Disease of the digestive system and intestines is unpleasant not only for humans, but also for animals. The danger and problem is that the animal does not speak and it is very difficult to diagnose the disease. After all, a cat has several dozen diseases of the stomach and digestive tract; often the symptoms coincide and it is extremely difficult to determine the disease without the intervention of a doctor. In no case should you engage in diagnosis and treatment on your own, because by choosing the wrong course of treatment, the owner exposes the pet not only to new problems, but also aggravates old. For example, isosporosis in cats is considered a fairly serious problem that requires close attention and must be treated carefully.
Our veterinarian provides a home call service. This is not only convenient for the owner in terms of saving time, but also beneficial for the animal. After all, moving to clinics, and even with pain in the stomach and intestines, will not have a beneficial effect on them. Due to the fact that our center has several reference points in Moscow and the Moscow region, the veterinarian arrives within an hour. He always carries the necessary tools and documents with him in the car. Therefore, right during the departure, a diagnosis will be carried out, and then a course of treatment will be immediately prescribed that will help the pet return to its usual lifestyle.
Pathogen
The causative agents can be two types of protozoa – Isospora rivolta/I.felis. These are the smallest single-celled organisms that live in the intestines of cats, other domestic and wild animals, as well as humans (there are specific species for each species). In most cases, isosporosis develops in kittens younger than six months of age, as well as in old and weakened animals. Often this disease is secondary, developing against the background of some other pathological processes, leading to a significant decrease in the immunity of animals.
Adult cats are resistant to isosporosis, but most often we are not talking about full immunity, but about carriage. In this case, Isospora rivolta/I.felis become a kind of “conditionally pathogenic” intestinal microflora, which can manifest itself only in cases of severe immune disorders (including age-related ones associated with the aging of the body). Such carriers act as a kind of reservoir host, since isospore cysts enter the external environment with the animal’s feces, infecting still healthy cats.
Symptoms of the disease
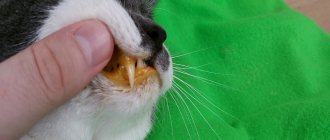
Kittens up to 6 months old, old cats and individuals with weak immune systems are at risk of developing isosporosis. Adult animals usually spread isospores, and symptoms do not appear at all or are mild until the immune system weakens, after which the pathogens begin to become more active. Manifestations of isosporosis resemble signs of diseases caused by other protozoa. Symptoms of the disease:
Protozoa provoke a state of lethargy in the animal.
- weight loss;
- diarrhea, sometimes with blood clots and mucus;
- vomit;
- dehydration;
- poor appetite;
- dull coat;
- lethargy;
- elevated temperature;
- neurological seizures in advanced form.
Isosporosis in cats appears after an incubation period 1-2 weeks after infection. In kittens, the disease develops much faster - after 2-3 days, starting with weakness and diarrhea.
Transmission routes
It must be emphasized that protozoa cannot overcome the placental barrier, and indeed, they live exclusively in the intestines. Therefore, even a cat whose intestines are full of pathogens gives birth to healthy kittens (of course, if the mother does not show clinical signs).
Attention! Infection occurs very quickly: the cat constantly licks itself, keeping its fur clean, and the cysts are spread over the entire surface of the body, including landing on the animal’s nipples. When kittens feed, infection occurs. In young animals the course of the disease is very severe. Often young animals (especially in animal shelters) die from severe dehydration, which in some cases develops within a couple of hours.
Diagnostics
For an accurate diagnosis, the pet is examined by a veterinarian and laboratory tests are performed. First, a smear of excrement is examined, which must be fresh and preserved for no more than 3 hours. Isosporosis is confirmed if 8-10 oocysts are found in the stool. The process is simplified by tinting the smear using a special solution. Additionally, feces are examined for parasites in the following ways:
- Darlington method. The excrement is mixed with water and a centrifuge is used.
- Fulleborn flotation method. The fecal sample is placed in a saturated salt solution.
Cryptosporidosis also has similar symptoms, which must be excluded when diagnosing the animal’s condition.
