Antibiotics are actively used in modern veterinary medicine; they have saved the lives and kept many cats healthy. This means that pet owners definitely need to have an idea about the most popular antimicrobial drugs, as well as contraindications and side effects from their use.
In order for the treatment of a cat to be effective, you need to carefully consider the choice of medications and correctly calculate the dosage.
Types of antibiotics
There are several different classifications of medications.
What are antibiotics and what are they?
By type of action
According to the mechanism of action, they are distinguished:
- bactericidal - destroying;
- bacteriostatic - locking.
Bactericidal drugs include drugs that destroy bacteria during exposure. These are quite strong agents, the use of which must be treated with caution. Example: With a staph infection, the killed bacteria can clog the urethra. However, in case of severe illnesses, bactericidal medications can save the life of a pet - their use is important in cases of sepsis, pyometra or other serious infection. This group also works well for local inflammation—the treatment of purulent wounds.
Antibiotics are prescribed to cats for the treatment of extensive wounds.
Bacteriostatic drugs act more gently, preventing the proliferation of bacteria, which eventually die on their own and are eliminated from the body.
According to the spectrum of action
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics are drugs that affect a specific type of pathogen. Broad-spectrum products destroy several types of bacteria at the same time.
By chemical composition
Like human drugs, all veterinary drugs are classified according to their chemical structure:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- tetracyclines;
- macrolides;
- chloramphenicol;
- aminoglycosides, etc.
More than 25 types of antibiotics are used in veterinary medicine.
By location of impact
Antibiotics are divided into local and general drugs. For each affected area, its own group of drugs has been developed:
- Ointments and sprays are used to treat skin lesions.
- Eye drops and ointments are the best remedy for treating bacterial conjunctivitis.
- For systemic infections, medications are prescribed in tablets or intramuscularly/intravenously.
- Aerosols have been developed for respiratory therapy.
- For the treatment of vaginitis, you can purchase suppositories.
Drops containing antibiotics are suitable for the treatment of ophthalmic diseases
Classification of antibiotics. Release forms
You shouldn’t try to remember all the possible commercial names of drugs that cats can use. It is always enough to ask which antibiotic or active substance is included in the antimicrobial drug.
According to their action, antibiotics are divided into:
- bacteriostatics (inhibit the ability of bacteria to reproduce and develop);
- bactericidal (kill pathogens).
According to the active substance:
- penicillins:
- cephalosporins:
- aminoglycosides:
- fluoroquinolones:
- nitrofurans:
- chloramphenicol:
- lincosamides:
- tetracyclines:
- macrolides:
- sulfonamides:
- glycopeptides:
- polymyxins:
- carbapenems:
According to the spectrum of action:
- wide spectrum;
- highly specific.
By method of administration to the body (how to give an antibiotic to a cat):
- oral (in the mouth);
- injection (in the form of injections);
- local (powders, ointments, gels, etc.).
By origin:
- natural (true) - chemical substances produced by some microorganisms to combat others;
- synthetic – artificially created antimicrobial agents.
The principle of action does not depend on the form of release of the medicine, the only question is the convenience of administration - for some it is convenient to inject, for others it is convenient to give the cat an antibiotic in tablets.
Why contact a veterinarian to prescribe antibiotic therapy?
It is very difficult to choose the right antibiotic and calculate the correct required dose yourself without consulting a veterinarian. Bacteria can adapt to conditions that are worse for them and get used to drugs. If the type of drug is chosen incorrectly, the bacteria may take on a different form that is resistant to this drug. In this case, it will be more difficult to defeat the disease.
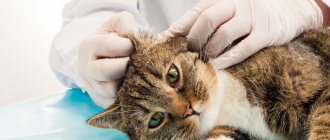
In some cases, a sensitivity test is necessary to determine the effectiveness of a medication against a specific type of bacteria. Therefore, if the disease has become severe and cannot be treated without antibiotics, a visit to the veterinarian is most advisable.
