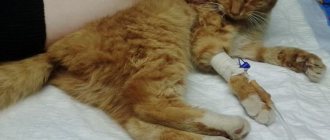
Cats are cute creatures, inhabitants of many apartments and houses. Breeders of four-legged friends try to raise their pets healthy, strong and active. If any problems arise with the health of your ward, you should immediately look for the cause of the illness and begin treatment. The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the easier it is to prevent the development of complications. Many owners, when visiting a veterinarian, note that the cat falls on its side when walking. As a rule, this is not the only symptom. The severe condition is accompanied by loss of activity, refusal of food and water, convulsions, fever, blurred vision, twitching of the limbs. All of the above signs indicate health problems.
How to deal with a shy cat?
Owners of nervous cats often become quiet. They believe that muffling the voice and tiptoeing from room to room is the right strategy to get the cat accustomed to not being afraid of people. Unfortunately, such actions, changing the natural way of life, only increase nervousness in the house, which can only lead to increased tension in your pet.
Normal behavior, giving a sense of familiarity and calm, will consequently have a positive impact. Do not make constant attempts to communicate and demonstrate love, do not rush to search for a hidden cat, do not rush to remove it from its “shelter”. Immediately fixating attention on a cat entering the room is also undesirable, as it makes the owner intrusive and potentially dangerous in its eyes.
It's best to give your cat a sense of "invisibility" so that she can move around the house without being the center of attention. Quiet living conditions do not involve direct eye contact, verbal or physical communication until she initiates it through her own actions.
Food can be used to develop positive associations and strengthen the bond between you and your cat. Offer a small amount of meat, fish or other tasty food in a saucer. This can encourage her to explore different rooms in the house or spend time close to you.
Positive playtime interactions can also have significant positive effects—many cats can't resist the urge to play. By using toys attached to a long rod or string, you can allow timid animals to fully enjoy play without feeling like you're too close.
Constantly “consoling” the cat in response to manifestations of timidity only increases its nervousness. It is best to simply ignore the nervous reaction and encourage (using any means that motivate the specific cat) calm behavior.
Never lose your temper or try to correct behavior too quickly - this will only increase your cat's fears. If you notice progress, no matter how small, you are probably dealing with an animal that is overcoming fear. Most likely, the kitten went through the necessary stages of socialization normally. Continue to build on your success little by little. Remember that cats feel safe in high places. So when your cat stays in a room with people, give her the opportunity to climb up high, sit in safety, and watch what goes on in the world from above.
Stress in a cat - is it dangerous and how to relieve it?
Signs of stress in a cat
- itself
too often and actively . One of our cats, for no apparent reason, began to lick its belly often. It got to the point where he was covered all over with bloody sores. We still don’t understand what brought him to this state. But it was clear that this was stress.
I had to go to the vet. We didn’t risk taking him to the clinic in winter. In addition, he never went outside, and this could lead to even greater stress. They called a doctor to the house. Stop Stress drops
. After a few days, the wounds began to heal. Now we keep this medicine in our medicine cabinet all the time.
- The cat stopped washing
and grooming itself. This also indicates psychological problems. - The cat hides in dark places all the time and does not come out even for food
. This condition indicates problems, either physiological or mental. You should not force the cat out of its shelter, but you should definitely contact a veterinarian. Often a cat hides from severe pain. - The cat has become aggressive
, the pupils are dilated, the ears are pressed to the head, hissing, spitting and scratching. These are clear signs of severe fear.
For example, a cat is out of the window, and nothing happened to it, but before that it had never gone outside. A sudden change of situation and fear leads to the cat rushing about, throwing itself at the walls, not recognizing its owners, and screaming wildly. The main thing here is to quickly catch her and take her to her usual home environment. Try to calm her down with kind words and gentle stroking. Give her a few drops of valerian diluted in water and then leave her alone. Let her walk around the apartment herself, sniff everything, and understand that this is her home.
- If a cat refuses to eat
or, conversely, begins to
endlessly touch the bowl of food
, then this should also alert you.
A person in a stressed state either does not eat anything, or eats to capacity and falls asleep. This is a protective reaction of the body.
- The animal begins to eat paper
or something else that is not typical for it. - The animal has stopped going to its own place, and is trying in the most unexpected places. Do not rush to punish the cat, much less scold it. By this she tells you that something does not suit her or torments her. She can’t speak, so she’s trying to draw your attention to her problems. She may have serious health problems.
- The cat began to actively damage the furniture. The reasons are the same as described above.
Causes of stress in cats
The causes of a cat's stress can be various:
- Moving to a new place of residence;
- Change of owner;
- Rearranging furniture in the apartment;
- Changing the toilet;
- The birth of a child in a family;
- The appearance of new people in the apartment;
- Apartment renovation;
- Loud and incomprehensible sounds for the cat;
- The appearance of a new animal;
- Lack of attention from the owner;
- A trip to the vet;
- Severe fear;
- Falling from height;
- Going outside if the cat has never been there;
- Lost Loved Ones;
- Changing your favorite house or bed;
- Punishing a cat;
- Change of food;
- Bathing;
- Various ;
- Etc.
