The kidneys play an important role in the process of eliminating waste products from the cat's body. Disruption of the functioning of these organs can lead to serious consequences for the health and life of the animal. It is important to carry out timely diagnosis when the first alarming symptoms of kidney disease appear. Kidney disease in cats, symptoms and treatment - about this in our article.
Kidney disease in cats: symptoms and treatment
Kidney functions
The kidneys perform the following functions:
- remove water and salts;
- remove toxic substances formed in the body or included in medications;
- maintain constant metabolism;
- maintain a constant blood reaction.
Location of the kidneys in a cat
Common diseases
Kidney diseases pose a great danger. When there are serious problems, there is always the possibility that the animal may die.
Table. Common kidney diseases in cats
| Name of the disease | Emerging problems |
| Chronic failure | The gradual destruction of an organ, as a result of which the activity of the entire organism is disrupted. Stays with the animal for its entire life. Pet owners can only carry out constant maintenance therapy, avoiding exacerbation of the disease. The impetus can be any unfavorable factors (hypothermia, inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, etc.) |
| Acute failure | Unforeseen inflammatory process. There is a violation of the functions performed by organs. It develops rapidly and poses a greater danger than the chronic form. Common causes of the problem: heart disease, shock, drop in blood pressure, urolithiasis |
| Pyelonephritis | An inflammatory process of a bacterial nature. A common source of the problem is diseases of the genitourinary system |
| Nephritis | An inflammatory disease that affects the glomeruli, tubules, and interstitial renal tissue |
| Hydronephrosis | Enlargement of the pyelocaliceal system, destruction of the renal parenchyma. As a result, a pathological process develops, blood circulation is disrupted, and the outflow of urine worsens. All functions of the kidney cease to be performed properly. The problem can be primary or secondary. In the first case, the cause is the presence of congenital pathologies (for example, ectopia of the ureter). In secondary hydronephrosis, problems arise due to systemic diseases (urolithiasis, tumors, etc.) |
| Nephrosclerosis | The tissue of part of the kidney or the entire organ is replaced by connective tissue. There is a gradual death of kidney cells - nephrons. As a result, the organ greatly decreases in size, shrinks and hardens. |
The structure of a cat's kidney
Symptoms and signs of kidney problems
Diagnostics
With kidney pathology, the animal suffers from chronic intoxication.
There are several reasons why the kidneys are the most vulnerable place in the cat family, especially domestic species:
- Cats have concentrated urine. This is necessary to save the body’s water balance in natural living conditions. An incorrectly selected diet becomes the basis for the appearance of genitourinary diseases.
- Fish and dairy products contain many mineral salts that settle on the walls of cats’ kidneys in the form of crystals. In cats' natural habitat, these products are rarely consumed and do not cause problems. Regularly feeding your pet these products becomes an impetus for the development of urolithiasis.
- The early stages of kidney disease in domesticated felines can only be noticed through close observation. The main features are:
- constant strong thirst, lack of desire to eat, sudden weight loss;
- frequent urination, blood clots in the urine, diarrhea, vomiting, possible dehydration;
- dental diseases, unpleasant odor of ammonia from the mouth, pale gums;
- increased sleep duration, decreased activity, desire to sleep on cool surfaces.
Symptoms of the disease in an animal appear periodically, so it is difficult to notice its progression. A final diagnosis can be made only after special laboratory tests.
Liver amyloidosis
- Abnormal proteins accumulated in the blood plasma are deposited in the tissues of the organ, which leads to the replacement of specialized elements and causes the death of the kidneys.
- In the early stages, diagnosis of the disease is difficult due to the absence of clinically evident signs.
- The acute form is characterized by:
- frequent urination;
- loss of appetite and vomiting;
- severely depressed state of the animal.
- Chronic form:
- loss of appetite, frequent vomiting;
- the animal drinks a lot, urinates frequently, and dark-colored urine is typical;
- the joints are swollen, their aseptic inflammation appears;
- drowsiness, reluctance to move and play.