Cats are tested to determine their sensitivity to specific antibiotics.
Rules of use for cats and dogs
- The first dose is always a shock dose, that is, twice the usual dose. Subsequently, the usual dose is prescribed
- Dermatological diseases take a long time to treat, antibiotic therapy lasts up to several months, and with increased doses
- For diseases of external organs - wounds, otitis media, inflammatory eye diseases - local antibiotics are prescribed
- You should not take antibiotics if microflora cultures have been performed and the results are negative.
- Antibacterial agents must be continued for three days after the symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
- Taking antibiotics continues throughout the course, without interruption. If you stop the course of the prescribed drug, then all the existing microflora in the cat’s body will become resistant to the drug and it will not work in the future.
Proper use of antibacterial agents contributes to the speedy recovery of the cat’s body.
The use of antibiotics is not dangerous if used correctly.
Therefore, you should not be afraid if veterinarians prescribe drugs from this group to your furry pet, because with their help the disease will recede much faster.
What diseases are antibiotics used to treat?
There are a huge number of diseases in animals, the successful treatment of which requires antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics are required for the treatment of the following diseases:
- cystitis, urethritis;
- ICD;
- pyelonephritis;
- bacterial gastritis;
- infectious diseases of the respiratory tract;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- pyometra;
- giardiasis;
- infectious diseases of the eyes, ears;
- bacterial and purulent skin lesions;
- feline herpes.
Antibiotic therapy is mandatory after surgery (including sterilization), administered during catheterization of the bladder and during other interventions to exclude the occurrence of inflammatory processes. Antibiotics are prescribed after the necessary tests and studies have been carried out and a diagnosis has been made.
The dosage is selected taking into account the weight and age of the pet
Indications for antibiotic therapy
For cats, a group of antimicrobial drugs is used in the treatment of:
- pneumonia;
- pyelonephritis;
- inflammation of the urinary system (cystitis, urethritis);
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- inflammatory eye diseases;
- leptospirosis;
- pseudomonosis;
- intestinal infections;
- deep or purulent wounds, abscesses after injuries;
- skin diseases;
- oncological diseases (as aids to prevent infection of tumor-affected tissues).
Antibiotics for cats are also used for prophylactic purposes: they are prescribed after operations to prevent purulent complications and shorten the rehabilitation period (for example, after sterilization of a cat).
Pros and cons of antibiotics
Antibiotic therapy has its pros and cons. All these medications not only promote faster healing, but also cause harm to the caudate. You can minimize the negative consequences by selecting the most effective medication for a specific disease and correctly calculating the dose. In this case, all the advantages of this treatment method will appear:
- several doses of antibiotics will be enough to achieve the effect;
- the pet’s condition will quickly improve;
- the number of side effects is minimized;
- the antimicrobial effect will be effective even with a large number of microorganisms.
A properly selected antibiotic quickly restores the animal
However, when using antibiotic therapy, the disadvantages of this process must also be taken into account. The main negative effect of long-term treatment with this group of drugs is a decrease in the quadruped’s immunity. In addition, the following disadvantages of antibiotic therapy can be listed:
- possible addiction to the medication with a long course;
- an error in dose calculation can lead to extremely serious consequences;
- possible side effects in the form of allergic reactions and gastrointestinal disturbances;
- After treatment, it is necessary to restore the disturbed intestinal microflora.
Where to give a cat an injection for cats
global $ads_google;
//data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?> $ads_google = true; ?> } ?> Well, you don’t want a kitten at all, and it’s not easy to survive the period of the cat’s sexual heat? In this case, the issue is resolved by sterilizing the animal. But for some reason, some owners believe that there is nothing easier than suppressing the reproductive instinct, forgetting that the consequences of such a decision can be very dire.
If you definitely want to experiment with your cat and give her a cat injection, then you will still have to visit the veterinarian - this should be the moment before the start of estrus, and not during it. The doctor will administer the medicine himself, and then, after 3 months, the next injection will be given according to the schedule. The third ampoule is administered after 4 months, and all subsequent ones every 5 months.
