Scottish fold cats, especially fold cats, have genetic health problems. They are susceptible to pathologies: lacrimation from the eyes, crooked teeth, deformation of the oral cavity, damage to bones and joints. Due to decreased immunity, there is a risk of contracting infectious diseases.
Prevention of diseases in Scottish Fold cats consists of proper care, which consists of a balanced diet supplemented with a full range of vitamins and minerals, as well as providing the pet with regular veterinary care and compliance with the vaccination schedule.
Breed health features
It is generally accepted that Scottish cats have strong immunity and rarely get sick. However, this rule applies only to straight-eared representatives of the Scottish Straight. Scottish Folds with fold ears are much more prone to illness.
Problems with folds are due to the origin of the species. Ears bent to the skull with tips pointing forward appeared as a result of a mutation of the straights. The altered gene simultaneously affects the development of bones, eyes, and the structural structure of the auditory shells. With repeated crossing of lop-eared animals, the likelihood of pathologies in the offspring increases. Therefore, mating is always done with straight-eared cats. Such crossing reduces the possibility of getting a genetic disease, but it is still impossible to completely eliminate the negative gene.
Hereditary anomalies entail a general instability of the cat's body to various kinds of ailments and contribute to the development of side diseases. Cats cannot treat themselves, so it is necessary to monitor your pet.
Hereditary anomalies lead to general weakening and contribute to the development of side diseases
Experts have identified the following fold risk areas:
- bones;
- blood;
- eyes;
- leather;
- ears;
- internal organs;
- teeth.
The cause of frequent illnesses among Scots
Scottish Straights have good health and good immunity, but Folds obtained as a result of a gene mutation are much more prone to disease. Most often, they have deviations in the development of the musculoskeletal and vestibular systems.
The mutation gene that leads to the appearance of lop ears in cats is dominant. It always appears in offspring obtained from the mating of two individuals of this breed.
At the same time, the influence of the mutation gene often leads to the following disorders:
- pathologies of skeletal bones, cartilage and ligaments;
- abnormal structure of the ear canals;
- improper formation of the eyelids.
To prevent genetic diseases that cannot be treated, breeding of fold-eared cats is carried out only with straight-eared individuals.
Such crossing cannot completely remove the influence of a negative gene, but it helps reduce the likelihood of the offspring developing genetic diseases, and following the recommendations for the care and education of Scots will make their lives longer and more fulfilling.
Genetic diseases of Scottish cats
There are 2 pathologies identified in this category:
- osteochondrodystrophy;
- hemophilia type B.
Osteochondrodystrophy is expressed in a deformed skeleton and arthritis that appears against this background. Mainly, these include curved front and rear limbs, an overly thick tail, and poorly developed cartilage tissue. It is impossible to cure the disease. Throughout the life of the cat, maintenance therapy is provided, but over time, paralysis occurs.
Osteochondrodystrophy on x-ray
An equally terrible result of gene mutation was B-type hemophilia . In individuals, blood clotting is impaired, bleeding increases when the integrity of the body's integument is violated. Often the problem remains a mystery until surgery or lacerations. A protective crust does not form on the damaged area. Lack of fibrin prevents bleeding from being blocked. It is not possible to save the animal in every case.
On a note! The best prevention of terrible genetic abnormalities is compliance with breeding rules.
Osteochondrodystrophy in a cat
Treatment Options
The owner can help the pet on his own only if he discovers an overgrown nail, a splinter, or a small wound on a limb. If lameness is caused by a wound, the wound surface should be thoroughly cleaned of contamination and treated with a disinfectant solution. Even with minor damage to the skin, the animal should be shown to a veterinarian.
If a dislocation is suspected as the cause of the lameness, under no circumstances should you adjust it yourself. If a cat has a swollen paw or is limping, the pet should be taken to a veterinarian immediately.
This should be done quickly, as swollen tissues make it difficult to diagnose and reduce the dislocation. In a clinical setting, if necessary, the animal will be given anesthesia to relieve pain and relieve muscle spasm, and the dislocated joint will be set back into place. After this manipulation, the cat will be given a fixing bandage or splint. In some cases, for dislocations, surgical treatment is resorted to.