Symptoms of isosporosis are not specific and can represent a wide range of protozoal pathologies. The veterinary clinic conducts differential testing for diseases such as cryptosporidiosis, giardiasis and other intestinal infections that are caused by protozoan parasites in cats. Diseases have similar manifestations, but they need to be treated differently.
Why is isosporosis dangerous?
The danger of microscopic infectious agents lies in their desire to penetrate the cells of the intestinal epithelium. In fact, Isospora rivolta/I.felis are intracellular parasites with all the ensuing consequences of this.
Simply put, they live and multiply in epithelial cells, as a result of which the latter begin to die and collapse en masse. Since the mucous membrane in the gastrointestinal tract plays the role of not only a “sponge” that absorbs nutrients, but also a protective shell, the internal structures of the intestine quickly become inflamed. Of course, the actual digestive function of the organ is impaired.
Eimeriosis (coccidiosis)
Coccidia of the genus Eimeria live inside the epithelial cells of the small intestine. Only kittens are affected, and adult animals can be asymptomatic carriers. Infection occurs through water or feed. The disease is more common in southern Russia.
Symptoms usually appear 2 weeks after infection and are associated with mechanical damage to the intestinal mucosa and the accumulation of secondary microflora. Digestion is disrupted, absorption of nutrients becomes impossible, which leads to constant starvation.
The signs of coccidiosis are the same as those of isosporosis, but young animals are sick, severely stunted and losing weight.
Preventive actions
Firstly, be sure to isolate the sick cat from his still healthy relatives! If the entire litter of kittens is sick, their mother is checked for carrier status by examining the feces. If the causative agents of isosporosis are identified, the cat is also treated.
Attention! Feces from sick animals are collected in sealed plastic bags and, if possible, burned. If there are other animals in the house (dogs, even cats), then the entire “menagerie” is treated at the same time, regardless of the presence or absence of clinical signs.
It should be taken into account that pathogen cysts are very stable in the external environment. It is highly advisable to boil all care items that have come into contact with a sick animal. Low-value items should simply be burned to prevent the pathogen from “circulating” in the room.
Common Cat Diseases
When deciding to have a pet, a person takes on a number of obligations. A kitten or an adult cat needs care; like all living beings, it can encounter diseases.
That is why in everyday life you need to pay attention to his well-being, playfulness, and appetite. There are a huge number of cat diseases in the world. If the behavior has somehow changed, then you can suspect problems.
The best solution in this case would be to contact a specialist.
If you notice the following signs, you should visit a veterinarian:
- Vomiting, excessive drooling
- Lethargy
- The desire to hide in a dark corner
- Discharge from eyes and nose, cough
- Lost appetite, weight loss
- Convulsions
Important: The normal body temperature of a cat is 37.5 - 39 degrees Celsius, moreover, in young cats and kittens it is within the upper limit, and in older cats it is within the lower limit. The breathing rate of a kitten is about 60 breaths per minute, in young individuals it is 22-24 breaths, and in adults it is 17 - 23. Normal heart rate for cats is 100 - 130 beats per minute.
How quickly you respond to a problem will directly affect your pet’s health. Therefore, try to pay attention to it when the cat’s disease is still at an early stage. So vomiting may be a sign that too much hair has accumulated in the stomach.
In this case, it is recommended to give your friend a special paste that will dissolve the fur. But regular vomiting is not a good sign; if it occurs, you need to consult a specialist. Vomiting can occur with worms, due to disruption of the intestines.
Remember that self-medicating animal diseases is quite dangerous.
Below is information about the most common diseases of cats and cats.
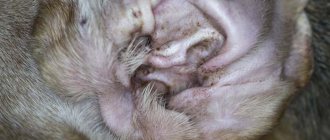
Among the common ailments are problems with the urinary system. Cystitis or urolithiasis may occur, which may result in your four-legged friend walking past the litter box.
There may also be a strong odor and blood in the urine. This is not a dangerous disease, but it can cause more serious negative consequences. By the way, this manifests itself due to sand in the bladder, diabetes, and lack of fluid.
Treatment
ATTENTION! Correct and effective treatment can only be prescribed by a specialist after laboratory tests.