The disease in this form is rarely detected. The cause of death of the animal is determined after an autopsy and laboratory examination of the organs. A clinical analysis reveals anemia and increased bilirubin levels. An accurate diagnosis can be made after a biopsy, ultrasound and x-ray.
It is impossible to cure a sick animal. To alleviate the cat's condition and prolong its life, measures are taken to stop the development of the disease. In the initial stage, special solutions are used. With further development, surgical intervention is possible to remove the damaged kidney.
Hydronephrosis in cats
Maintenance therapy is the only way to normalize the cat's condition.
Second, the cause is a narrowing of the urinary tract, leading to stretching of the organ and the subsequent death of its functional tissues.
- The cause of the development of the disease can be either injury or tumor, or any inflammatory process with complicated urine output.
- A symptom indicating the development of the disease is difficulty urinating in small portions or its complete absence;
- The process can be one-way or two-way.
When performing an ultrasound, an enlargement of the pelvis is clearly visible. Treatment involves measures aimed at therapeutic or surgical elimination of the causes of disorders. With bilateral kidney damage, or the impossibility of removing the diseased organ, death is possible. After normalization of the patient's condition, maintenance therapy is carried out.
During the disease, healthy organ tissue is completely or partially replaced by connective tissue.
- Symptoms in the initial stage indicate other diseases.
- Positive treatment is possible only at the beginning of the disease. Cure in advanced cases is impossible.
- The main features are:
- high pressure;
- a sharp increase in body temperature, possible fever;
- painful urination;
- urine is reddish in color, streaks of blood are possible;
- loss of appetite, while the animal drinks a lot and often.
- Trying to stabilize the functioning of the kidneys, the body compensates for the lack of nephrocytes by enhancing the work of healthy cells, which leads to their overload and death. Connective tissue forms in place of dead cells.
Hydronephrosis in cats
Causes of problems
Often it is not possible to determine the reasons why the disease occurred. The most common reasons:
- age (cats from 7 years of age are most susceptible to diseases, so it is necessary to conduct their annual full examinations: blood test, urine test, ultrasound, blood pressure measurement);
- genetic predisposition (the presence of similar problems in representatives of a certain breed to which the animal belongs);
- congenital anomaly;
- ecology;
- infectious diseases;
- systemic diseases;
- poisoning;
- injuries;
- poor nutrition;
- negative processes in the urinary canals (the problem is more common in cats, since their canals are longer and narrower than those of cats).
Cats over 7 years of age are most susceptible to diseases, so it is necessary to conduct their annual full examinations.
Predisposing factors that provoke kidney diseases:
- lack of fluid consumed by the animal;
- drinking contaminated water;
- excess salt contained in the feed;
- Exceeding the required amount of sugar in the diet;
- frequent feeding of meat and fish;
- large mass;
- lack of weight;
- keeping in dampness, in drafts;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- untimely urination (occurs when an animal is periodically unable to go to the toilet on time due to closed doors or dirty litter);
- oral problems.
Kidney diseases in cats and kittens
Steps
Signs of kidney problems
- Watch your cat drink water.
Check the water level in your cat's bowl every morning. Find out if your pet has started drinking more water. This can also be determined by whether you have recently had to clean your cat's wet litter box more often. As a rule, cats use moisture sparingly and do not need a lot of water, so if the animal begins to drink more and visit its litter box more often, it may have kidney problems.
- Kidney disease causes your cat to lose more fluid through urine and require more water to compensate for these losses. Diseased kidneys cannot concentrate urine properly and leave water in the blood.
- If a cat eats liquid food, it needs even less water compared to its counterparts who eat dry food. In this case, the animal receives part of the water along with food. Because of this, liquid food is usually preferable for those cats that may have kidney problems.
- See if your cat is vomiting or showing interest in food.
If your pet refuses to eat, it may be trying to avoid stomach pain. Kidney problems can lead to uremia, which is accompanied by painful inflammation of the stomach. In this case, cats often lose their appetite and may even vomit blood due to the formation of ulcers.
- Uremia occurs in part because the kidneys are unable to effectively remove toxins from the blood.
