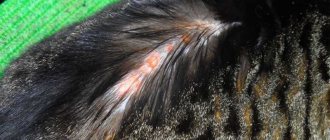
Skin (external) parasites in cats
The most common skin parasites in cats are fleas, lice and ticks. Their distinctive feature is the fact that they live on the skin and fur of the pet.
Fleas
Fleas are one of the most common types of external parasites on cats. Their characteristics, signs and tips on how to remove them from the animal and from the apartment:
| Signs | Location | Reproduction method | Nutrition |
|
| Laying eggs that transform into larvae within 2-14 days. Depending on the living conditions, an adult can develop from a larva either after a few days or after a few months. | Cat blood (temporarily can be dog or human). An adult flea can go without food for several months. |
To remove fleas the following are used:
- Medicinal shampoos (are the most effective and gentle means);
- Drops (applied to the withers, allow you to quickly get rid of insects, but can cause allergies and residual effects);
- Sprays (effective, but sometimes an allergic reaction occurs);
- Collar (an effective preventive measure).
After this, the apartment is sanitized.
Lice
Lice are the second most common external parasite in cats. We’ll tell you how to deal with them, signs and characteristics:
| Appearance | Habitats | Reproduction | Nutrition |
| Areas where the coat is thicker, as well as the head and neck. | Laying and attaching to hairs small white eggs (nits) up to 7 pieces per day. Individual lice emerge from them within a few days. | They suck blood and often feed on pieces of skin and hair. |
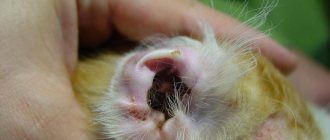
Ear and ixodid ticks
Ticks are one of the most unpleasant and dangerous skin parasites on cats.
| Signs | Reproduction | Nutrition |
“Tasty” areas for mites: the head (ears for ear mites), chin and back. | The female lays up to 5 eggs per day, on the 4th day they hatch into larvae, from which nymphs are formed. | Ticks attached to the skin actively suck the animal's blood. |
To get rid of ticks in cats, use shampoos based on benzoyl peroxide or chlorhexidine. To treat the skin, use special solutions, ointments and sprays prescribed by a veterinarian. In combination with these drugs, immunostimulating agents are prescribed. When secondary infections occur, antibiotics are used in treatment.
Causes of skin parasites in cats
The main causes of external parasites in cats include:
- Contact with an infected animal;
- Insufficient hygiene of skin and coat;
- Transmission through wool clipping tools, in some cases rugs;
- People can bring ticks into the house on personal belongings.
Symptoms of skin parasites in cats
Common symptoms of external parasites in cats include:
- Pronounced anxiety;
- Scratched and bitten areas of skin;
- Frequent weight loss;
- Signs of dermatitis - redness, crusts;
- Partial baldness;
- Sleep disorders;
- Anemia - in severe cases.
The most distinctive symptoms of skin parasites in cats include:
- With fleas, small white grains (eggs) are noticeable in the fur; in addition, fleas, unlike lice, are jumping;
- With lice, nits attached to the hairs and black dots (excrement of individuals) are visible;
- With ear mites, brown liquid sometimes flows out of the scratched ear, forming dark lumps in the shell: ear scabies occurs - otodectosis;
- Ixodid ticks embedded in the skin are visible to the naked eye.
Detailed seminar on skin parasites in cats on video:
Subcutaneous parasites in cats
All parasites that live in the layers of skin in cats are conventionally called “subcutaneous mites” or internal parasites in cats. Among them the most famous are:
Types, names and photos
Demodex
(Demodex cati). Microscopic worm-like organism. Lives in the hair follicle of the animal, moves at night. It feeds on excess subcutaneous fat. When immunity declines, the tick manifests itself by releasing toxic waste. Insufficient nutrition causes its death after 2-3 weeks. As the tick decomposes, it causes inflammation in the cat.
Scabies
. Localizes near the ears and on the face. Deeply affects the subcutaneous layer. Can lead to blood poisoning.
Notoedres cati
. It goes unnoticed for a long time. It provokes the development of scabies, which is often replaced by fungus and dangerous bacterial infections.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for the appearance of subcutaneous parasites in cats are as follows:
- Interaction with the owner’s clothes and shoes, on which he could bring ticks;
- Contact with infected relatives;
- Lack of hygiene;
- Failure to complete vaccination on time;
- Lack of inspections.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of subcutaneous parasites in cats are:
- Itching;
- Redness;
- Irritation and inflammation;
- Dandruff rash;
- Hair loss in some areas;
- Lethargy;
- Loss of appetite;
- The appearance of weeping wounds;
- The appearance of pustules.
Amoebic dysentery
The amoeba Entamoeba histolytica, entering the cat's body, causes disease. The main symptom is prolonged diarrhea. As a result, inflammation of the colon occurs. People, dogs, cats and some other animals are at risk. Often, a person can be a source of protozoan infection for his pets, even if he himself is not sick, but is only a carrier of these protozoa.
