Common diseases affecting cats' ears
- hematoma;
- shell necrosis;
- lymphatic extravasate;
- internal and median otitis;
- otitis externa;
- presence of foreign objects;
- tumors.
The listed ailments are non-communicable diseases. Contagious diseases include otodectosis - the presence of ear mites.
Diseases affecting the ears of cats are non-contagious diseases.
Preventive measures
To avoid headaches and protect your pet from illness, you should take the following measures:
- Features of the breed. Many cat breeds are predisposed to migraines and headaches. Often they cannot stand bright light and noise, so when purchasing a purebred kitten, take an interest in the characteristics of its breed. Veterinary websites with descriptions of animal breeds also write about diseases to which animals may be susceptible;
- Protect your cat from injury, make sure that she does not jump on high objects and calculate the distance correctly. Remove objects that may become potential sources of injury, and if a traumatic situation occurs on the street, immediately contact a specialist;
- Watch your diet. Abuse of salty foods, dry food and improper drinking regimen can cause headaches in the animal;
- Treat comorbidities. Severe headaches can be caused by periodontal disease, glaucoma, otitis media and infectious diseases. In some cases, a persistent headache may be a sign of kidney disease or an imbalance of water and salt balance in the body. If you notice changes in behavior or alarming symptoms, consult a doctor. He will accurately determine the cause of the disease;
- If you suspect a brain tumor or other pathologies, do not refuse surgical intervention. Often this is the only way to save your pet's life.
My cat has ear pain, what should I do?
First you need to examine your ear!
Mechanical damage to the shell, such as injuries, bruises, bites and scratching, provokes the appearance of a hematoma.
- As a rule, compaction develops on the inside and very rarely on the outside. Characterized by swelling and sagging.
- A significant swelling may form, which is hyperemic, painful and hot to the touch.
- Prolonged ignoring of symptoms provokes the development of secondary pathology and serious complications, which can result in cartilage necrosis.
- The animal's behavior also changes: the pet makes sudden movements of its head, constantly rubs the affected area with its paws or scratches.
- Shows nervousness and aggression.
Scratching provokes the appearance of a hematoma.
Treatment at home
Treatment consists of applying a fixing bandage.
Treatment consists of using a fixing bandage and applying ice.
After a day, you can use warm compresses and local treatment with irritating ointments. Advanced cases require surgical opening of the hematoma, cleaning and disinfection. It is recommended to use novocaine with an antibiotic to prevent further development of pathogenic microflora.
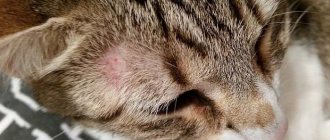
Miliary dermatitis
If the sores on the cat’s neck under the fur look like a scattering of small pimples, then the doctor can make such a diagnosis. In fact, this will only mean one thing: you need to immediately look for a new veterinarian who is more competent. The fact is that miliary dermatitis is not a disease, but only a symptom of it. Moreover, there can be countless reasons, which the doctor must deal with. You need to start from the localization of the rash. In some cases it covers only the neck, in others it spreads to the entire body.
This condition can be caused by allergic reactions. In this case, it is extremely important to determine the cause of its occurrence. This could be a reaction to fleas, inhaled allergens, or food. Based on the location of the rash, you can roughly tell what exactly was the cause. If pimples and wounds are concentrated in the neck area, then the problem is most often a food allergy.
Shell necrosis
Necrosis of the shell can provoke a complication of the purulent process.
Necrosis of the shell can be provoked by the following factors: prolonged pressure on the ear, a complication of a purulent process that has spread from other tissues, the spread of pathogenic microflora due to hematomas or abscesses.
If purulent inflammation is not treated in time, inflammatory foci may open and areas of necrosis of the skin may appear, which leads to thinning of the cartilage. This phenomenon provokes a violation of blood flow , the affected area darkens and an unpleasant smell of rot may appear. The entire ear is deformed.
The only help is surgical – the affected area or the entire organ is removed.
Option number 1: blood-sucking parasites
Indeed, it often happens that insects choose the neck as their favorite area for life. Therefore, the cat intensively scratches these places with its claws. As a result, if action is not taken, things will take a bad turn. Itching provokes scratching, and small sores appear on the cat’s neck. But the insects do not stop their activity and continue to bite the animal. As a result, scratching continues, dirty claws can become infected and an abscess begins.
What should the owner do? Examine the animal. If he has fleas, then their locations should be visible on the neck and near the tail. Adult insects and their eggs can be found. In this case, you need to treat the animal for insects, and then treat the wounds. You can use a special collar or drops on the withers. Once the source of the itching is eliminated, it will be much more effective.
Dirty ears
Dirt in the ear can lead to inflammation.
A cat's sink may contain plant particles, leaves, wax plugs, and sand. This state of affairs most often leads to an inflammatory process .
Help consists of removing the foreign object, washing with a soda solution or hydrogen peroxide solution. The pain is relieved by instillation of camphor oil.
Otodectosis
Perhaps the most common invasion is otodectosis. The causative agent is a microscopic mite.
The causative agent of otodectosis is a microscopic mite.
- The transmission route is mainly contact.
- Symptoms are typical for all parasitic diseases.
- The animal is restless and constantly itches.
- Brownish discharge is observed from the ears.