Kidney problems may cause your cat to develop painful sores on her gums, in which case she may be less likely to want to brush her fur. The animal may completely refuse grooming. As a result, the coat may appear dull and dirty.
See if the cat seems lethargic.
Cats love to sleep. However, take a closer look to see if your pet is sleeping more than usual, or if he has lost interest in his favorite games and entertainment. If your cat is acting too lethargic, she may have developed anemia or low potassium levels due to kidney disease. The accumulation of waste in the body can also worsen the animal’s well-being.
- Kidney disease can cause blood problems because the kidneys help repair blood cells, regulate electrolytes, including potassium, and remove toxic substances from the body.
Anemia caused by kidney disease is also indicated by dull or white eyelids (in healthy cats they are pink).
Sometimes it can be difficult to determine whether a cat is really unwell or if she just decided to lie down. Call your cat and see how she reacts to this. If your pet doesn't come to you, see if he raises his head or vocalizes in response. If your cat's gaze remains dull and she does not respond to your call, this may indicate that she has diseased kidneys.
- Cats have a very heavy head compared to the rest of their body, and require considerable muscle effort to keep it straight. When potassium levels are low, cats tend to lower their head.
However, this sign is quite rare, and its absence does not mean that the cat does not have kidney problems.
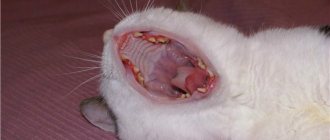
If your cat's kidneys don't remove toxins from her body, she may develop ulcers in her stomach, throat, and gums. Gently hold the cat by the head and slowly open its mouth. Look inside and see if there are any red or irritated areas in your mouth. The sores may appear as white or gray dots. They can be on the gums and under the tongue.
- Ulcers may cause your cat's breath to smell bad.
Establishing diagnosis
- Ask your veterinarian to do a urine test.
If you suspect your pet has kidney problems, the first step your veterinarian should order is a urine test. The doctor will take a sample of your cat's urine and send it to a laboratory, where they will test its density to see how dilute it is.
- The same urine sample can also be used to detect other diseases, such as diabetes.
The veterinarian may also prescribe a biochemical test, which determines the protein-creatinine ratio in the urine. This test helps determine whether low urea concentrations in urine are actually due to kidney disease or due to shock.
- Ask your veterinarian to take a blood test from your pet to rule out other possible diseases.
Although a blood test may not always detect kidney problems in cats, it can help narrow down the list of possible health problems, such as diabetes or an infectious disease.
Thematic materials:
Fracture of the tubercle of the humerus Orbit: structure, functions and diseases Auscultation of the heart: heart sounds What is transaminase, the norm by age in men and women Normal levels of alt and ast in adults Second degree atrioventricular block: signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis Therapy of the syndrome Morgagni-Adams-Stokes Is it painful to have a bronchoscopy? What is systole and diastole? Human cardiac cycle
103583
If you notice an error, select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Symptoms of kidney diseases
Attention! The first signs of disease appear when the organ is affected by 70% or more. For this reason, early diagnosis plays a huge role and significantly increases the chances of a positive outcome.
The main points that may appear at the onset of the disease are:
- weight loss;
- reluctance to eat;
- strong thirst;
- frequent urination;
- strong smell of urine;
- ammonia odor, most pronounced in the morning;
- decreased activity;
- faded wool;
- digestive disorders.
Signs of kidney disease in a cat
Symptoms appear at the following stages:
- fluid loss;
- frequent urination;
- painful sensations;
- increased protein levels in the urine;
- inflammations, ulcers;
- cracks in the mouth;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- pale gums;
- refusal to eat;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bowel disorders;
- weight loss;
- retinal disinsertion.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method that provides complete information is a urine test. An additional diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. During an ultrasound, the kidneys and urinary ducts are examined for the presence of pathological processes, stones, and sand.
Symptoms of urinary tract diseases in cats
If the results of a blood test and ultrasound reveal problems that require additional examination, the following are prescribed:
- biopsy;
- blood analysis;
- genetic research;
- virus detection;
- pressure measurement.
Based on the final diagnostic results, conclusions are drawn about the type of kidney disease, the stage of the disease and its treatment options. The most effective drug regimen is prescribed.
