How is the disease classified?
According to etiology, vaginitis can be primary or secondary.
Vaginitis causes inflammation of the cat's genital mucosa.
According to the nature of the exudate, the pathology is:
- Serous.
- Catarrhal-purulent.
- Phlegmonous.
- Diphtheria.
Depending on the course, acute and chronic forms of pathology are distinguished.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctor carefully examines the patient and examines the external genitalia. A vaginoscopy is required. A smear is taken from the vaginal wall and sent for cytological examination. The doctor may also prescribe a microbiological examination of the discharge (determination of the causative agent of the infection, selection of specific antibiotics).
To assess the condition of the uterus, an abdominal ultrasound is performed.
General and biochemical blood tests, as a rule, do not reveal any abnormalities.
Why does it develop?
Feline vaginitis is provoked by:
- infection of the genitourinary tract;
- abnormal structure of the vagina;
- damage;
- penetration of a foreign object;
- development of neoplasm;
- penetration of viruses;
- penetration of bacterial infection.
Important. Sometimes the bacterial infection spreads to the uterus and bladder.
Causes of the primary form
Pathology develops against the background of:
- unsuccessful mating;
- consequences of artificial insemination;
- injuries..
Causes of the secondary form
The root cause is the development of an invasive or infectious disease. Vaginitis is a consequence of trichomoniasis, vibriosis.
Prevention of vaginitis in cats
To keep your cat healthy and have a strong immune system, it is important to follow the recommendations of experts:
- Respond in a timely manner to changes in the animal’s behavior - increased drowsiness, nervousness, the appearance of any atypical discharge. A timely examination by a veterinarian will help avoid the development of pathology. It is easier to treat vaginitis at the initial stage, before the disease becomes advanced.
- If the cat is not intended for mating, it is better to sterilize it in time. This will not only help eliminate the likelihood of having offspring, but will also reduce the risk of developing vaginitis and other health problems to a minimum.
- Only healthy males should be invited for mating. The animal's documents should be checked to ensure there are no genitourinary infections.
- Monitor your pet's diet. It is better to feed her with premium food so that she receives all the necessary nutrients and microelements. If you are predisposed to allergies, it is better to buy special food, which usually has the word “sensitive” in its name.
- After the birth of the offspring, even if the cat has lambed safely, it is advisable to visit a veterinary clinic. The doctor will examine the animal and recommend preventive measures.
- Visit your veterinarian regularly.
- Vaccinate your pet in a timely manner according to the vaccination schedule.
Your pets are completely safe with us. Many years of experience working with animals speaks of our status and confidence. We have cured more than a thousand animals, and we continue to save the lives of our little brothers.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics – Modern high-tech equipment. Ultrasound, ECG, ECHO, endoscopy, tests.
therapy
Timely treatment of diseases, emergency care for animals in emergency situations.
surgery
All types of operations: from cupping to treatment of injuries and diseases of organs. Treatment of oral cavities.
vaccination
Prevention of disease in pets.
About Us
Our veterinary clinic is modern, cozy and technically equipped, located in Rostov-on-Don, specializing in providing a wide range of services for pets. Certified specialists of the Radan veterinary clinic have many years of experience in the field of veterinary medicine, constantly improve their skills in the profession, undergo internships, and attend specialized conferences. The equipment of our veterinary clinic allows us to provide a wide range of diagnostic services. Laboratory examination of urine, blood, feces; electrocardiography, ultrasound diagnostics, radiology, microscopy for skin problems, testing for infectious diseases - and this is an incomplete list of diagnostic services that we provide in our veterinary clinic. “The cat has vaginitis Rostov-on-Don” - your solution is here. The Radan Veterinary Clinic provides vaccinations and state registration of your pets. We also microchip pets. We understand that the services of a veterinary clinic should not only be of high quality, professional and practical, but also accessible to a wide range of pet owners. To achieve this, our veterinary clinic constantly holds promotions that allow you to receive quality services at an attractive price.
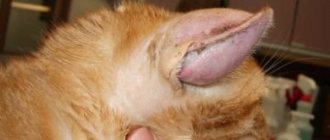
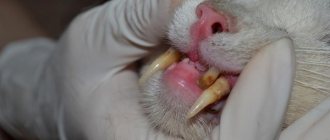
How does the disease manifest itself?
The following symptoms appear:
- vaginal discharge;
- frequent urination;
- swelling of the vulva;
- minor hemorrhages;
- the appearance of ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- irritation in the areas surrounding the vulva.
Often with vaginitis, a foul-smelling fluid is released from the vagina.
The general condition of the animal remains normal. With phlegmonous form, the general temperature rises slightly. With diphtheria, a specific fluid is released that has an unpleasant “aroma”.
Our advantages
A cat has vaginitis Rostov-on-Don - we have the solution.