For fractures, veterinary specialists use immobilizing bandages and apply plaster. In the case of an open fracture, bone fragments are removed from the wound and, if necessary, surgical excision of the damaged tissue is performed.
Treatment of hip dysplasia and arthrosis of certain joints at first is conservative in nature and includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, and chondroprotectors. Massage and physiotherapy provide good results. For exacerbations, painkillers are used.
For lameness caused by antiviral and antibacterial therapy. In case of osteodystrophy, the sick pet is prescribed mineral supplements of calcium and phosphorus, vitamin D. Correction of the animal’s diet and dosed ultraviolet irradiation have a good effect.
Arthritis requires complex treatment, which is based on anti-inflammatory, antibacterial agents and painkillers. An important role in the treatment of inflammatory phenomena in the joint is played by adherence to a special therapeutic diet.
If you notice lameness in your pet, you should not hesitate to visit a veterinarian, and also self-medicate. The phenomenon associated with gait disturbance can be caused by serious reasons (dislocations, fractures, joint dysplasia) that require professional help.
X-rays help make a correct diagnosis of a sick animal. In severe cases, veterinary specialists resort not only to conservative treatment, but also to surgery on the joint.
To learn how osteosynthesis is used to treat a tibia fracture in a cat, watch this video:
Sudden lameness in a pet can be caused by various reasons, from simple damage to the pads to joint pathologies. It is impossible to determine exactly why a cat is limping on its front leg without taking an x-ray of the affected limb.
The obvious cause of lameness is injury to a pet's paw. A cat can protect a limb for the following reasons:
- Splinter in the paw pad.
- Injury.
- Sprain.
- Damage to claws.
It is important to try to recall in memory all the events preceding the onset of lameness. If the cat fought with other animals or fell from a great height, the paw hurts due to a bruise or sprain.
A splinter caught in the foot pad can cause severe discomfort. In this case, the cat cannot remove a small foreign body on its own. Since acute pain is felt when putting pressure on the damaged paw, the animal begins to protect it, which is why lameness appears.
The cat does not step on its front paw due to damaged claws. This can also happen if you fall from a great height or get hit. In addition, if someone accidentally steps on a cat's paw, the claw may be broken, which causes the animal a lot of discomfort.
Eye diseases
They are divided into two groups.
Table 1. Types of eye diseases
| Congenital | Purchased |
| Eversion (inversion) of eyelids, photosensitivity | Infections, cataracts, glaucoma |
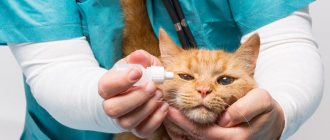
Congenital are associated with the structure of the skull. The skin covers the muzzle in such a way that one or both eyelids may turn out. The ciliary edge begins to touch the eyeball, constantly irritating it and causing pain. Without treatment, the pupil can be damaged to the point of blindness. A poorly covered eye reacts sharply to too aggressive light. It is contraindicated for Scottish Folds to be in rooms with fluorescent devices. Wide-open eyes need more gentle, soft lamps.
The problem of the structure of the eyelid can only be corrected surgically. If the pet experiences only mild discomfort, prevention is sometimes suggested with regular rinses, drops, or eye ointments.
Acquired eye pathologies are also associated with the structure of the eyelid, but arise due to an infection. The mucous membrane of the Scottish Fold has little protection, so any dirt can lead to infection with conjunctivitis, keratitis, and blepharitis . Especially often, trouble occurs in childhood, when the immune system is not yet formed.
The mucous membrane of the Scottish Fold cat has little protection, so any dirt can lead to infection
Glaucoma and cataracts appear gradually. They can go unnoticed for a very long time. With glaucoma, the pressure inside the eye increases and the eye begins to swell and enlarge. Cats with cataracts suffer from clouding of the lens. Both cases can result in complete blindness. Veterinarians recommend checking your pet's vision at least once every six months. This is the only way to identify structural changes in time.
Third eyelid disease in cats
Read more about eye diseases in cats in a special article on our portal.