Why shouldn't you give injections yourself ? This is a big risk even without an inexperienced person, so the entire process must be supervised by a doctor.
Commonly used antibiotics for cats
What medications are most often used?
- Amikacin is an effective drug prescribed for the treatment of infectious diseases caused by Salmonella, Klebsiella, and Escherichia coli. The medicine is injected into the muscle every 8 hours at 5-10 mg per kilogram of body weight. The drug is not prescribed if the cat has urolithiasis or suffers from kidney disease.
- Gentamicin 4% is a long-known aminoglycoside that is effective against gram-negative microbes. Intramuscular administration of gentamicin will help quickly cure pneumonia, peritonitis, arthrosis, and cope with colds. Injections are given 2 times a day at a rate of no more than 4.4 mg per kilogram of the pet’s weight. The course should not be longer than 5 days. Gentamicin is not prescribed to elderly and weakened cats suffering from nephrotic diseases. The antibiotic may cause hearing complications.
- Neomycin is an antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action, effective against almost all infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and skin staphylococcal infections. Neomycin is available in different forms: as an ointment, as an injection for injection into a muscle, or as a powder (which must be dissolved in water) for drinking. Neomycin is administered 3 times a day for 3-7 days at a dose of 10 mg per kilogram of body weight.
- Amoxiclav is a mixture of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. The highly effective product is available in the form of an injection solution and in tablets, which are given to pets in a quarter for every 5 kg of body weight, 2 times a day for a course of 10 days.
- Enrofloxacin (Baytril) is a fluoroquinolone and acts on any bacteria. The dosage of the injection solution is 0.5 ml per 5 kilograms of body weight. Treatment lasts from 5 to 10 days. The effect is observed within 30 minutes after the injection into the muscle.
- Ciprofloxacin is also a fluoroquinolone. It can be bought in the form of a solution for injections and tablets. The medication is effective against staphylococci, streptococci, enterobacteria, intestinal, pseudomonas, hemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma and chlamydia.
- Tetracycline can also cope with the treatment of many diseases, including diseases of the genitourinary system, pneumonia, etc. It is prescribed for herpes and conjunctivitis.
All these drugs must be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy.
Regular pet stores do not sell medicinal veterinary drugs.
What antibacterial agents are most often prescribed to cats?
Without contacting a specialist, it is extremely difficult to select the necessary antibiotic and calculate the dosage. Sometimes cats are given a sensitivity test to determine the resistance of a particular type of bacteria to the drug. Most often, veterinarians prescribe one of the following antimicrobial agents to treat cats.
Amoxicillin
Medicines containing amoxicillin belong to the penicillin group and are used to fight infections of the urinary tract, bones, skin, upper respiratory tract and lungs. These antibiotics can also be given to cats after surgery to prevent inflammation.
Commercial names of drugs containing amoxicillin:
- Amoxivet;
- Amoxil (tablets);
- Clamoxil LA;
- Betamox LA (suspension) and others.
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
Drugs containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are very effective. They are used to treat various infections of the skin, respiratory tract, joints, gastrointestinal tract, mucous membranes, and genitourinary organs in cats, as well as to prevent complications after surgery.
Commercial names of drugs containing amoxicillin:
- Xiclav;
- Sinulox;
- Amoxiclav.
Xiclav is available only in tablet form, while Sinulox and Amoxiclav are available both in tablets and as a solution for injections. In severe cases of the disease or, for example, in cases of urolithiasis, antibiotics for cats are prescribed only in the form of a suspension.
Azithromycin
Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that belongs to the group of macrolides. Azithromycin is used to treat infections of the genitourinary system, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract and skin. The drug is safe for animals, so it is prescribed to pregnant and lactating cats.
Commercial names of drugs containing azithromycin:
- Avimecin;
- Azikan;
- Azitronit (available in the form of injection solutions);
- Sumamed (available in tablets).