Video - Diagnosis and stages of chronic renal failure in cats
Types of jade
Inflammation of the kidneys is distinguished by the severity of the process. It can be manifest or chronic. Depending on the tissue damage, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Glomerulonephritis. The kidney glomeruli are destroyed and gradually die.
- Pyelonephritis is a purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis.
- Interstitial. In this case, the kidney tubules become inflamed and urine filtration is impaired. It is rare in cats.
Hurt
Treatment
General treatment of kidney diseases is carried out in the following areas:
- Elimination of factors and diseases that caused the problem.
- The use of medications prescribed by a veterinarian, taking into account the age, weight, nature of the disease, and stage of the animal’s disease. Systematic use of correctly selected drugs will help stabilize the condition and prevent active progress.
- Use of antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed if an infectious process occurs. Antibacterial drugs help suppress the activity of harmful microorganisms that were the source of the development of the pathological process.
- The use of droppers. Special solutions are introduced into the animal’s body, which allow the correction of pathological processes. When dehydrated, the required amount of fluid is restored.
- Compliance with the prescribed diet. Animals with kidney problems need to eat special food. The level of nutrients in these feeds corresponds to the required norm.
Treatment can be carried out using droppers
Kidney failure
It is always necessary to promptly contact a specialist for diagnosis and treatment. In the acute form, it is important to quickly identify the factor that triggered the development of the process and eliminate this factor. For example, if you have urolithiasis, it is impossible to relieve the symptoms of kidney failure without treating this problem. The main methods of treatment used in the acute form:
- Intravenous injections (“Sulfokamphokai”n). Helps restore water balance and relieve symptoms of intoxication.
- Diuretics (Temisal, Diacarb). When there is insufficient amount of urine excreted relative to the fluid consumed.
- Symptomatic treatment: for vomiting - antiemetics (Papaverine, Cerucal, Enterosgel), for elevated glucose levels - insulin, etc.
- Hardware hemodialysis. Hardware blood purification, which allows you to prolong the life of the animal.
- Surgical intervention. If all of the above treatment methods are ineffective, the diseased organ is removed and a healthy one is transplanted.
The drug "Eufillin"
Treatment for the chronic form includes:
- Regular checks (blood, urine). If deviations are detected, additional diagnostics are carried out and the prescribed systematic treatment is adjusted.
- Use of infusion therapy (administration of solutions).
- Taking vitamin and mineral preparations (Polidex, Beafar, Anivital Feliimmune).
- Use of nutritional supplements (“Feliimmune”).
- Application of phytotherapeutic methods. Ready-made mixtures and preparations based on medicinal herbs are highly effective along with a low level of side effects.
- Hardware hemodialysis.
- Surgical intervention.
"Feliimmune" to support the immune system of cats
The prognosis in the chronic and initial stages of the disease is quite favorable. If you follow doctors' recommendations regarding diet and use of prescribed medications, the animal's life can be extended for a considerable time.
Important! In the acute form of the disease, the prognosis is unfavorable. The likelihood of death is very high.
Pyelonephritis
Treatment regimen:
- painkillers (“No-shpa”, “Baralgin”, etc.);
- perinephric block;
- a course of antibiotics (“Penicillin”, “Carbenicillin”, “Amoxicillin”, etc.);
- a course of sulfonamides (“Sulfadimethoxine”, “Sulfen”, etc.);
- chemical diuretics (“Diacarb”, “Eufillin”);
- herbal diuretics (rose hips, calendula);
- droppers.
The drug "Diacarb"
Nephritis
Treatment regimen:
- chemical diuretics (“Temisal”, “Eufillin”);
- herbal diuretics (lingonberry leaf, bearberry);
- sedatives for heart failure (digital infusion, strophanthus infusion);
- iron preparations and vitamins (“Cyanocobalamin”, “Ferroglukin”, “Campolon”);
- strengthening agents - for diarrhea;
- laxatives - for constipation.
"Cyanocobalamin"
Hydronephrosis
For minor damage:
- catheterization;
- washing the urethra and bladder.