Prevention of lameness
Some cats, due to their natural predisposition, may suffer from lameness. Proper maintenance of the cat can avoid its occurrence or at least reduce the intensity of its manifestations: protect it from injury, adjust the diet, adding more foods with calcium and vitamins.
If you want to know whether a kitten will limp in the future, study its pedigree. Perhaps this is due to heredity and does not pose a danger to the health and life of the animal.
Cats that have crossed the border of old age, as a rule, move little and therefore begin to limp due to atrophy of the limbs. Play with them more often, provoking them to take active actions.
To prevent splinters from getting into your paws, do not be lazy to clean the room as thoroughly as possible, making sure that there are no objects lying on the floor that are potentially dangerous to the animal.
Lameness in cats is not that uncommon. If nothing else bothers your pet except it, then it is quite possible that in a couple of days the situation will return to normal. If you see that the cat has become restless and has been limping for a long time, then professional help is required.
Lameness - A cat is considered lame if it is unable to walk normally or cannot support itself on one or more paws.
Lameness in cats. Causes.
Lameness is most likely not an independent disease, but symptoms of other hidden diseases, most of which cause pain to the cat.
Often, lameness is caused by foreign bodies (grass seeds, plant thorns) that dig into the paw pads, and these can also be cuts or wounds received in a fight with other cats. Another cause of lameness may be a disease of the claws or nerves that affect the sensitivity of the paws.
Lameness in cats. General symptoms.
Common symptoms depend on your cat's health as well as the severity of each individual case, but they include:
The cat does not step on the sore paw and tries to transfer its weight to the healthy one.
The gait is uneven and slow.
External changes in the sore paw (swelling, redness).
The cat won't let you touch his sore paw.
The cat constantly licks his sore paw.
Your actions.
If your cat suddenly starts limping suddenly, contact your veterinary center immediately. If your cat is limping slightly, try to determine which paw she is not stepping on. If the lameness is sudden, in most cases only one limb will be affected. If you cannot immediately determine which limb is damaged, and the cat does not allow you to touch itself, then just watch the cat for a while.
Once you determine which limb is damaged, try to examine it, starting with the claws. If the reason is not visible, then lightly press in different places and watch the cat’s reaction.
Lameness in cats. If the reason:
Foreign body. In this case, simply remove it with tweezers and treat the wound.
A cut or other wound. Check the cat's body for other bites or puncture wounds. If you find them, treat the wounds.
Painful or swollen joint. Apply a cold compress or a container of ice to it.
If you find no visible cause for lameness.
Leave the cat to rest for 24 hours and then observe her. If lameness does not go away, contact a veterinarian.
Removing a foreign body from a cat's paws.
Have someone hold the cat. Using tweezers, remove the foreign body, then soak the affected paw in warm salt water for a few minutes, then rinse it with a veterinary disinfectant solution, and then dry it thoroughly.
Health to you and your pets.
Cats are particularly mobile. This may also result in some injuries. If a cat is limping on its front leg, the owner should definitely find out the cause of the problem and provide quality treatment to the animal. Without this, there is a high risk that the damage will not go away on its own, and the pet’s condition will continue to worsen. The owner can determine on his own the reason why the front leg is limping only if there are external signs of a violation of the integrity of the limb. In other cases, only a veterinarian can make the correct diagnosis.
Ear diseases
Congenital ear problems are rare. Usually they are expressed in an underdeveloped internal part or its irregular shape. In this case, the shell is simply not adapted to perceive sounds, and it cannot be corrected. In addition, lop ears contribute to the accumulation of dirt in the sink. Against this background, an infection may develop. Otitis media and tumors reduce the cat's hearing. In the advanced version, complete deafness occurs. Treatment is carried out using injections, local drops, and ointments.
How to care for a sick cat?
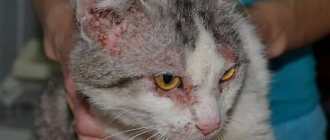
Skin diseases
Skin lesions in Scottish Folds are almost always found in conjunction with immune disorders, nervous disorders and diseases of the internal organs. The list includes:
- Demodecosis. Skin mites settle on animals in conditions of unsanitary conditions and nutritional deficiency. Small kittens weakened by diseases and anthelmintic drugs are especially susceptible. Spots, sores, and irritations appear on the body.
