR).
Diet therapy is a method that is always accepted by veterinarians as a stabilizing one. It is noteworthy that “wet”, moist food gave better treatment dynamics compared to dry food. When feeding ready-made industrial food, it is imperative to “force” cats to drink more so that the urine is less concentrated. We need food with Omega-3 and amino acids; this is the product of choice, reducing the risks of idiopathic cystitis.
Symptoms of FCI will resolve spontaneously (without any treatment) in most cats within five to seven days. However, given the level of discomfort of the affected cat, it can be very difficult to simply wait and watch. There are several treatment options from which you can choose the best one to cope with ICC.
Most experts agree that eliminating environmental stressors and implementing interventions aimed at producing dilute urine provide the most beneficial effects. Note that antibiotics are not mentioned because ICC is a sterile (bacteria-free) inflammatory process. The most commonly recommended procedures are listed below:
- Diet changes – There are several specialized diets on the market that have been designed specifically to control FCI. Most foods change urine pH and may contain antioxidants and additional omega-3 fatty acids. Diet changes should be made gradually, and your veterinarian should be notified immediately if the cat is unwilling to eat the new food.
- Additional fluids are added to the diet—the goal is to create more dilute urine. This can be achieved by feeding canned rather than dry food, adding liquids (water, broth, tuna liquid) to the food and feeding several meals a day.
- Analgesics (painkillers) medications – opioids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs—non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids.
- Amitriptyline is an antidepressant that has benefited some cats with FCI.
- Pheromones – Cat pheromones can reduce stress by affecting the limbic system and hypothalamus. Available commercially as aerosols or sprays.
- Environmental changes – changes that improve the environment and reduce psychological stress for the affected cat can be beneficial.
- Increasing the number of cat litter boxes in the house;
- Cleaning cat litter boxes more frequently;
- Maintaining a daily routine/regime, especially in terms of food intake;
- Installation of several sources of drinking water with fresh, clean water;
- Isolating a nervous cat from new people or animals entering the house;
- Increased petting/playing/grooming time alone with your loved one.
The principles of treating dogs and cats are similar. They practice drug and dietary therapy.
Antiseptic drugs are started before bacteriological tests are obtained. The optimal solution is to use Furacilin or other nitrofuran agents. They are excreted in urine and sanitize the urinary tract. If there are severe pain symptoms, analgesics, anesthetics, and antispasmodics are used.
Based on the results of bacteriological cultures, antibiotics or sulfonamides are determined, which inhibit pathogenic microflora. Their use is limited to 7...10 days. After this, they begin to use herbal remedies. Stop-Cystitis, Cat Erwin, Canephron are in demand. Feedback from animal owners about the treatment is predominantly pessimistic. The disease is incurable, but with proper care, dietary feeding, and herbal medicine courses, communication with your pet can be extended for years.
A side effect of antimicrobial agents is dysbiosis, manifested by diarrhea, which will require a course of probiotic therapy to eliminate. Your veterinarian may also prescribe antihistamines and hemostatic medications. When the above treatment methods do not help, to eliminate the mediators of inflammation, a cat with idiopathic cystitis is given Amitriptyline tablets. The medicine brings relief, but has side effects, greatly weakening the body's immune defense.
Diet therapy
If your pet has cystitis, a successful result will not be possible without organizing dietary nutrition. You will have to switch from forage or economy-class feed to medicinal dry or wet mixtures. When the acute process can be stopped, it is possible to change the therapeutic diet to high-quality feed. An attempt to return to the previous food inevitably leads to a relapse.
Prevention
Prevention of cystitis consists of providing comfortable living conditions and feeding with premium food. To avoid infection from infected animals, accidental matings should be prevented. Routine annual vaccinations against other diseases will allow you to maintain a strong immune system.
Conclusion
Pets are susceptible to urogenital diseases. To prevent them, it is necessary to provide pets with comfortable housing and a balanced diet with ready-made factory-prepared food. If the animal does get sick, it needs the attention of its owner.
Types of pathology
Piroplasmosis in cats: symptoms and treatment
In veterinary medicine, there are two types of cystitis:
- acute form. It manifests itself as a sharp deterioration in the functioning of the genitourinary system. The animal owner’s task is to immediately take the animal to the veterinarian for examination if signs of concern are detected;
- chronic form. Its difficulty lies in the fact that the pet rarely shows anxiety and only during urination. The owner may not notice the symptoms. This will cause the condition to worsen every day, weakening the immune system.
