Why doesn't a cat open one eye?
A constantly squinted or completely closed visual organ is a consequence of a pathological process in the body. All ophthalmological diseases in pets are divided into 3 groups:
- eye diseases;
- pathologies that arose against the background of other disorders;
- traumatic diseases.
If a cat’s eyes cannot open, the most common causes are the following pathologies:
- Keratitis, or inflammation of the cornea. Damage occurs due to injury, entry of a foreign body or chemical substance, or infection. Sometimes keratitis occurs against the background of helminthic infestation. It is accompanied by photophobia, lacrimation, discharge of pus, and redness of the corners of the eyes. Due to severe pain, the animal behaves restlessly and refuses to eat and drink.
- Conjunctivitis, or inflammation of the mucous membrane. The disease develops due to bacteria, viruses, and fungi entering the body. Inflammation of the conjunctiva may be one of the manifestations of allergies (to pollen or dust). Symptoms of the pathology include increased lacrimation, redness and swelling of the eyes, and discharge of pus.
- Glaucoma. Intracranial pressure increases due to injury or systemic disease. The outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted. This leads to an enlargement of the eyeball, decreased visual acuity, and clouding of the pupil. At first, the cat or cat squints because it feels discomfort. In later stages, blindness is possible.
- Blepharitis, or inflammation of the edge of the eyelid. The disease occurs against the background of injury, infection, vitamin deficiency, parasite infection, burn (thermal or chemical). With blepharitis, the eyelids become red and thickened. The purulent scales that appear at the base of the eyelashes fall off and leave behind ulcers. The animal is in pain and constantly squints.
- Corneal erosion. The causes of its appearance are injuries, burns, viral, bacterial and fungal infections. The pet squints and scratches its eye with its paw, and behaves restlessly. Orientation in space is disrupted. If erosion is left untreated for a long time, a corneal ulcer may appear.
- Epiphora, or excessive tear production. Outwardly, the disease looks as if the animal is crying all the time. This leads to partial or complete blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. Epiphora can be congenital or acquired. An advanced form of pathology leads to the appearance of dermatitis.
A cat or cat may squint the visual organ due to mechanical injuries to the cornea. Most often this happens to pets that have free access to the street. Eye injuries received during fights or games with other animals often lead to inflammatory processes.
Cat squinting one eye photo
Click to see photo
There are times when it is not possible to see a doctor on the day of injury, and the animal needs first aid. Therefore, for an antibacterial effect, you can use taufon or torbex. But, remember that for a complete recovery it is necessary to assess the degree of damage (if it is an injury) or eliminate the irritating factor (if it is a foreign body or congenital pathologies).
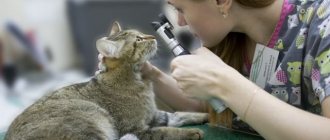
Diagnosis of the disease
If your pet constantly closes its eye, a veterinarian will find out the reasons. If alarming symptoms are detected, it is necessary to take the cat to the clinic.
Diagnostics includes procedures such as:
- visual acuity test;
- assessment of the general condition of the body;
- examination of the visual organs for damage;
- comparison of symmetrical features (size and shape of pupils, eyelids, eyeballs and slits);
- Ultrasound of the affected area;
- staining test;
- CT or MRI of the brain;
- X-ray of the skull.
Ophthalmological pathology may be a consequence of traumatic brain injury. Therefore, the examination must be comprehensive.
It is recommended to donate blood, urine and feces for analysis. Problems with the eyes can be caused by pathologies of internal organs or parasitic diseases.
Everyday facial expressions of cats
Calmness and excitement are two extreme situations, and between them there is a whole range of other features of the expression of a cat’s face. So, if a cat is hunting or is very interested in what is happening, an attentive expression will appear on its face: in this case, the ears are maximally open and raised up, and are in constant motion and try to catch the slightest sounds, the eyes are open wide, and the pupil is dilated.
In some situations, the nose may twitch distinctly, indicating the cat's desire to recognize any odors. If these odors are pleasant for the animal, it will stretch its neck and open its mouth slightly, trying to swallow air in small sips.
Methods for treating eye diseases in cats
If your cat squints or squints, it needs to be seen by a veterinarian. The specialist will find out the cause of this phenomenon and prescribe treatment.
However, not everyone has the opportunity to immediately take their pet to the clinic. In this case, it is recommended to examine the animal at home and provide first aid.
To do this you need:
- check whether a foreign body has entered the eye;
- rinse the damaged visual organ with saline solution or warm boiled water;
- Carefully remove the pus, moving from the outer corner of the eye to the inner.
Without the doctor's permission, it is prohibited to use antiseptic solutions or antibiotics for rinsing and treatment. Medicines, eye drops and ointments are prescribed only by a veterinarian after diagnosis.
Severe cases require surgery and suturing. This treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Description of possible causes
If you look at the statistics, most often when owners complain that their cat is constantly squinting one eye, injuries to the organ of vision and infectious diseases (especially in kittens) are diagnosed.
Of the accompanying symptoms, great importance is given to discharge from the eyes, sudden cloudiness and redness of the whites. If any of the above symptoms appear, the following options must be excluded.
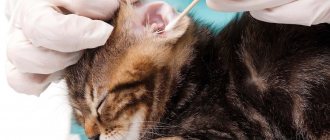
Foreign body
It can get under the third eyelid or directly into the cornea. Plant seeds, branches from trees or bushes, glass fragments (after an accident), and food debris can act as splinters. Each blink causes discomfort and pain, which causes the cat to often squint one eye.
The danger is that if the cornea is injured, there is a risk of secondary infection and the onset of an inflammatory process. It’s even worse if the pet tries to get the splinter out on its own using its paws and claws, which can significantly worsen the situation.