- Scabies. Occurs due to nervousness due to infection with parasites or as a result of an allergy to shampoo, food or other external irritant. Along with external influences with creams and lotions, it is necessary to treat the original cause, eliminate ticks, fleas, and the source of the allergy.
- Eczema. External manifestation of malfunction of internal organs - digestive disorders, infection with worms, oncology, endocrine problems.
Manifestation of skin diseases in cats
Attention! Skin diseases are similar to each other, and you cannot do without a medical diagnosis.
Osteochondrodystrophy
As I mentioned earlier, most often Scottish Folds have problems with the skeleton and musculoskeletal system. One of the most common diseases is osteochondrodystrophy. OCD is inherited among cats whose parents both had drooping ears.
The main cause of OCD is a violation of endochondral ossification, in other words, improper replacement of cartilage and bone formation. OCD sometimes appears in the last stages of osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of OCD:
- Shortened, thickened tail;
- Dwarfism;
- Undeveloped or shortened limbs;
- Lameness;
- Incorrect gait;
- Passivity.
Diagnosis can be made using radiography. Therapy is not aimed at complete recovery of the cat, but rather at suppressing symptoms. Because it is almost impossible to completely cure a pet’s OCD. Various types of chondroprotectors and non-steroidal drugs are used for treatment. Radiation therapy is successfully used, and corrective surgeries are performed.
But I strongly recommend that you consult your veterinarian before undertaking any treatment!
Pathologies of internal organs
The list of possible diseases of internal organs is very extensive. Most often, owners of Scottish Folds come to the veterinarian with the following problem areas:
- heart: failure, arrhythmia, often associated with hemophilia;
- digestion: inflammation of the stomach, intestinal obstruction, liver disease, accompanied by infectious and parasitic infections, allergies, poisoning with poor-quality food;
- immunity: colds, viral diseases;
- genitourinary system: urolithiasis (urolithiasis), cystitis. Read about kidney diseases
Attention! None of the points can be diagnosed and treated without the participation of a doctor. Many face death without timely help.
Video - Diseases of joints and bones in cats
Lameness due to injury
By injuries we do not necessarily mean sprains, fractures or dislocations. It could be a simple wound on the pad of the paw. The pain associated with such a wound may be unpleasant for the cat - and it will begin to spare the paw.
However, if there are no visible injuries, check the cat's reaction by feeling its entire paw - carefully and gently, but with pressure. Perhaps it is a matter of deep trauma. If your cat reacts painfully to touch in a particular place, you should go to the veterinarian. He will take an x-ray to find out the real reason. Moreover, sometimes wounds are observed not because of splinters, insect bites and injuries, but because of the disease described below. This disease is dangerous, and therefore an accurate diagnosis must be made as early as possible.
Symptoms
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the general condition and mood of the cat. An unhealthy Scottish Fold will be characterized by lethargy, apathy, lack of appetite, sometimes irritable reactions and unreasonable aggression. The nose becomes dry and very hot to the touch. Perspiration may appear on the fur. When measuring temperature, the readings will exceed 38.5 °C.
On a note! A dry nose in hot weather and after sleep is a variant of the physiological norm. Under such conditions, the signs most likely will not indicate illness.
An unhealthy Scottish Fold will be lethargic, apathetic, and lack of appetite.
In specific diseases, the cat owner can focus on the symptoms.