Gentamicin
Gentamicin is an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group. It is used to treat bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, bones and joints, genitourinary system, ears, eyes. Gentamicin is also prescribed for peritonitis.
This antibiotic is a toxic drug and is therefore prescribed only in the most severe cases. Improper use of the medicine may cause hearing damage. Gentamicin is not prescribed to weakened and elderly cats, as well as animals with kidney disease.
Commercial names of drugs containing gentamicin (produced in the form of solutions for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration):
- Gentaprim;
- Ghentam;
- Gentavet.
Enrofloxacin
Enrofloxacin belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones. Most often, it is used to treat infectious diseases of the skin and genitourinary system in cats. An overdose of this drug can lead to destruction of the retina.
It is important! Enrofloxacin is not prescribed to kittens.
Enrofloxacin has a bitter taste, which causes excessive salivation. For this reason, it is administered to cats only in the form of injections.
Commercial names of drugs containing enrofloxacin:
- Enroxil;
- Baytril;
- Enromag.
Tylosin
Tylosin is considered a low-toxic antibiotic that destroys most dangerous bacteria: streptococci, chlamydia, staphylococci, mycoplasma and others. It is prescribed for infections of the lungs, respiratory tract, joints, and intestines.
Tylosin is available only in the form of injection solutions (50 or 200 mg per 1 ml). For cats, veterinarians recommend purchasing Tylosin 50.
It is important! This drug is used only in veterinary medicine.
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is an antibiotic of a number of cephalosporins, it is used to treat both animals and humans. Ceftriaxone has a detrimental effect on streptococci, pneumococci, staphylococci, E. coli and other microorganisms.
Used for infectious lesions of nerve and bone tissues, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, and respiratory organs. This antibiotic is often prescribed to cats after bites from other animals and to prevent complications after operations.
It is important! The drug should not be used for kittens, pregnant or lactating cats.
Ceftriaxone is produced in powder form, which must be diluted in an injection solution before use. The drug must be combined with anesthetics, since the administration of ceftriaxone is very painful.
Commercial names of drugs containing ceftriaxone:
- Rocephin;
- Loraxone (“human” antibiotics);
- Ceftrivet (antimicrobial drug for animals).
Convenia
Convenia is an antimicrobial “cat” drug, the active ingredient is cefovecin (a group of cephalosporins). It is prescribed to get rid of acute gum and periodontal infections, treat diseases of the urinary tract, soft tissues, and skin.
The antibiotic Convenia is intended for subcutaneous administration. The packaging of this medicine includes 2 bottles: powder with the active substance and a special solvent.
Tetracycline
Antibiotics that include tetracycline are available in the form of tablets, drops and ointments. Tetracycline tablets are used to treat pneumonia, borreliosis, genitourinary tract infections, otitis media, and food poisoning. It also helps greatly in the initial stages of peritonitis.
It is important! Tetracycline is contraindicated in cats during lactation, as it quickly passes into milk and can harm the health of kittens.
Tetracycline drops and ointments are used to treat infections of the eyes, skin, burns and purulent wounds.
Analogues of the drug Tetracycline in tablets containing the same active ingredient are Oxytetracycline and Chlortetracycline.
Antifungal drugs
It is traditionally believed that fungal diseases cannot be treated with antibiotics. On the contrary, long-term use of antibiotics causes mycoses. However, there are a number of antibiotics that are prescribed to treat fungal diseases in cats. These include:
- Nystatin, which in commonly used doses acts fungistatically (slowing down the growth of fungi), and in high concentrations - fungicidal (destroying fungi). Nystatin is especially effective against Candida fungi. Nystatin is used for candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract, mucous membranes, and genitourinary organs. Nystatin is used topically as an ointment.
- Levorin is also used to combat candidiasis in the form of a 5% ointment or aqueous suspension, as well as orally.
- "Griseofulvin" is prescribed for trichophytosis and is given along with food.