In more serious cases, surgery is performed.
Nephrosclerosis
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. Applicable:
- cardiac drugs (cardiac glycosides, drugs with potassium, anticoagulants);
- diuretics (“Eufillin”, “Temisal”, “Diakarb”);
- glucose therapy;
- laxatives, antiseptics (for intestinal intoxication);
- antibiotics.
Diuretic Eufillin
general information
In cats, like all mammals, a pair of kidneys is located in the abdominal cavity in the area of the lumbar spine. These bean-shaped organs have a complex structure, the structural unit of which is the nephron. It is in these glomeruli, entangled with blood vessels, that the main function of the kidneys is carried out - filtering metabolic products.
Main, but not the only one. In addition, the kidneys play an important role in the hormonal regulation of the body, regulate the acid and electrolyte composition of the blood plasma, and participate in maintaining blood pressure. The cups of the kidneys collect urine, which travels through the paired ureters into the bladder. And it is already removed from the body.
Remember, in 90% of cases, kidney pathologies are discovered either by accident, or when nothing can be done and the animal is in a half-dead state. Keep an eye on your pet and don't miss the onset of the disease. Symptoms can be pronounced or vague. Common signs that your cat has problems include:
- If the excretory function of the nephrons is impaired, the cat’s urine becomes almost colorless, has almost no smell, but there is a lot of it. The body is dehydrated, which is easy to determine by pulling back the skin on the cat’s neck - it does not return to its original position immediately, but only after a while. The cat drinks a lot and goes to the toilet often. Possible diarrhea.
- Due to a violation of the removal of harmful substances and nitrogenous bases (creatinine and urea) from the body, they accumulate and cause general intoxication of the body (uremia). As a result, the cat loses its appetite, vomiting and diarrhea are observed. A specific nitrogen odor appears from the mouth.
- An increased level of urea in the blood leads to an increase in its content in saliva. As a result, ulcers, gingivitis, and stomatitis appear on the oral mucosa.
- Impaired kidney function leads to hormonal imbalance - the hormone chymosin, which controls blood pressure, and erythropoietin, which regulates the production of red blood cells, are produced in insufficient quantities. The level of hemoglobin in the blood decreases, which leads to anemia. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the lightening of the nose and gums. Oxygen starvation of tissues causes muscle weakness and apathy.
- Deep kidney damage is characterized by intraocular hemorrhage. In one or both eyes, blood spills into the retinal area, which can lead to retinal detachment and blindness.
The diet is selected by the doctor individually based on the specific etiology of the disease, but there are rules that all cat owners should adhere to:
- The cat should be given bottled or filtered water.
- The cat must have constant free access to drink.
- Reduce the amount of protein and phosphorus in your pet's diet.
- The diet should not be monotonous.
Urolithiasis (UCD) is the formation of stones in the kidneys or bladder. Leads to the development of pyelonephritis and renal failure. It is the most common disease in cats, as it is closely related to their ability to excrete highly concentrated urine.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Standard and characteristics of the German Shepherd
X-ray of urolithiasis in a cat
Causes of ICD:
- excess or lack of protein in the diet;
- drinking water saturated with natural salts;
- genetic predisposition;
- early castration.
Symptoms of ICD:
- Hematuria is the appearance of blood in the urine.
- Dysuria is a problem with urination.
- Urethral blockage occurs almost exclusively in cats.
The process is chronic. The formation of stones can last for months or years.
Causes
Factors leading to impaired renal function:
- Limiting fluid intake.
- High salt content in food.
- Poor nutrition – predominance of meat or fish in the diet.
- Overweight.
- Poor living conditions - cold and damp or, conversely, too hot room; drafts.
- Physical inactivity is the low activity of an animal.
- Psychologically caused urinary retention - a dirty tray or lack of access to it.
- The source of infection in the body - for example, diseases of the oral cavity.
- Exposure to toxins.
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
Symptoms are the same for all kidney diseases:
- Polydipsia is an unnaturally strong, unquenchable thirst.
- Anorexia is a complete lack of appetite.