Table 2. Symptoms of diseases of internal organs
| Type of disease | First symptoms |
| Viruses | Sneezing, discharge from mouth and nose, fever |
| Ear | The cat shakes its head, discharge from the ears (pus, fluid), putrid smell from the shells, redness of the skin in the shells, the cat scratches its ears |
| Ophthalmic | Redness, lacrimation, purulent discharge, swelling of the eyelids of varying degrees, the cat tries to scratch the eyes, poor orientation in space, cloudy pupils |
| Digestive | Refusal to eat, vomiting, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, undigested pieces in feces, increased thirst |
| Skin | Scabies, redness, bald patches, rashes, sores, blisters, peeling, nodules |
| Heartfelt | Shortness of breath, cough, swelling, increased frequency of sighs, low temperature, fainting |
| Genitourinary system | Sudden weight loss, pink urine, apathy, frequent urination, the cat meows when urinating, fussing |
| Bone | Disproportionately large head, crooked, protruding jaw, shortened limbs, curvature of the spine, twisted front legs, joints with a swollen effect, too massive joints, growths on them, slow or absent growth of the cat, shortened thick tail, inactivity, clumsiness of movements, attempts not to bend the paws when moving |
| Dental | Foam, pus, excessive drool from the mouth, bad odor from the mouth, yellow, brown, gray growths on the teeth, brittle teeth, refusal to eat (it hurts to eat) |
In the early stages, 2-3 mild symptoms may be observed. As the pathology develops, the number of manifestations increases. It is necessary to monitor your fold ear and consult a doctor at the first suspicion of abnormalities.
Refusal to eat may indicate health problems in your cat.
Vaccination of Scottish Fold cats
Vaccination is one of the first preventive measures for animals. The risk of developing the disease with timely vaccinations decreases significantly. The doctor chooses a set of medications based on the living conditions.
The first vaccine (usually complex or rabies) is given after 1.5 months, but no later than 2.5 months. You will need to come back for a second vaccination in six months. Upon reaching 12 months, vaccination is carried out annually at regular intervals. Before a year, medications for rhinotracheitis, microsporia, panleukopenia, calicivirus and calicivirosis must be supplied.
The offspring of a vaccinated cat, subject to mating rules, provides an increased level of immunity. Depending on the date of the mother's last vaccination, the baby's first vaccination may be delayed by 12 weeks. If there is no information about the cat, it is better not to delay the procedure beyond 8 weeks.
Offspring from a vaccinated cat, subject to mating rules, provides an increased level of immunity
Important! When feeding, the cat gives the babies a lot of energy and internal resources, forming their immunity. The mother cannot be vaccinated annually until her body is restored. Kittens are excluded from the procedure during the period of age-related changes in the dentition.
The procedure requires preparation:
- general inspection. The pet must have normal body temperature, no signs of any diseases, and be active;
- studying the vaccination card. The doctor should know what medications have already been given. Some of them are needed only once in a lifetime;
- deworming. The vaccine can provoke massive death of parasites in the body, which will lead to severe poisoning;
- eliminating other medications a week before vaccination to avoid unwanted reactions. If the animal takes medications regularly, it is necessary to notify the doctor in advance.
Veterinarians constantly remind that even a domestic cat without outdoor walking needs disease prevention. The virus can come randomly from food, a person’s clothing, a toy, or water.
Vaccination scheme
Advice. After the first vaccination, you should ask your doctor for a vaccination schedule for your Scottish cat. The dates and types of recommended medications are indicated there.
No vaccine provides 100% protection against the disease, but it significantly reduces the risk of severe forms.
Reasons why a cat is limping on its front leg
The cat is limping on its hind leg with no visible damage.
In addition to injuries, some diseases also cause lameness.
Joint diseases
Joints may hurt due to calicivirus infection. The course of this disease was observed in detail in adult cats and kittens. And it has been proven that this cat cold often causes a virus to appear in the tissues of the joints, as a result of which the pet can begin to limp.
Infections
Mycoplasmosis and chlamydia in rare cases can cause lameness. In this case, the infection affects all the limbs of the animal, so it will limp on all limbs. Painful sensations appear due to infectious inflammation.
Chlamydia is often the cause of lameness
Bone tumor
Cancer, although rare, is a very dangerous disease. It is characterized by the appearance of multiple metastases throughout the animal’s body, which can result in lameness.
Arthritis and arthrosis
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints that is common in older cats. This is an inflammatory disease that occurs as a result of pathological changes in the joints. With it, an animal at rest does not feel pain, but when walking and, especially running, the joints begin to ache. Arthritis can be identified by lack of appetite, weakness and elevated body temperature.