The localization zone of this parasite is the large intestine; in some cases, the disease can be asymptomatic when it enters the chronic stage or with pronounced diarrhea. In the absence of treatment and with incorrectly selected therapy, the cat quickly loses appetite and weight. Stool samples are taken for diagnosis, and antibiotics are often prescribed for treatment.
© shutterstock
Internal (intestinal) parasites in cats
Cats can harbor many types of helminths in their bodies. There are 3 main types of internal intestinal parasitic worms in cats - nematodes, cestodes and trematodes. We will tell you about them in detail - about the reasons for the appearance, symptoms of internal parasites in cats, as well as other features of each species. Most often, these parasites can be visually detected in the feces of cats. Here is as much detail as possible about all worms in cats.
Nematodes (roundworms)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
| The most common worms are roundworms, of which there are a huge number of varieties. Most often, the cat's body is affected by roundworms. Their length can reach 5 cm. The worms move through the contents of the small intestine. but can also affect other internal organs. When there are too many of them, the worms can clog the intestines or bile ducts. Cause allergies and severe poisoning of the body. Nematodes feed on the blood of an infected animal. |
|
|
The most famous nematodes include roundworms. Roundworms are one of the most dangerous parasites in cats, which, among other things, are also transmitted to humans. For treatment of these worms, universal types of anthelmintics are recommended. The drug is administered to the animal orally in two doses, with 14 days between them. Disinfection of “cat things” is carried out. If re-treatment is required, another drug is prescribed.
Cestodes (tapeworms)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
| These flatworms can reach up to 70 cm in length. They live on the walls of the small intestine. White worms and their segments with larvae resembling sesame seeds are passed in the feces. Segments can be found on the animal's bedding, or in severe cases of the disease - in the vomit. A frequently encountered representative of tapeworms is the cucumber tapeworm. It is 20-30 cm in length. Affects the intestines. Causes a dangerous helminthic disease - dipilidia. |
|
|
Treatment of cats for internal parasites such as tapeworms aims to destroy the causative agent of the disease. Anthelmintic drugs based on praziquantel and febantel are used. As a preventive measure, the animal is treated with insectoacaricidal preparations against insect parasites, in particular fleas that carry tapeworms.
Trematodes (flat flukes)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
White filamentous helminths parasitize both the intestines (white parasites in cats) and other internal organs - the liver, bladder and even lungs. Although they are rare, their harm is enormous and the disease can be fatal. Cats are parasitized by 2 types of trematodes:
|
| The symptoms of the disease are the same as when infected with other helminths. |
For prevention purposes, it is recommended to deworm your pet with special anthelmintic drugs. They also treat the animal. You must strictly follow the instructions and remember that you need to select medications by category:
- For the treatment of kittens;
- For pregnant cats;
- For adults.
Detailed video on how to remove internal parasites from cats. How to treat, how to diagnose correctly, etc.:
How does protozoa infection occur?
A cat can become infected after eating food or water contaminated with parasite spores. Another route of transmission is the bites of blood-sucking insects. At risk are kittens that still have weak immunity and animals that have recently undergone illness or surgery; they also still have weak immunity. Protozoa in cats are also dangerous for humans. Therefore, when treating pets for protozoa and disinfecting the premises, certain safety rules must be followed. This is especially important if there are children or elderly people in the house. In this case, the sick animal will need to be isolated.
What parasites can a person become infected with?
Contrary to the naive idea that domestic cats are clean animals and cannot infect humans with anything, it has been scientifically proven that many types of parasites are transmitted to humans in two ways:
- Directly through the fur and tongue;
- Through any fabrics and furs that the cat touches, as well as through the litter box.
External cat parasites do not pose any particular danger to humans, although they can cause some trouble.
But many worms willingly transfer to it, which as a result leads to human infection with parasites from cats. Roundworms are very dangerous for people
, which change the structure of the intestinal walls and affect the stomach.
These worms provoke dangerous allergic reactions and vitamin deficiency. A large accumulation of dead helminth bodies leads to blockage of the veins and respiratory tract. Ascariasis is very difficult to diagnose and is confused with lung diseases. Any nematodes are dangerous for humans
, since, affecting internal organs, they lead to the development of anemia, severe allergies, and the appearance of granulomas.
Tapeworms are very dangerous
not only for adults. They often penetrate the child’s body, causing various deviations in its development. Metabolism is disrupted, and as a result, general weakness and lethargy appears. Anemia often occurs.
Echinococci can be deadly to humans. By parasitizing and multiplying in the liver, they form their own “dwelling” - a cystic bladder. As the tumor grows, it increasingly compresses the lobes of the liver, and it cannot function normally. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and stagnation occurs in the bile ducts and blood. If the disease is not detected in time and treatment is not started, the bladder may fester, or simply rupture, which will lead to infection of the entire body.
A person can also become infected with a dangerous parasite for many body systems - toxoplasma - from a cat. Directly - no, but through contact with the cat's litter box, or rather with the animal's feces - it is quite possible. As a result of infection, the heart, nervous system, muscle structure and other organs are affected. This disease is especially dangerous for pregnant women, as it can affect the development of the unborn child and cause various abnormalities in him. People with weakened immune systems should avoid infection at all costs.