- Treatment consists of daily cleaning of the sore spot and instillation of drops, for example, tsipam.
- The course of treatment is seven days.
- If it does not give the desired effect, it is allowed to drip in two drops of stronghold after thorough cleaning.
- Repeat in about a month.
Lymphextravasate
Signs of lymphatic extravasation development are similar to hematoma.
The reasons for the development of lymphatic extravasation are in many ways similar to the reasons for the occurrence of hematoma.
Clinical signs are also almost the same. The only difference is the treatment. The use of any thermal procedures - cold or heat - is strictly prohibited .
Therapy
Therapy should only be carried out by a veterinarian.
Therapy should only be carried out by a veterinarian. In a hospital setting, fluid is pumped out using a syringe. In more complex cases, surgical opening of the skin and removal of exudate, followed by the use of antiseptics and suturing, is recommended.
Treatment of the disease
When cats have a headache, the doctor determines the cause and gives recommendations on how to treat the animal. Depending on the cause, he may take the following measures :
- Changes in diet. If the headache is caused by an excess of salt in the animal’s body, or anorexia, it requires food with a high protein or liquid content. During the treatment period, give up dry food, choose natural foods with low salt content, change the water more often and add more milk to your cat’s diet. With advanced anorexia, treatment will be long-term;
- If the cause is poisoning, the doctor will carry out a set of measures to neutralize and remove toxins from the animal’s body. These can be cleansing droppers, copious amounts of fluid, or a cleansing catheter with a special solution that allows you to remove toxic substances from the cat’s body. In case of poisoning, a dense and rich diet is not recommended; it is better to drink more fluids;
- For injuries and concussions, the doctor prescribes complex therapy. To reduce cerebral edema, the cat is prescribed the drugs Indap, Hypothiazide and Indapamide. In some cases, the veterinarian prescribes diuretics Veroshpiron, Furosemide, Diacarb and potassium supplements. Painkillers No-Shpa, baralgin and analgin are prescribed, and caffeine and camphor are given to stimulate cardiac activity. During treatment, the animal needs rest; it should be protected from children, loud sounds and bright light;
- If the cause is a tumor or glaucoma, increased intracranial pressure associated with urolithiasis may require surgery. The doctor places the main emphasis on treating the underlying disease. After the operation, the animal must be provided with complete rest and proper nutrition, which should be discussed with a specialist;
- If your cat suffers from migraines or a hereditary tendency to headaches, doctors recommend giving her painkillers along with food and water from time to time. Analgin helps as a pain reliever, the dosage of which is prescribed by the doctor.
© shutterstock
Otitis
The symptoms of otitis are in many ways similar to many ear diseases.
With otitis media, ear discharge and redness are observed.
The pet's behavior changes, the cat becomes restless and aggressive, ear discharge, redness and swelling of the diseased organ are observed. There may be an unpleasant odor coming from the sink. In more complex cases, appetite disappears and the temperature rises.
Treatment
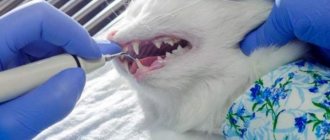
At the beginning of treatment, clean the affected area with a cotton swab.
Treatment is carried out in a complex: local treatment and drug therapy.
- First of all, clean the affected area with a cotton swab dipped in a solution of boric acid, hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin.
- Dry with a cloth.
- Use ear drops.
- It is possible to relieve pain with novocaine blockade.
- A course of antibiotic therapy and medications that support the general condition of the animal are prescribed - immunostimulants, vitamins.
- At the same time, they provide the cat with a complete diet with vitamin and mineral supplements.
Itching caused by helminths
There are a large number of varieties of parasitic worms that take up residence in a cat’s body. They can be:
- round;
- flat;
- tape.
Usually at the very beginning of infection it is difficult to consider any of its symptoms, but after a while the animal:
- loses appetite and activity;
- becomes restless;
- Constantly licks and itches.
Worms found in the intestines are considered almost harmless.
Difficulties with your pet’s health arise when there are too many helminths and their larvae begin to migrate.
The movement of worms throughout the animal’s body is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sudden weight loss, increased fatigue, growth retardation in small pets;
- disheveled wool;
- enlarged liver and icteric staining of visible mucous membranes;
- disruption of the digestive system, expressed in constipation, vomiting, diarrhea;
- appearance of cough;
- discharge from the eyes;
- itching in the anus;
- presence of blood in feces;
- premature birth or miscarriage in cats;
- convulsions and paresis of the limbs.
The cat may not notice the presence of parasites in the body in small quantities. However, their increase will not only exhaust the animal, but will also lead to its death. The harm caused to pets by worms can be completely different :
- eating lymph, tissue and blood;
- release of substances that promote intoxication;
- damage to the mucous membranes by suction cups, leading to internal bleeding.
After the worms die, decomposition products are formed that poison the animal’s body.
The appearance of parasites leads to metabolic disorders, as a result of which the cat’s skin becomes dry and dandruff appears on it. Just like an allergic reaction, these factors are accompanied by itching, which causes the animal to scratch its neck until it bleeds. A pet can become infected with helminths in the following ways :
- eating raw meat or fish (especially river fish);
- flea bites;
- contacts with other animals.
To prevent itching, which causes painful scratching, animal owners need to regularly take a preventive course using anthelmintic medications.