There may be many reasons, but the result is the same - the cat becomes lethargic, or vice versa, aggressive. Perhaps this list will help you better understand your cat and avoid many problems.
Despite the more stable organization of the nervous system, cats, compared to other domestic animals, such as dogs, are less susceptible to nervous system disorders. Owners often mistake the symptoms of a nervous disorder for bad behavior or oddities in the pet’s character, groundlessly punishing the animal, thereby aggravating its condition.
Knowing how nervousness manifests itself in a cat, the owner will be able to take preventive measures, as well as reduce the symptoms of the developing disease.
Read in this article
Factors provoking the disorder
The factors that most often provoke the development of nervous disorders in domestic cats, veterinary experts include the following moments in the life of an animal:
- moving to a new place;
- change of owner;
- traveling by car or public transport;
- visit to the veterinary clinic;
- exhibition events;
- the appearance of another animal in the house;
- the arrival of a new family member;
- weaning kittens from their mother cat;
- changing furniture in the room;
- new tray, bowl, filler;
- change of food or diet;
- guests or a noisy party;
- fireworks, firecracker explosions.
A special group of provoking factors includes physical ailments of the pet. Experiencing pain and discomfort, the cat feels fear and helplessness.
Emotional distress over the loss of an owner or companion animal causes deep neuroses that last for months.
Not all cats develop a nervous disorder; individual mental characteristics are of paramount importance in this illness. Some animals calmly react to noisy companies, do not notice changes in the environment, and feel comfortable in a car.
The nervous system of other pets reacts negatively even to changing the usual litter box. Owners need to take these features into account when keeping cats, be able to recognize the symptoms of neuroses and provide timely assistance.
Types of ataxia
Ataxia is divided into several types, depending on the affected area:
- Sensitive . Affects the cat's ability to bend and straighten its joints. Chances of cure only with the earliest possible diagnosis;
- Cerebellar . It can be static (loss of balance) or dynamic (impaired movement). It starts with small manifestations of awkwardness and maintaining balance. In the case of a genetic factor, it is incurable; in the case of a traumatic cause, the chances of recovery are real;
- Vestibular . It starts with all movements becoming slow and very careful. At later stages, the body tilt changes to the left or right, and the animal stops moving straight.
Nervous diseases and disorders in cats
Most often, the owner encounters such disorders in the cat as a nervous breakdown, neurosis, and convulsions.
Teak
Such a phenomenon as a nervous tic (rhythmic twitching of the muscles of the muzzle, fore and hind limbs) is not an independent disease. There are many reasons for its occurrence: from dental problems (twitching of the temporal muscles) to complications after infectious diseases and organic brain lesions.
In neurological practice, nervous tics in domestic cats are rare. The clinical sign requires detailed examination by an experienced neurologist.
Convulsions
Seizures are rare in domestic cats. First of all, the owner should exclude such a severe neurological disease as.
The disease is accompanied by clonic-tonic convulsions, the duration and intensity of which depends on the severity of the disease. There is evidence that the tendency to epilepsy is due to genetic predisposition. The use of anticonvulsants helps prevent seizures.
Convulsions and seizures are characteristic of neuroses, neuropathies of various origins and neurological disorders. Only a veterinarian can determine the exact cause and exclude organic pathologies (poisoning, infectious diseases, brain injuries, etc.).
Neurosis
Depletion of the body's nervous system under the influence of a strong or prolonged external stress factor leads to the development of neurosis in pets. At the same time, the symptoms of a nervous system malfunction can be very diverse - from aggression towards the owner to the development of spontaneous hyperesthesia syndrome.
Most often, the owner encounters the following manifestations of neurosis in a furry couch potato:
- Fear of previously familiar objects, premises, rooms. Often a cat is afraid even of its litter box.
- Pointless movement around the room. A call or a sharp sound does not have any effect on the pet.
- Pathological licking of fur, which lasts for hours.
- Pet hyperactivity or, conversely, a state of complete apathy.
- Fear of touch, inadequate reaction from stroking - hyperesthesia syndrome. The slightest touch to an animal causes a storm of negative emotions and hyperactivity: the cat begins to hiss, run around as if scalded, and scream.
Experienced breeders and veterinarians believe that Oriental cats are more susceptible to the disease than other breeds. Their nervous system is less adapted to the changing external environment and often malfunctions.
Oriental cats
Disruption
There are many reasons for a domestic cat to have a nervous breakdown: from changing furniture to moving to a new place. A mental disorder manifests itself in the form of repetitive actions of an animal. The cat constantly licks itself non-stop, rushes from side to side, meows loudly and constantly.
Stress affects the animal's body, leading to a violation of control over its behavior. Rhythmically repeated actions (licking and pulling out fur, meaningless movement around the room) are aimed at turning off the animal’s consciousness in order to protect the nervous system from overwork.