The first thing the owner should do is wash the eyes with lotion (Opticlia, Rosinka) and try to conduct an independent examination. There are times when the splinter digs in shallowly and can be easily removed with tweezers.
If the irritant cannot be detected or it has entered an inaccessible part of the eye, then it is best to seek help from an ophthalmologist. He will remove the foreign body and assess the extent of damage to the cornea and third eyelid. If necessary, prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs.
Injury
Can happen at any age. A fight, a game, climbing trees, an accident, falling from a height - all this often ends in eye damage.
If the third eyelid is injured, then for shallow scratches, antiseptic treatments for 3-7 days will be sufficient.
If the cornea is injured, an examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary to assess the extent of the damage. If a cat squints one eye for more than one day after any damage, then it is better to show it to a doctor, since some processes associated with vision are irreversible if medical assistance is not provided in time.
Corneal ulcer
The most common reason is that a cat constantly squints one eye. There is also almost always profuse lacrimation and redness of the third eyelid.
Injury to the cornea can occur during play, fighting, or getting a foreign body under the eyelid. Districhiasis and trichiasis, in which the cornea is often injured, can also be the cause.
The extent of the damage can be assessed only after a visual examination by an ophthalmologist and a special procedure for staining the cornea, which will show a clear location of the damage and the estimated depth.
In most cases, it is possible to manage with conservative treatment using antibacterial drugs (Torbex, Tsiprovet, Floxal) and Korneregel or Solcoseryl. The healing period may take 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the size of the ulcer.
If severe souring of the eye and purulent discharge occurs, it is recommended to see a doctor to rule out bacterial damage.
Trichiasis
Congenital pathology that manifests itself in the first year of life. Due to improper growth of even one eyelash, a cat may squint one eye, as there is discomfort during blinking.
In some cases, the eyelashes grow soft and do not interfere with the pet in any way, being only a cosmetic defect. But usually such eyelashes are hard and can seriously injure the cornea, so they must be removed without fail.
Depending on the location and number of eyelashes, anesthesia may be used under which hair removal is performed. In severe cases, several procedures may be needed to ensure that the hair follicle atrophies and the eyelash becomes thinner and softer.
Districhiasis
It is also considered a congenital pathology in which a double row of eyelashes is observed. Some of which necessarily injure the cornea and cause conjunctivitis and uveitis.
With this diagnosis, it is mandatory to remove all abnormally growing eyelashes. If this is not done, then at first the cat will squint its eye, then lacrimation, purulent discharge and clouding will appear. Ultimately, the eye becomes swollen with a cloudy film.
Measures to prevent eye diseases
It is easier to prevent an ophthalmic disease in an animal than to treat it. Prevention includes:
- regular vaccination;
- preventing pet hypothermia;
- examination of the animal’s visual organs after street walks;
- washing the mucous membrane and eyelids with saline solution if wounds are found on them;
- timely contact a veterinarian.
A cat squinting its eye is not necessarily due to illness. Sometimes this is a variant of the norm, for example, when the animal is sleepy or calm. It is necessary to seek veterinary help if this symptom persists for a long time and is accompanied by lacrimation, pus discharge and deterioration in the pet’s physical condition.
How to understand what a cat wants: extreme situations
When calm, a cat's face is round and peaceful. In this case, the facial expressions of cats emphasize the calmness of the animal even in the smallest details: the ears look up, the eyes are wide open (but the pupil is of normal size), the whiskers and whiskers are directed upward.
An anxious cat looks very tense. In this case, facial expressions easily reveal anxiety: the ears are pressed to the head, the eyes are strongly squinted, and the pupil is constricted.
Fear manifests itself even more clearly: the ears are pressed very tightly to the head, sometimes they are almost not noticeable, the cat’s head is pulled into the shoulders, and the cat itself seems to be gathered into a ball. As for facial expressions directly, in this case a characteristic feature is the raising of the upper lip and the appearance of bared fangs - this is responsible for the nervous tension of the muscles that lift the lip upward.
Aggression in a cat is extremely rare, so the facial expression that accompanies it looks quite characteristic and is easily recognizable. The reaction is similar to fear, but in this case the ears turn outward slightly, and attentive eyes look straight at the enemy.
Also, a cat’s aggressive mood can be recognized by a slight tilt of the head to the side and tension of the whole body - this indicates that the animal is about to attack.
Looks straight and does not blink, while the pupils are wide
This state of the pet, rich in consequences, is extreme excitement, emotionality associated with play, or may be fear. You've probably noticed that when you play with a kitten or a young cat, during the game, when the pampering has reached its maximum and the cat begins to release its claws, its eyes turn completely black, beautifully reflecting the light.
A dilated pupil often implies something crazy is on the cat's mind, and if the cat is looking at you like that, it's best to move his face away. He may just want to play, but you may not like it. Dilated pupils are also common in cats during estrus. Hormones and the general condition of the body control the look and behavior of the animal.
Depending on the situation, you can also assume that the cat is showing you his emotions of impatience if you offer to throw him a toy or feed him. If the cat lies dispassionately in its place, and everything around is calm, then its gaze with wide pupils, directed at you, clearly indicates the pet’s hidden fascination with some zookeches in the house.
The cat winks with one eye
Experienced cat owners claim that a cat, devoted to its owners and feeling sympathy for them, cannot look them straight in the eyes for a long time, so it either blinks or tries to turn away. Scientists explain this by saying that a cat is a predator, and when it looks at something or someone, it does not want to lose a potential enemy or potential prey from its field of vision, so it always has one eye open, which does not miss anything. mind.
This is a defense mechanism that helps wild animals survive. However, it cannot be said that when a cat looks at its already familiar and beloved owners, it experiences wild instincts. With a loved one, a wink rather means that the cat loves you, and accepts your presence next to him, telling you that everything is fine.