That's why they choose us to bake.
Pet taxi
We will help your friend at home, or transport him to the clinic, using our own zoo-taxi
Seven days a week
Our only day off is January 1st. You can contact us any day, we work around the clock, without days off or breaks.
New technologies
The clinic’s equipment makes it possible to perform operations that are inaccessible to other veterinary hospitals in the city.
Good plus
You can purchase medicines and food for your animal directly from our clinic.
Let's be professional
Our doctors are professionals with extensive experience and a responsible approach to their work.
Let's improve
We are members of the Union of Pet Business Enterprises of Russia, initiators of programs for the development of progressive veterinary medicine and animal care.
How you can help
For serous and catarrhal-purulent forms, vaginal rinsing with solutions is prescribed:
- potassium permanganate;
- furatsilina;
- chamomile;
- chlorhexidine.
Attention. With diphtheritic form, it is not recommended to douche your pet.
Emulsions in oil are prescribed. It is allowed to use Vishnevsky's liniment. Ulcers are cauterized with a 3% lapis solution. If a bacterial pathogen is detected, then treatment of vaginitis in a cat is carried out with the help of medications. Your veterinarian may prescribe Metronidazole (Stomorgyl) or Amoxicillin.
If neoplasms or foreign objects are found in the vagina, the specialist resorts to surgical intervention. Juvenile vaginitis does not require medical intervention. It goes away after the first heat. If treatment was timely, the prognosis is favorable.
For some forms of vaginitis, your veterinarian will prescribe antibiotic treatment.
Diagnosis of disease in a veterinary clinic
If you notice symptoms of vaginitis in your pet, you should consult a veterinarian. Based on tests and examination of the animal, the doctor will be able to confirm or refute the owner’s suspicions. Diagnostics includes:
- external examination of the cat;
- cytological examination (analysis of tissue from the walls of the vagina);
- microbiological examination (bacteria culture to identify pathogenic microflora);
- a simple and detailed blood test (the leukocyte formula will show the presence of inflammation in the body).
Sometimes the doctor prescribes additional examinations if a differentiated diagnosis is required. For example, a urine test will help exclude the presence of cystitis, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity will show the condition of the reproductive organs (sometimes the development of vaginitis is accompanied by pathological processes in the animal’s uterus). If the use of antibacterial drugs is required, it is advisable to take a smear test for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Physiological causes of discharge
Discharge appears after and during estrus, after pregnancy, and also in the first few days after sterilization. If the nature and color of the discharge corresponds to the physiological period, then there is no reason to worry. However, it is recommended that the assessment be carried out by a specialist.
- During sexual heat, the discharge changes its color, depending on the period of the cycle: a pink-red hue turns into transparent mucus. After estrus, yellow discharge that lasts more than 2-3 days is already a reason to take the cat to the veterinarian. The symptom may be a sign of some gynecological disease.
- In a pregnant cat, yellow discharge cannot be normal. During a normal pregnancy, the cervix is closed and there can be no discharge.
- The end of labor may also be accompanied by a certain amount of reddish discharge, turning yellowish. Within a week after giving birth, there is no cause for concern if the cat’s general condition does not deteriorate. 1-3 days before birth, yellowish discharge may indicate that the body is preparing for the process of giving birth to kittens. The receding mucous plug usually looks the same color, but in most cases the cat immediately licks the perineum and the owners do not notice anything at all.
- A sterilized cat may have a certain amount of yellowish-mucous discharge in the first few days after surgery, but without any foreign odor and in the normal general condition of the animal. If a lot of time has passed after the operation, and discharge appears or does not stop, then the most common causes are cultitis (inflammation of the stump at the site of removal of the uterus), stump cyst or inflammation of the uterus, when not complete sterilization was performed, but only oophorectomy (the ovaries were removed, but the uterus was removed). left).
Where does purulent discharge come from?
Purulent vaginal discharge is very diverse, so there may be several reasons. Most of them are an immediate danger to the cat's health. However, there are also more passive prerequisites that can be taken more calmly.
It is important to determine the nature of the clots, understand whether they are purulent, and only then take action.
Safe discharge
One of the standard types of discharge in cats is estrus. This can happen several times a year, according to the cycle. There are no purulent formations, so the owner can be absolutely calm about the health of his pet. This usually lasts no more than a few days and is accompanied by an increase in the cat's activity. Therefore, even a layman can classify such processes. It is worth understanding that with any vaginal discharge you need to remain vigilant.
Normal discharge
Safe manifestations of the postpartum period include:
- the cat bleeds immediately after birth and for 24-48 hours;
- the discharge contains patches of green or brown for seven days;
- Clear, odorless mucus comes out of the genitals; this continues for up to two weeks.
For your information! The recovery process takes place without any extraneous symptoms such as fever, lethargy, refusal to eat or neglect of children and communication with the owner.