Antibiotics are effective against fungal infections in cats
Indications and contraindications
The drug "Azithromycin" is used to treat such diseases in cats:
- respiratory infections;
- pharyngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- laryngitis;
- pneumonia of different types;
- bronchitis;
- chlamydia;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- gastritis of various types;
- skin infections;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
© shutterstock
The drug fights pathologies that may be a consequence of the pathogenic effects of viruses, bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms. For example, it is recommended to treat a cat with “Azithromycin” for rhinotracheitis (inflammation of the respiratory tract, which is caused by the herpes virus). However, its use is undesirable if the cat is pregnant or breastfeeding. And also in the presence of such diseases :
- chronic liver pathologies;
- kidney disorders;
- the presence of an allergy to the active ingredients of the drug (macrolides or azalides).
In any case, the use of the medicine and the dosage of Azithromycin for the cat must be previously agreed upon with the veterinarian.
Which antibiotic to choose?
When choosing a medication, it is advisable to determine the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to a specific drug. You immediately have to take into account other factors: the animal’s susceptibility, the characteristics of its metabolism depending on age and the presence of certain pathologies - renal/liver failure or diabetes mellitus.
For an unspecified diagnosis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which include penicillins, cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones.
If the diagnosis is not in doubt, preference is given to narrow drugs. It is advisable to use one drug as monotherapy. Complex use of antimicrobial agents is prescribed if:
- mixed type infection;
- severe infection requires immediate treatment even before diagnosis to expand the spectrum of exposure;
- you need to enhance the effect of one antibiotic with another;
- as a result of a combination of drugs, their toxic effect is reduced by prescribing smaller doses of each medication;
- if monotherapy was ineffective.
Monotherapy with antibiotics is considered more gentle for cats
The duration of antibiotic therapy depends on the virulence of the pathogen, the duration of the disease, and the danger to the pet. In acute forms, the course is shorter. After the symptoms disappear, therapy continues for another 2-3 days. Stop the medicine immediately.
Rules of application
Only a veterinarian should select the medicine and dosage to treat a cat. If the dose is too small, the infection will take hold in the body, even if the pet’s condition has returned to normal.
Only a veterinarian should select the medicine and dosage for treating a cat.
Exceeding the required dose can cause intoxication and even death of the animal due to the toxic effects of antibacterial drugs.
It is important not to use the medicine after its expiration date.
The drug should be purchased only from licensed pharmacies that specialize in veterinary medicines.
If the doctor prescribed the drug by injection, he must administer the first one in the clinic.
This will allow you to evaluate the reaction of the cat’s body to a foreign substance, and in case of individual intolerance, take action and prescribe another antibiotic.
It is important not to use the medicine after its expiration date
The remaining injections can be given at home according to the schedule prescribed by the veterinarian.
The least sensitive place for a puncture in a cat is the withers. The skin on it should be squeezed, insert the needle there so that it is inside and not out, and quickly inject the solution. There is no need to treat the puncture area with alcohol.
If the cat is prescribed the drug in tablet form, it is placed deeper on the tongue or crushed with food. If you need to give the tablet to a kitten, it is recommended to first divide it into parts.
It is important not to stop treatment after symptoms disappear, but to complete the full course of antibiotic therapy.
Otherwise, the pathogenic microflora will not be completely eliminated, but will go into a dormant form and become resistant to this product.
Be sure to read:
Laxative for cats: types, instructions for use, medications and folk remedies
Antibiotics usually last 1-3 weeks.
The course of treatment for some dermatological infections can last 2-3 months and interrupting it is contraindicated.
What human antibiotics can be used for cats?
The use of human medicinal drugs for cats is not recommended because it is very difficult to calculate the dosage of the active substance. However, in some cases, when the veterinary pharmacy is far away, it is better to use human antibiotics than to abandon a sick animal to its fate. For treatment, you can take the medications listed below (dosage is calculated per kilogram of animal weight).