- Vomiting and diarrhea.
- Pollakiuria – frequent urination.
- Dysuria is painful urination.
- Polyuria is an increase in the daily volume of urine.
- Anuria is a decrease in diuresis up to the complete cessation of urine output.
- Acetonuria – the appearance of acetone and acetoacetic acid in the urine, bad breath.
- Hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine. Accompanied by noticeable redness.
- Anemia is a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood and a simultaneous decrease in hemoglobin concentration. Manifested by pallor of the mucous membranes and weight loss.
- Dehydration is dehydration of the body. Characterized by dry skin, thinning and brittle hair, and weight loss.
- Overhydration is excess water content in the body. Clinically manifested by edema and ascites.
- Azotemia is an increase in the blood levels of nitrogen metabolism products: urea, uric acid and creatinine.
- Uremia is the accumulation in the body of metabolic products that are normally excreted in the urine.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of renal diseases, objective data from laboratory tests, ultrasound diagnostics and radiography play an important role.
In cases of kidney disease, edema is diagnosed in a cat.
Kidney diseases in cats and cats are quite similar in symptoms, but their treatment is different. Therefore, it is especially important to make a correct diagnosis initially.
Nephritis
A severe, rapidly progressing disease of acute and chronic form, developing after an animal has suffered a bacterial or viral infection, hypothermia, poisoning or injury.
- Depending on the location it happens:
- The main symptoms of the disease are:
- depressed state;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- the shells of the ears, eyelids and paws swell;
- frequent urination, urine contains blood elements;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- in the advanced stage, vomiting and persistent diarrhea are possible.
- Clinical examination of urine will show blood, epithelial debris and protein in it.
- When examined by a specialist, an increase in blood pressure is detected, an increased body temperature is possible, and disruption of the functioning of the pelvic limbs.
- The diagnosis is made after examining the animal and laboratory testing of the urine composition.
Self-medication of the disease can lead to its transition to a chronic form. To alleviate the cat's condition, it is kept warm for 2 days and on a starvation diet. Subsequently, they are transferred to frequent feeding of food without salt, with a high content of carbohydrates, calcium and potassium. As therapy, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, decoctions of diuretic herbs, calcium supplements and B vitamins.
Pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, body temperature rises and weakness occurs.
Inflammation of the connective tissue of the kidneys and renal pelvis in most cases is of bacterial origin. Often appears after infection of the genital organs, or stagnation of urine in the renal pelvis and. Affects both kidneys.
- It occurs in acute and chronic forms. The acute form is life-threatening for the animal. Death can occur within 12 hours.
- The acute course is characterized by:
- , increased heart rate;
- painful urination, stools are viscous and cloudy;
- the urine has an increased protein content and is colored red;
- the animal has severe thirst;
- Palpation in the kidney area causes pain.
- In the chronic form in cats, a thick purulent mass may be released from the vagina.
- The animal quickly depletes.
- The diagnosis is made based on examination of the patient and the results of urine and blood tests.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis leads to irreversible damage to the cat's health.
The disease occurs in subacute and acute forms. It is characterized by inflammation of the glomerular apparatus.
- The reasons may be infectious-allergic, or disturbances in nutrition and maintenance, injury to the animal, or hypothermia.
- The main symptoms of the disease are:
- the appearance of blood streaks in the urine, painful urination;
- difficulty breathing, slight swelling of the muzzle and eyelids;
- weakness, drowsiness, reluctance to play, lack of coordination;
- decreased hearing and vision, whistling during inhalations and exhalations.
- When examining and testing blood and urine, the following is revealed:
- increased ESR, protein and leukocytes;
- there are blood spots in the fundus area;
- there may be water in the lung area.
A course of treatment is used, including diet therapy, antibiotics, sulfa drugs, painkillers and aminoglycosides, and the addition of vitamins and microelements to the diet. It is necessary to review the conditions of keeping the animal, to exclude its presence in places with drafts or high humidity.
Polycystic kidney disease
Apathy and exhaustion are symptoms of progressive polycystic kidney disease.