Orchitis in dogs and cats
Orchitis in dogs or cats is inflammation of the testicles and their appendages (epididymitis). It can be one-sided or two-sided. Occurs due to injury, infection of the genitourinary tract or prostate.
Main pathogens:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- Brucella;
- mycoplasma.
Symptoms of orchitis
Clinical signs of acute orchitis:
- swelling, hyperthermia, severe pain of the affected testicle;
- increased body temperature;
- pain when walking;
- stiffness of gait;
- decreased physical activity;
- When the disease becomes chronic, the testes change in size - they increase inadequately or, conversely, atrophy; acquire a dense or loose-cystic structure. Acute orchitis threatens the occurrence of abscess and necrosis.
Treatment of orchitis
To treat orchitis in a dog, broad-spectrum antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are used. If there are no results - castration.
The prognosis is cautious - irreversible disorders of spermiogenesis are possible, up to complete infertility.
What is considered a physiological norm?
It is completely natural for a cat to have discharge during heat or estrus. The color of the discharge during this period is transparent, and the consistency is uniform without an unpleasant odor. The heat does not stop for several days, and the cat arches her back, exposes her hindquarters, and shows excessive playfulness and affection.
Pregnancy and childbirth
Discharge during pregnancy may appear in a cat up to the third week. This is due to the fact that a mucus plug forms in the cervix, the excess of which flows out. This is usually clear or stringy mucus that is difficult to notice because it comes out along with urine. Until the 6th week, yellowish discharge is very rarely observed in small quantities - excess amniotic fluid.
And only a day or two before birth does the mucous plug come off (at 9 weeks). This is a small clot of yellow or greenish tint.
During contractions and pushing in a cat, the presence of brown and bloody discharge from the uterus is normal. For some time after childbirth, liquid greenish discharge appears, gradually becoming lighter, and then completely disappearing.
Scarlet blood at any stage of a cat’s pregnancy is always a sign of pathology and can be a signal of uterine rupture. The reason for the discharge of brown clots is placental abruption or death of the fetus. Green ones with an unpleasant odor indicate a bacterial infection, most likely due to the death of the kitten and the beginning of the decomposition process.
Necessary treatment
If there is an infection in these organs, the animal takes antibiotics.
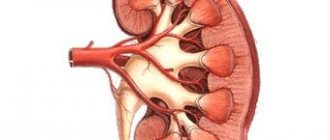
If a cat has enlarged kidneys or other abnormalities of the internal organs, then urgent treatment is required; in especially severe cases, partial or complete removal of the affected area is carried out. If the disease is caused by an infectious focus, then antibacterial treatment prescribed by a veterinarian is necessary. When a cat develops a kidney tumor, surgical intervention is prescribed. To eliminate signs of intoxication, it is necessary to conduct a course with intradroplet administration of special solutions. For any disease, it is important to follow a dietary diet, giving the animal natural food that contains minimal protein, sodium and phosphorus.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the development of abnormalities in the postpartum period, you must adhere to the following rules:
- stop abusing hormonal drugs that are used to control estrus: it is prohibited to independently increase the dosage and duration of use;
- comply with the requirements of antiseptics during labor, carry out hygiene procedures after childbirth for a young mother who does not know how to care for herself;
- Before mating, check the cat’s health to ensure that he does not have genitourinary infectious diseases;
- Any discharge during pregnancy is a reason for an emergency visit to the veterinarian.
The birth of babies is a serious stress for their mother's body. Maximum efforts are required from the animal owner to facilitate the birth and postpartum periods. Blood during childbirth in a cat is a standard manifestation, but its excessive amount should attract the attention of the owner. Ignoring deviations can cost not only the health, but also the life of your furry pet.
Pregnancy and childbirth are a difficult period for a cat, both physically and mentally. The pet needs additional care. During this difficult period of time, the owner must provide the animal with conditions for a comfortable stay. You should be especially attentive to the physical health of a young mother. Discharge from a cat after giving birth should alert the owner.
Pyometra
Among the most common diseases of cats with bloody discharge is pyometra, a form of purulent endometritis in which pus accumulates in the uterine cavity. The disease is most often provoked by rash actions of the owners themselves, namely:
- abuse of hormonal drugs during estrus;
- uncontrolled mating;
- infection in the vagina during childbirth.
There are two types of pyometra:
- Open form - blood clots come out of the vagina. The cat licks itself frequently, approximately every 15-20 minutes. The animal's temperature rises, the cat often drinks water.
- Closed form - no discharge visible, because blood accumulates in the uterine cavity. Symptoms of the closed form of pyometra: enlarged, tight abdomen, frequent urination, apathy, rapid breathing.
Of these two forms, the second poses the greatest threat to health, because. excessive accumulation of pus in the uterus can lead to the death of the animal.