For your information! There are often situations when, without lack of treatment, the chronic stage turns into acute.
Prevention recommendations for cat owners
The main measure to prevent cystitis and other diseases in cats is to increase immunity. You can strengthen the body's defenses with the help of a well-designed diet, performing basic hygiene procedures, and providing the cat with moderate physical activity. In addition, the following measures will help avoid cystitis:
- avoiding hypothermia and drafts;
- providing a safe environment for your pet to avoid injury;
- maintaining a prosperous atmosphere in the home that does not allow the development of stressful conditions.
It is important to periodically take your cat to the veterinarian for preventive examinations and get vaccinated on schedule. Thanks to vaccinations, the animal will receive immunity to a number of strains of viruses and bacteria, which will reduce the risk of cystitis. If the disease does occur, it will be easier to cure; therapy will not last long. Don’t forget about regular deworming and taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
The development of idiopathic (interstitial) cystitis can be prevented if:
- place a sufficient number of trays (according to the number of cats 1);
- do not punish the animal if it went outside;
- feed wet (premium) food from cans;
- create comfortable living conditions for the cat (its own place, toys, corner for the tray, food).
That is, in general, minimize the risks of stress factors when the cat feels uncomfortable. But in general, when treating idiopathic cystitis, it is necessary to exclude a lot of possible causes in order to achieve a stable treatment result and reduce the likelihood of relapses.
If the owner notices that the pet has signs of urological syndrome, it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinarian-urologist. Be sure to take the animal to the Ros-Vet VC or call.
Establishing diagnosis
A diagnosis such as idiopathic cystitis is very difficult to make. Most often, veterinarians use the method of excluding other pathologies. To examine the animal, the following procedures are prescribed:
- taking a general blood and urine test;
- X-ray examination of the bladder;
- ultrasound examination;
- performing cystoscopy.
A cat urine test will show specks of blood and inflammatory cells. In addition, the composition will contain crystals. Only after a comprehensive examination of the animal has been carried out and diseases of the lower parts of the urinary system have been excluded, can a diagnosis of idiopathic cystitis be made.
Testing is an important step in making a diagnosis.
Diagnostics
A urine test reveals hematuria (a huge number of red blood cells). To exclude infection, a bacteriological examination of urine is carried out - culture on nutrient media. For such an analysis, a sample of the material must be obtained sterilely, by cystocentesis - a puncture of the bladder through the abdominal wall. Although this procedure is performed without anesthesia, it has not yet become routine practice in Russian veterinary clinics.
If cystitis recurs, culture is necessary. It is also recommended for all animals over 10 years old and cats with immune disorders:
- diabetes;
- VIC;
- treatment with steroid hormones.
Ultrasound and radiography can detect stones and sand in the urinary tract, assess the thickness and tone, and fullness of the bladder.
In exceptional cases, contrast radiography or urethrocystoscopy may be required, most often if neoplasia is suspected.
Treatment with drugs
Pathology therapy is based on antimicrobial and diuretic drugs. If cystitis develops as a sign of another disease, treatment will be comprehensive.
The animal is prescribed:
- furatsilin;
- potassium permanganate for the procedure of washing the bladder if there is pus and blood in it;
- When an infectious inflammatory process develops, furadonin is prescribed.
Papaverine is included in complex therapy to relieve spasms. It helps reduce painful tone of the urinary tract.
In severe cases, when it is necessary to urgently improve the pet's condition, the drug prednisolone is used.
Ways to treat cystitis with drugs
Antibiotics
Treatment with antibiotics should only be prescribed by a doctor. The drugs help relieve acute symptoms within a few days. But it is very important not to stop treatment until the full course is completed. Bacteria can be present in the blood and then reactivate.
Important! Antibiotics are administered intramuscularly to cats. Do not crush the tablets or give them with food. This method will not give the desired results.
The dosage is prescribed depending on the complexity of the disease and the weight of the animal. The main course is two weeks. During the course, it is recommended to give your pet medications to normalize the intestinal microflora.
Veterinarians often prescribe complex medications that have an effective effect on the pathology. These remedies include stop cystitis. It is aimed at eliminating the main symptoms. Appointments are scheduled twice a day. Often the drug is prescribed for preventive purposes. But it is contraindicated for pregnant cats and pets prone to allergic reactions.
Veterinarians often prescribe stop cystitis for this disease.