Forum KOTODOM
Hello! We really need your advice! The cat suddenly became ill, coordination of movements was impaired, it was almost impossible to walk, its paws moved apart, buckled, constantly fell, weakness, mood, the mood was either sluggish or aggressive.
Our cat is a little over 3 years old; 2 years ago she had pyometra; she underwent surgery. Then there were suspicions of cultitis, they were treated with antibiotics and rinsing was done. The last time I was dewormed was 4-5 months ago with cestal. The cat eats meat, fish, and sometimes baby cheese.. It does not accept any food, although we have repeatedly tried to switch it to it. On March 8, the cat began to have pain somewhere in the back, she stuck out her butt, meowed and growled pitifully when you approached her, did not get up, did not eat, but by the evening it went away, she was cheerful, and ate with pleasure. .Until 03/11/10 everything was fine, no signs of illness. On the evening of March 11, she became lethargic, her paws began to move apart a little, the cat sagged, sticking out the back of her body upward. On the morning of March 12, the condition worsened, they called the doctor and advised him to inject him with no-shpa. They injected it, the cat went limp, its eyes rolled back, while its hind legs were convulsively clenched.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
Not every stress and its impact on a pet should cause anxiety for the owner. A healthy cat copes with a stressful situation quite quickly on its own. However, there are symptoms that require the owner to show the pet to a veterinarian. These clinical warning signs include:
After a clinical examination, your veterinarian will perform specific physical tests to look for abnormal neurological responses.
To exclude neoplasms and other pathologies, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, general and biochemical blood tests are used. Magnetic resonance therapy helps in making a diagnosis. Based on the results of the examination, a consultation with a neurologist is scheduled.
Causes of paralysis of the hind legs
If paralysis of a cat's hind legs occurs, a visit to the veterinarian should be urgent.
When a cat does not stand up on its hind legs, it can take hours to save it. Various reasons can provoke a violation of the pet's condition. Whatever the reason that the cat does not stand on its hind legs, it must be urgently shown to a veterinarian for proper therapy. Even with a severe violation, an immediate visit to a specialist and timely treatment can save your four-legged pet. If the cat only slightly drags its paws, the problem is usually solved as soon as possible.
What to do when your cat is nervous
Having an idea of the signs of increased nervous excitability, the owner is able to prevent the development of a nervous system disorder in a pet in a stressful situation (moving to a new place, traveling on public transport or by car, the arrival of a new family member or the arrival of guests, etc.).
In car
Some cats take the forced journey hard: they scream heart-rendingly, rush around the carrier, and try to escape. The animal’s fear is caused by a change in the usual environment, many new unfamiliar smells, and sharp sounds. In public transport, in addition to the smells and sounds of the car, numerous odors of strangers are added, which frightens the animal even more.
Car panic in a furry couch potato can last for hours, exhausting the animal itself and causing inconvenience to the owner. The cat develops increased salivation, rapid breathing, increased heartbeat, and muscle tremors.
The pet does not respond to its name, does not respond to affection, and does not accept treats. This behavior indicates a panicked state of the animal and requires assistance.
First of all, knowing about his pet’s fear of vehicles, the owner should accustom the cat to traveling gradually: first, just let him sit in the car, getting used to the smell, then stay in the car with the engine on, and drive a short distance. It is better to accustom your furry family member to travel from a young age.
When transporting a cat in a car, it is necessary to use a special carrier. A plastic container that provides air circulation to the animal is best suited for this. It can be secured in the back seat using seat belts. Under no circumstances should you carry a nervous animal in your arms. The cat's reaction is unpredictable; it can scratch, break out, get under the pedals and cause a traffic accident.
Serious disorders of the nervous system occur infrequently in cats. However, the owner should have an idea of what symptoms should raise the alarm and seek advice from a veterinarian.
Why does a cat fall over on its side when walking: reasons
However, the list of medications for each case is individual, and the veterinarian draws it up based on the diagnosis. The same goes for aftercare.
Most neurologists recommend examinations every two weeks to monitor the progress of treatment. Secondary symptoms such as vomiting and dehydration should also not be ignored. Experience shows that cats recover faster after diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
Prevention of "shifty" eyes
It is impossible to formulate a specific system of preventive measures for nystagmus, because There are many reasons, including congenitality. The only thing we can advise is to avoid poisoning your cat with lead and other toxins. In addition to Siamese cats, cats with albinism are predisposed to this disease, keep this in mind. Some kittens under one year of age may exhibit nystagmus, but this is very rare and will go away soon.
Category Cat diseases.
Ataxia in cats is a pathology of motor activity characterized by a lack of coordination of muscle movements, coordination and loss of orientation in space.
Most often it is genetic in nature, but can be acquired as a result of a severe form of group B hypovitaminosis or cerebellar injury. What is characteristic is that the animal remains strong, it is simply more difficult for him to maintain balance and the sequence of each action.
This neurological disorder does not have any age, breed or gender restrictions and can be diagnosed almost from birth, as soon as the kitten begins to move. It is practically incurable.