For this disease, veterinarians prescribe specific drugs, as well as medications, the main task of which is to eliminate the symptoms and reduce their negative impact on the body.
Specific drugs can be highly toxic because they are supposed to eliminate parasites in the body. Therefore, they are prescribed by a specialist; only he can select a safe dosage and dosage schedule. Among these drugs are toltrazuril, sulfadimethoxine, trimethoprim. How are medications taken?
- The course of toltrazuril is 1 time per day, 3 days of administration.
- Sulfadimethoxine - 1 tablet per day, 10 days of use.
- Trimethoprim is taken for 5 days.
An important part of the treatment course is taking medications for symptomatic therapy:
- To reduce pain, antispasmodic medications are prescribed. They will also help eliminate abdominal discomfort in the animal.
- If there is blood in the stool, hemostatic agents are prescribed.
- Droppers are required to reduce and completely eliminate diarrhea and vomiting.
- Inflammation in the intestines is relieved with antibiotics.
To strengthen the immune system, it is important to take vitamin complexes, especially vitamin B 12. At the treatment stage, the care and attention of the owner play an important role. Many of the medications do not taste good, and the cat may refuse to take them. You must be patient and persistent to ensure that the body receives the drug in the required quantity.
Sometimes veterinarians advise giving bitters along with food, but this may reduce their effectiveness . When treating and rehabilitating a pet, the owner will need to adhere to all dietary requirements for feeding. The veterinarian will tell you what the diet should be, what foods to include in the diet, and in what quantity.
The diet will reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and will quickly remove inflammation of the lining of its organs. A sick cat needs to be provided with peace and comfort, since her health has been significantly destroyed by the disease.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Within a week or two after the oocysts enter the cat’s body, dangerous symptoms of isosporosis can be observed. The process moves even faster when small kittens are infected. An attentive owner can immediately notice changes in the physical condition of the pet. The main symptoms of the disease caused by isospores:
- There is an immediate decrease in appetite.
- The cat is quickly losing weight.
- Weakness, apathy, and indifference to games and communication appear.
- The animal vomits and feels sick.
- Watery diarrhea is also present.
- Due to the symptoms listed above, dehydration occurs.
- You may notice blood in the animal's stool.
- The coat loses its shine and may fall out.
The most important thing in this situation is quick diagnosis and treatment. The deterioration of the condition occurs very quickly, every hour matters. To save an animal, small or adult, you must immediately, when the first symptoms appear, take it to a veterinary clinic, to a good specialist.
Symptoms similar to isosporiasis are also observed with cryptosporidiosis - diarrhea, vomiting, weakness, dehydration. An accurate diagnosis is established only after laboratory tests. But in any case, a quick reaction from the owner and contacting the clinic on the first day is important.
The most important thing in this situation is quick diagnosis and treatment. The condition worsens very quickly, every hour matters. To save an animal, small or adult, you must immediately, when the first symptoms appear, take it to a veterinary clinic, to a good specialist.
But, unfortunately, even experienced veterinarians can rarely save kittens, since their body is still too weak to fight such a dangerous parasite and the malfunction of all infected organs. Kittens die in almost all cases.
Symptoms similar to isosporiasis are also observed with cryptosporidiosis - diarrhea, vomiting, weakness, dehydration. An accurate diagnosis is established only after laboratory tests. But in any case, a quick reaction from the owner and contacting the clinic on the first day is important.
Consequences
Giardiasis
The disease is caused by Giardia canis. Infection occurs with water and food. Giardia does not live inside cells, attaching to the intestinal villi from the outside.
Carriage of these parasites is often asymptomatic. But pathogenic strains cause diarrhea and interfere with digestion. Then the chair becomes:
- liquid;
- smelly;
- mixed with mucus and blood.
A scatological examination (using the Fulleborn or Darling method) is carried out three times, every 2-3 days, since oocysts are not released regularly or in insufficient quantities.