- The penicillin group is used to treat sepsis, pleurisy, purulent inflammation of the skin, purulent peritonitis, respiratory tract infections, endometritis in all locations. Before use, add 2-4 ml of sodium chloride into the bottle:
- benzylpenicillin novocaine salt is administered intramuscularly at 30,000-40,000 units per kilogram of weight;
- benzylpenicillin sodium and potassium salts (penvetin in veterinary medicine) are administered intramuscularly every 6 hours at 10,000-20,000 units per kilogram of weight;
- ampicillin sodium salt - intramuscularly every 6-8 hours at a dosage of 15-30 mg per kilogram of body weight;
- bicillin 5 (used for the treatment of chronic forms of the disease after exacerbations) - intramuscularly once every 2 weeks, 40,000-60,000 units per kilogram of weight;
- Antibiotics of the tetracycline group are necessary for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract. Medicines are given orally (by mouth) at the rate of 20-25 mg per kilogram of weight, 2 times a day;
- tetracycline eye ointments are placed under the eyelid for inflammation of the eye mucosa 2 times a day. Tetracycline eye drops are instilled 1-2 drops 3 times a day;
- The cephalosporin group is used mainly for sepsis, respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal diseases. Cephaloridine and cephalothin are administered intramuscularly 3 times a day, 5-10 mg per kilogram of body weight (due to pain, the medicine is diluted with novocaine).
Some human medications are suitable for cats
How to give an injection to a cat at the withers
global $ads_google;
//data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?> $ads_google = true; ?> } ?> If the medicine is quite painful and also of large volume, it is better to insert the needle with the medicine subcutaneously. To correctly give an injection at the withers, no special experience is required. If when administered intramuscularly there is a chance of getting into a joint, then there is nowhere else to get there other than in the right place. Why is it easier to administer medicine here? Because the animal finds itself in a “mother cat and kitten” situation, when the mother carried the stupid little one in her teeth precisely by the withers. Therefore, it is easier to immobilize the animal, but it is still better to ask an assistant about this - the skin in this place is very thick, and sometimes it is not easy to pierce it.
The procedure for preparing the syringe is the same as for injection into the animal’s thigh.
The direction of the needle should be strictly at an angle of 45°. The fold on the neck is pulled up, and the injection is made at the base of the withers. The cat's head is pressed with a free hand or an assistant. The lower back also needs to be pressed so that the cat does not twitch and cause pain to itself. During the insertion of the needle, the resistance of the skin layer will be clearly felt - but as soon as it stops, it means that the needle is inserted and you can release the syringe plunger. Do not rush when inserting the needle - you can accidentally pierce the skin through.
It doesn’t matter at what speed the medicine is injected, the volume should not exceed 90 ml per 1 kg of weight. If a larger amount is required, the syringe itself is changed and the needle is left in place.
Once the medication has been completely injected, the needle can be removed and the animal released.
Side effects
Both people and animals can develop negative reactions to any medication. The body may react to the first entry of the active substance into the body, or negative phenomena may develop during a long course of treatment. The most common ways a cat may respond to antibiotic therapy are:
- diarrhea;
- allergic reaction - itching of the skin, rashes, hives.
An allergy to antibiotics in cats can cause severe itching.
In particularly difficult cases, the animal may develop swelling, seizures, and liver damage. After a long course of antibiotics, a cat may develop a fungal disease.
How to reduce side effects?
After a long course of antibiotics, an animal, like a person, can develop dysbiosis. To avoid unpleasant phenomena, it is recommended to take probiotics during and after antibiotic therapy. They should be given 2 hours after the tablets or after the injection once a day, preferably in the evening. The course should continue for two weeks after the last dose of the medicine.
The most effective drugs are “Bifitrilak”, “Enterol”, “Zoonorm”, “Subtilis”, “Viyo”.
Nutritional drink for cats
For dermatological reactions, which usually indicate the development of an allergy, it is recommended that the cat be given an antihistamine and discontinue treatment with this drug. In cats, the development of allergies may be indicated by pharyngitis in the absence of inflammation of the tonsils.