A disease transmitted at the genetic level and inherited as a dominant trait. It is characterized by the formation of multiple cysts in each kidney.
- The disease can remain latent for a long time. Appears mainly after 3 years.
- The size of the cyst ranges from 1 mm to 1.5 cm.
- Characterized by a gradual increase in the size and number of cysts and their replacement of normal organ tissue.
- The symptoms of the disease are:
- loss of appetite, weight loss and exhaustion of the cat;
- difficult, painful urination;
- vomiting, which becomes more frequent as the disease progresses.
Slowing down the development of the disease is achieved by following a special balanced diet that allows you to partially replenish the washed-out proteins, electrolytes and fluid.
Liver amyloidosis
Prevention
Preventing problems in cats is much easier than treating them later. To maintain your pet’s health, the following recommendations must be followed on an ongoing basis:
- Do not allow the animal to sleep on a cold floor, lie in a draft, etc. Under the influence of low temperatures, vasoconstriction occurs and the blood supply to organs is disrupted. Hypothermia immediately has a negative impact on the functioning of the genitourinary system. The inflammatory process that began as a result of hypothermia can serve as an impetus for the further development of diseases.
- Protect from heat. In the heat, the animal consumes an increased amount of fluid, the load on the kidneys increases significantly.
- Monitor your cat's diet. The animal must receive the necessary set of vitamins and microelements during feeding. It is important not to limit the diet only to meat, fish, and dry food. Food should be balanced and varied. It is necessary to give your pet as little fatty, salty foods as possible. Eliminate from the diet all food that is harmful to the animal’s stomach: sausages, baked goods, pasta, fried foods, etc.
- Give the animal only high-quality water - clean, but not boiled. It is recommended to use filtered water. Unsuitable water can serve as a provoking factor, since the animal’s kidneys are very sensitive to its quality.
- Monitor the availability of water. A lack of fluid leads to the fact that all its reserves are consumed, and the accumulated breakdown products are not removed from the body in the required quantities.
- Keep your pet active.
To avoid health problems, give your animal only high-quality water.
Important! Active movements contribute to good functioning of the urinary system, so animals with an active lifestyle have a significantly lower risk of problems.
Diet for a cat
How to feed a cat with an enlarged kidney? An individual diet, as already mentioned, is prescribed by the attending veterinarian, but the general recommendations for feeding the animal are almost always the same.
Firstly, you should pay attention to the water that the animal drinks. Under no circumstances should you give your cat unfiltered tap water. Water should be either filtered or bottled. In addition, you should ensure that the animal always has access to drink - this will help avoid dehydration.
Secondly, it is imperative to review your pet’s diet. If the kidneys are enlarged, cheap, low-quality food should be excluded from the diet. The amount of protein foods and foods high in phosphorus is also often reduced.
The danger of kidney disease
The danger is as follows:
- late diagnosis caused by the absence of symptoms in the initial stages;
- inability of kidney tissue to recover;
- the possibility of severe complications;
- the presence of a genetic predisposition factor in a number of breeds;
- males are prone to problems due to the structural features of their genitourinary system;
- high risk of death due to serious types of illnesses.
Only a veterinarian can prescribe the correct treatment
Enlarged organs
When pathology is identified, the underlying disease is treated. So, if the reason for the increase is inflammatory processes in them (pyelonephritis, nephritis), antibacterial therapy is prescribed. To eliminate dehydration and relieve symptoms of intoxication, droppers are prescribed. Complex therapy necessarily includes therapeutic nutrition. The animal is placed in a warm, dry place. Dehydration is not allowed.
Causes of the problem: congenital pathology, improper care, kidney disease.
Breeds with a predisposition to kidney disease
There are cat breeds in which the problem is hereditary:
- Persians. A common problem is polycystic kidney disease. Often the disease is detected even in kittens.
- Abyssinian breed. Predisposition to amyloidosis.
- Persian crossbreeds. They suffer from infantile polycystic disease.
Thus, the kidneys are a weak point for cats. In a number of breeds, the predisposition to kidney disease is hereditary. Compliance with preventive measures and timely identification of problems in an animal allows you to prolong its life.