Treatment of idiopathic cystitis in cats with folk remedies
Idiopathic cystitis can be treated using conservative methods. Often taking medications is combined with traditional methods. You can prepare special tinctures for cats yourself. For example, a decoction of 2 tbsp. spoons of plantain leaves, 1 tbsp. spoons of cinquefoil and horsetail. All ingredients are mixed and poured with a glass of boiling water. Then you need to infuse the drink for 30 minutes. The resulting remedy is given four times a day, 1 teaspoon.
Traditional methods should be used together with medications
Diet therapy
If a cat has developed cystitis, it will be impossible to get rid of it without following a diet. It is recommended to abandon dry formulas and switch to wet food. Once the treatment is completed, you can switch to dry food, but it should only be of high quality. The transition to the previous nutrition system will inevitably lead to a recurrence of the pathology.
During the treatment process, it is important not only to avoid the development of obesity, but also to take care of urine dilution. Its density greatly affects bladder irritation.
Treatment
Although in 8 cases out of 10 the symptoms of cystitis will go away on their own, the doctor’s task is to alleviate the symptoms of the acute period for the animal. Apply:
- antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine);
- painkillers (Butorphanol, Meloxicam).
For blockage of the urethra and urinary disorders, alpha-blockers (Terazosin, Prazosin) are used, which relax the internal sphincter of the bladder and the urethral canal.
Treatment aimed at the long term involves changing the conditions of detention. Eliminating the cause of stress is necessary to avoid relapse of the disease. Idiopathic cystitis is not a problem that can be solved by taking medications.
Products based on cat pheromones may be useful. Feliway in the form of a diffuser or spray stabilizes the psychological state of a cat without side effects or contraindications. An analogue of the substance secreted by the cat’s facial glands will give the pet a signal: “there is nothing to worry about.”
Supplements with alpha-casozepine (derived from casein, a milk protein) and L-tryptophan (an amino acid from which serotonin, the happiness hormone, are formed) reduce the risk of developing depression and reduce stress. There are industrial complete diets that include both harmless substances:
- Royal Canin Calm 36;
- Hill's c/d Feline Urinary Stress.
This diet is suitable for long-term feeding of a cat with idiopathic cystitis, if there are no associated problems:
- urolithiasis disease;
- obesity;
- renal failure.
Caring for an animal when sick
Treatment of idiopathic cystitis in cats should be comprehensive. An important component of therapy is creating favorable living conditions for the pet.
During the acute form of cystitis, it is necessary to teach the cat to drink as much water as possible. This will help concentrate the urine and make it easier to pass out. To get your pet used to drinking more, it is recommended to place bowls in different places in the house.
Each cat in the house should have its own hiding place, where no one can find it. This could be a special box or shelf.
Dietary adherence is especially important during treatment
For your information! If favorable living conditions for pets are observed and nutrition is controlled, the disease can be defeated. Statistics show that animals whose owners take care of the state of their nervous system, feed their pets a balanced diet, do not experience a relapse of the pathology.
Disease prevention
The high probability of transition of idiopathic cystitis to a chronic form and the occurrence of relapses make the prevention of the disease quite urgent.
Improving conditions of detention
Each cat should have its own place to rest, eat and toilet. The bedding, basket, house and other sleeping devices should not be located in a draft, cold or noisy room.
Improved emotional state
Cats react very painfully to conflicts and a tense atmosphere in the house, the arrival of strangers, moving and the appearance of other pets. Also, idiopathic cystitis can occur against the background of a stress factor caused by punishment for the fact that the animal does not relieve itself in the tray.
Therefore it is worth:
- closely monitor the emotional atmosphere in the house;
- give all animals an equal amount of attention and affection;
- provide each of them with their own toys;
- pick up the cat when strangers appear.
If relocation is necessary, you should consult with a veterinarian about the advisability of using sedatives before the trip.
Increasing water consumption
You should provide high-quality, nutritious food and sufficient fluids for your pet. In addition to water containers at home, you need to take care of maintaining your cat's water balance while walking or traveling.
At the first manifestation of clinical signs of idiopathic cystitis, the animal should be immediately shown to a veterinarian. You should not postpone your visit and try to cope with the disease on your own.
An exacerbation of the disease requiring catheterization may begin at night. And in the absence of emergency assistance, this will lead to death.
Unfortunately, even timely treatment does not guarantee complete recovery and absence of relapses. Therefore, you should prevent this disease from an early age by providing good living conditions, feeding and minimizing stress factors for your pets.