The reaction may manifest itself as enlarged lymph nodes. In case of allergic reactions, taking Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil is indicated, and in especially severe cases, corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone). If after treatment the cat develops candidiasis (usually in the mouth), antifungal agents are prescribed.
What are the dangers of unauthorized prescription of antibiotics?
It is very difficult for a cat owner to calculate the correct dose of antibiotic on his own. If the drug group is selected incorrectly, the cat may become accustomed to this group. In case of overdose, when the medication is used for a long time at the maximum dose or with a single overestimation of the dose, as well as when the pet develops individual intolerance, a toxic reaction may develop.
Table. Complications that arise when doses of different groups of antibiotics are exceeded
| Antibiotic groups | Complications |
| Penicillins | Neuro-, nephrotoxic reaction |
| Cephalosporins | Neuro-, nephrotoxic reaction |
| Tetracyclines | Gastrointestinal complications: loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Macrolides | Gastrointestinal complications: loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Aminoglycosides | neurotoxic effect - decreased blood pressure, respiratory depression, hearing impairment |
| Sulfonamides | Lesions of the hematopoietic system |
An overdose of antibiotics causes severe reactions in the body
Indications for the use of anti-inflammatory drugs
A group of drugs that are different in chemical structure, but have similar properties, designed to eliminate pain and inflammation in the body are called anti-inflammatory drugs. There are two main groups of these medications - non-steroidal and steroidal.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs contain hormones that are highly effective in treating dangerous conditions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have less effect, while being as safe as possible for the animal body.
In order to understand the functions of anti-inflammatory drugs and their necessity, it is important to understand the very development of pain and the inflammatory process. At their core, inflammation and pain are specific reactions of the body aimed at survival. The development of the inflammatory process is created by the body in order to limit the lesion as quickly as possible, destroying the pathogenic microflora inside.
With normal functioning of the body's defenses (excellent state of the immune system), the inflammatory process develops and goes away on its own, ending with complete recovery. Violation of protective functions leads to the development of a protracted inflammatory process, characterized by the development of dangerous complications.
As for the appearance of pain, this is a kind of signal from the body, indicating serious malfunctions. Discomfort and painful sensations do not allow you to forget about yourself, indicating inflammation. For example, chronic inflammatory processes that develop in the joint area do not go away on their own, so prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs is indispensable.
The use of NSAIDs makes it possible to alleviate the suffering of a cat with a large number of pathological processes in the body, accompanied by pain and inflammation.
How to give antibiotic tablets to a cat?
If the veterinarian prescribed the pet to take medication in tablets, the cat owner will have to learn a new skill for him - how to give the tablet to the cat. Some tailed animals will happily eat the medicine, crushed and added to a small amount of their favorite treat (favorite wet food, for example, a piece of butter, etc.). You can roll the tablet into a bread crumb or a piece of cheese. However, there is always a danger that your pet will chew the lump and spit out the medicine.
Video - Giving the cat a pill
At a veterinary pharmacy you can buy a good inexpensive device called a tablet dispenser. The tablet is attached to the end of a syringe-like device and inserted deep into the pet's mouth at the back of the tongue so that he cannot spit it out. After this, you need to cover your pet’s mouth and nose so that he makes a swallowing movement. You can simply master the skill and throw the tablet also deep into the root of the tongue.
Dosage
The dosage of Cephalexin for cats and dogs will be the same. The veterinarian may prescribe this medication, either orally, intramuscularly or subcutaneously at 10-25 mg/kg. When taking the veterinary drug Cephalexin orally, an interval of 8-12 hours is observed, and in other cases - a day . If your pet has dermatological problems, then the dose of the drug becomes 22-30 ml/kg. In this case, an interval of 12 hours is maintained. But the duration of treatment depends on the degree of complexity of the disease, so it is determined by the doctor for each cat individually.
How to administer an antibiotic intramuscularly?