The main factors for its appearance:
- heredity;
- a sedentary lifestyle typical of neutered cats;
- improper diet;
- infections.
Additional Information! Poor environmental conditions may be among the causes of arthrosis. It has a negative impact not only on people, but also on animals.
Lameness after injection
Sometimes the injection may cause pain. This happens if the needle has hit a nerve, or if the medication you are taking has side effects. Usually the pain in the paw goes away after a few days.
Age-related changes
The musculoskeletal system of cats, like that of people, works worse with age. As a result, the bones become brittle and the joints wear out. This is an extremely rare occurrence, but if lameness appears in an older cat, it is worth considering this cause.
Paw problems in older cats
Back or brain injury
Sometimes pain in a limb does not always mean that the problem lies there. As a result of injury to the lumbar back or brain, the animal may begin to limp. It is likely that a nerve may be pinched, causing the animal to experience discomfort when moving.
Lack of microelements
Lameness in the limbs can occur due to a lack of useful elements, especially calcium. It is unlikely that the animal will eat so poorly, however, this reason is typical for pregnant or lactating cats, because all the nutrients they receive go to feed the offspring.
Elbow dysplasia
The disease is typical for purebred cats. It appears at a young age and progresses over the years, resulting in the cat limping on one or both front legs.
Osteomyelitis
A disease characteristic of Persian cats. With it, partial destruction of bone tissue occurs. This disease is common in young animals and can affect any limb.
Questions and answers about cats
Below are the most popular questions about Scottish Fold cats and their answers.
Table 3. Answers to questions about keeping and caring for the Scottish Fold cat
| Question | Answer |
| How long do Scottish Fold cats live? | With proper care, breed diet, and timely vaccinations, a male cat can live from 15 to 18 years. Life expectancy is influenced by genetics, early treatment of emerging problems, an active lifestyle, and regular hygiene. There are cases where Scottish Folds lived for more than 20 years. |
| How to care for a sick cat? | Self-indulgence in treatment can have the opposite effect. All procedures must be coordinated with a veterinarian after diagnosis. At home, it is necessary to give your pet peace, provide easy access to clean water, fresh food, and a toilet. This is especially true in cases with bone diseases, when it is difficult for a cat to move. During illness, you need to follow a diet to avoid obesity. Regular hygiene procedures will be required to remove secretions, clean bedding and bowls from germs |
| What is disease prevention? | Proper care, regular vaccinations, supplementation with vitamin complexes. Vitamin A and D courses for kittens up to one year old. There are special preparations for the British Fold breed. |
| How to remove fleas from a Scottish cat? | Any special product for cats with allergies from a veterinary pharmacy. Shampoos and drops are preferred |
Causes of lacrimation
Scottish cats of all types, both straight-eared - Scottish Straight, Highland Straight, and fold-eared - Scottish Fold, Highland Fold, have anatomical features in the structure of the skull. As a result, their nasolacrimal duct is incorrectly arranged with distorted tear ducts. This leads to the fact that the secreted tear does not go inward, but flows out. For the Scottish breed, slight lacrimation, which is called epiphora, is a common phenomenon and is considered a physiological norm. They may appear after sleep.
When a Scottish kitten has watery eyes, the color of the discharge can be caused by various reasons:
- if they are excessive, watery, transparent, then this is caused by an allergy or the ingress of irritating microelements, such as dust, into the shell;
- greenish-yellow indicate the appearance of an infection, bacterial contamination;
- in the presence of worms, red-brown thick discharge appears in the corners of the eyes.
Why are the tears brown?
Why a Scottish Fold or Straight-eared kitten's eyes water with brown tear discharge is explained by various reasons:
- eye injuries with blood in the tears;
- the baby has picked up a bacterial infection with harmful microorganisms that causes suppuration;
- the kitten has worms, a common occurrence for babies;
- low immunity in newborns, manifested by discharge of tears until vaccinations are given;
- allergies, which can be caused by the introduction of new foods into the diet.
If your pet constantly suffers from lacrimation with brown discharge, his eyes are inflamed, he scratches them with his paw, then consult a veterinarian.