How to prevent the appearance of cystitis
Preventive measures to prevent the development of pathology are as follows:
- It is recommended to ensure that the animal has its own place at home where it will feel safe;
- the bowl of food should be placed in a quiet place so that the pet can calmly eat;
- It is important to keep the tray clean and change the filler regularly;
- keep the animal active. Play with him more often. Veterinarians recommend using interactive bowls. The cat will have to work hard to get food.
It is important to maintain both the physical and psychological condition of your pet in a normal manner.
Thus, cystitis in a kitten is a serious disease that is difficult to diagnose. Pet owners need to closely monitor the health of their pets and changes in their behavior. If the pathology is left untreated, it can lead to the development of serious complications.
Prevention
Prevention consists of providing the cat with conditions that satisfy its basic instinctual needs:
- Shelter.
The cat should have a shelter where no one will disturb it. This could be a house or a box, a closet shelf, a mezzanine - if the animal likes to sleep on high places.
- Relaxed meal.
The bowl of food should not be in the aisle. If there are several animals in the house, it is necessary to exclude competition for food.
- Toilet.
The tray is placed in a secluded, quiet place where no one will disturb the cat. It is recommended to give your pet the opportunity to dig for litter. The tray is kept clean by removing excrement and regularly disinfecting the plastic.
- Activity.
The older a cat gets, the more important it is to stimulate its hunting instincts. Gradually, the animal in the apartment gets tired of the monotony and becomes inactive. The owner should play with the pet every day. Interactive feeding bowls and other puzzles from which the cat must “get” food can be useful.
In addition to psychological comfort, it is important to keep the animal in good physical shape.
In addition to preventing obesity, they strive to ensure urine dilution. Reducing urine density has a positive effect on the treatment of cystitis and is extremely important for preventing relapses. Less concentrated urine does not irritate the damaged bladder wall as much.
You can increase the amount of water your cat drinks by switching from dry food to canned food. For drinking, they offer water with flavoring additives and an attractive aroma: shrimp broth, tuna juice. Many cats prefer running water, in which case a drinking fountain should be installed.
To dilute urine, special diets are used:
- Royal Canin Urinary S/O Feline High Delution;
- Purina Veterinary Diets UR St/Ox – Urinary Feline;
- Eukanuba Urinary Struvite Feline;
- Hill's PD Feline C/D or S/D.
Situations that cause discomfort to the cat should be avoided as much as possible. If stress is inevitable (the birth of a child, a change of owners, moving to a new home), the cat can be prepared for it in advance:
- 10-30 days before the event, the animal is switched to RC Calm food and continues to be given it for another 2-3 months.
- During a stressful situation, use Feliway, and for particularly anxious individuals, the use of antidepressants is justified.
Tricyclic antidepressants are relatively safe, although they cause side effects - drowsiness, physical inactivity. Amitriptyline is widely used in cats orally or intramuscularly.
Treatment depends on the cause of USC
- ICC - antispasmodics, stress factor reduction. Diet therapy. Antidepressants - Stop-Stress, Amitriptyline. If the bacterial infection is complicated, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
- Urolithiasis - diet therapy depending on the pH of the urine and the type of uroliths determined using a urine test. Antispasmodics and antibiotic therapy; if the size of the uroliths significantly exceeds the diameter of the urethra, cystotomy and stone removal are indicated; in the presence of stones of small diameter and frequent relapses, urethrostomy is indicated.
- Bacterial infections should be treated according to the results of culture and antibiotic sensitivity.
- Neoplasia - when confirmed by ultrasound and contrast pneumocystography, cystotomy and excision of the neoplasm and confirmation of the diagnosis histologically are indicated.
It should be remembered that in 75% of cases of the development of USC, the underlying cause is ICC, but surgical intervention is indicated only for a number of specific symptoms, clinical signs and confirmed changes. Often, urethral obstruction is associated with the presence of urethral plugs consisting of a protein-colloidal matrix, which develops against the background of ICC, and crystalluria contributes to increased obstruction, but not always, often crystalluria occurs without visible clinical symptoms, and often obstruction occurs against the background of ICC. Indications for urethrostomy: - recurrent and treatment-resistant attacks of urinary canal obstruction, against the background of ICC, urolithiasis.
Indications for cystotomy: - Confirmed presence of stones with a diameter larger than the urethra, and not amenable to dissolution. — Confirmed presence of neoplasia.
In conclusion, let me remind you that if your pet has problems or absence of urination, you should immediately contact a specialist to carry out the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic measures.