To diagnose giardiasis, there is a rapid test (the answer will be in 5-10 minutes), feces are examined using the ELISA method.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Hungarian motley duck mulard - BROILER CHICKENS, DUCKINGS, daily allowances, broilers Dnepropetrovsk, Buy chickens, buy ducklings, grown up, buy drinkers, chickens, Ukraine
Features of oocysts
In appearance, oocysts are bodies up to 33x19 microns in size, oval in shape, at the end of which there are two ends, slightly narrowed. Oocysts have a pale, smooth shell. Such isosporosis pathogens can even live in the soil for a long time before they enter the human or animal body.
We invite you to read: Stop stress drops for cats: instructions for use, analogues, price
But isospore in the body does not always cause illness and leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Often people, cats, and dogs are simply carriers of such a pathogen for a long time. If a cat has a strong immune system, its physical condition will not change. But the situation is completely different with pets that are weakened by long-term illnesses or have a weak immune system from birth.
In this case, the oocysts begin to actively influence the body. What happens to a kitten or weak adult animal? His digestion process is significantly disrupted, and also, which is no less dangerous, nutrients are not absorbed correctly.
Babesiosis
Caused by parasites of the genus Babesia . The infection occurs throughout the world with the exception of Antarctica, but veterinary practice clearly shows that the incidence rate is significantly increasing in more southern regions. The pathology is transmitted by the bites of blood-sucking ixodid ticks . There are no symptoms during the incubation period. Again, in many pets the disease itself can be completely asymptomatic, while other animals end up dying.
Prevention of protozoa
- Chemical coccide. Effective against any protozoosis. Give orally with food at a dose of 24 mg/kg for 3 days. If necessary, three-day courses are repeated with an interval of 10 days, and for toxoplasmosis, after a 3-day course, they continue to give a dose of 12 mg/kg for another 25 days to prevent re-infection.
- Toltrazuline: drugs Baycox or Stop-coccid. Baycox 5% is given to adult animals at a dose of 10-30 mg/kg for 3 days, which corresponds to 0.2-0.6 ml per 1 kg of weight. Stop-coccid for young animals is recommended at a dose of 10 mg/kg, or 0.2 ml per 1 kg of weight, for 3 days in a row.
In addition to combating the causative agent of the disease (protozoa), it is necessary to eliminate dehydration and nutritional deficiencies in the body.
- Subcutaneous or intravenous injections of solutions are used: Ringer's, 5% glucose, Refortan, Reamberin.
- In case of severe exhaustion, solutions for parenteral nutrition containing amino acids are indicated - Infezol, Duphalight. Use multivitamins (Hemobalance).
- Astringents and enveloping agents are prescribed internally - flax seed decoction, rice decoction.
- In case of severe damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, sorbents are used - Phosphalugel, Enterosgel, Polypefan.
- If the doctor suspects that a pathogenic microflora caused by damage to the intestinal mucosa has joined the protozoa, an antibiotic or metronidazole (Trichopol) is prescribed.
- If the cat has previously eaten a commercial diet, special diets are used to maintain the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: Hill's i/d; Royal Canin GastroIntestinal and others.
- If you are used to homemade food, use liquid slimy rice porridge with boiled beef and fermented milk products.
Feed should be easily digestible and not irritate the digestive tract.
- Promptly remove feces, disinfect animal care items, and maintain cleanliness in the premises.
- Isolation from stray dogs and cats.
- Do not feed raw meat and offal.
- Avoid eating rodents (in house keeping, a bell on the collar when kept outdoors).
Diet
- If the cat has previously eaten a commercial diet, special diets are used to maintain the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: i/d; GastroIntestinal and others.
- If you are used to homemade food, use liquid slimy rice porridge with boiled beef and fermented milk products.
Methods of infection
Isosporosis (synonyms for the disease - coccidiosis, isosporosis in cats) is transmitted when oocysts of the parasite enter the animal's body. Then they begin to actively mature in the intestines.
The main routes of transmission of isospores:
- through contaminated water;
- through food containing oocysts;
- when eating intermediate hosts of parasites (small rodents);
- from mother to baby.
The active development of single-celled organisms leads to the fact that they begin to leak through the intestinal lining into the blood vessels, and then into the liver, spleen and lymph nodes.