You need to inject medications using a new syringe each time. The cat needs to be secured with the elbow of your free hand so that it does not jerk when the medicine is administered - some antibiotics are very painful. There is no need to lubricate the injection site with alcohol.
The drug in the syringe must be warmed by hand to at least room temperature. There is no need to inject the solution directly from the refrigerator. The selection of needles is carried out in accordance with the volume and viscosity of the medication. If the medicine is administered no more than one cube and the solution is of aqueous consistency, you can take an insulin syringe. If the antibiotic is of the oily type, you will need a regular syringe with a medium needle.
Where to give an injection to a cat
global $ads_google;
//data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?> $ads_google = true; ?> } ?> Despite the fact that in theory you can hit almost any place, there are places on the animal’s body where it will be more effective and less painful. The cat can be injected subcutaneously into the withers (between the shoulder blades) or intramuscularly into the thigh. The muscle tissue of the thigh has a large number of vessels, so any injected medicine is very quickly delivered to the blood. An injection is given into the thigh if the drug is not very painful. In some cases, intramuscular administration is preferable, so you should carefully read the instructions. Intramuscular injections are limited in volume - liquid injected inside causes greater muscle separation, which is a microtrauma.
The skin on the withers is denser, so it is better to address “painful” solutions to this particular place - just remember how animals fight and grab each other precisely by it.
Drug interactions
According to the instructions, azithromycin should not be used in animals taking cisapride.
Azithromycin can be combined with rifampicin. Oral antacids may reduce the rate of absorption of azithromycin. Overdose of any macrolide antibiotic can cause serious gastrointestinal side effects. Some veterinarians use oral probiotics in foals treated with macrolide antibiotics to reduce the incidence or severity of antibiotic-induced diarrhea.
Review and use of broad-spectrum antibiotics for cats
A large number of different types of antibacterial agents are used in veterinary medicine. They differ in their mode of action and type of origin - natural or synthetic.
But they all have one common goal - treating the animal from parasites, fungi and other harmful organisms. These drugs are used both in the treatment of an already established disease and for preventive purposes.
For example, during sterilization of cats, to quickly tighten stitches and prevent inflammation.
In what situations should antibiotics be used for cats?
Before using antibacterial agents, you should familiarize yourself in detail with the features of their action and determine whether it is suitable in a particular case.
Cat
For your information! In each individual case, when using antibacterial agents, it is necessary to become familiar with the course of the infectious process, the spectrum of action of the drug and the sensitivity of the source of the disease to the drug.
Purulent wound
Cats are not used to sitting still. They can climb trees, attics and basements. As a result of such travel, a pet may develop a wound on its paws or face, which may subsequently fester. In this case, you should not wait until the infection goes away on its own, but it is better to immediately begin surgical treatment.
First of all, it is necessary to trim the hair around the wound received by the pet. Inspect it for the presence of any foreign objects (shards, sawdust, dirt, etc.). If blood clots or pus are present, they should be carefully removed. The wound is treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, iodine or brilliant green. If the damage is too extensive, then it is necessary to apply a sterile bandage.
Important! If there is heavy bleeding, the damaged surface must be tied with a tourniquet and immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
In order to prevent wound infection, it is recommended to give antibiotics for cats that help with purulent wounds, for example, amoxiclav. It is given in proportions of 15 mg per kilogram of weight for seven days.
If, despite preventive measures, your pet still develops a purulent infection or abscess, then it should be shown to a doctor.
The veterinarian will eliminate inflammation in the wound and apply antibiotics such as levomikol or streptomycin to it.
Infection
Antibiotics should be used very carefully for infections and only after consulting a doctor. It is necessary to know what effect the drug has on the body in a particular case.
So, when treating staphylococcus, bactericidal drugs will kill harmful microorganisms, they will accumulate in the bladder and contribute to the appearance of urolithiasis.
But the use of such antibiotics when a pet has sepsis can save it.
Treatment
To understand which antibiotic to give your cat, and whether it needs to be done at all, you need to know the entire list of indications for use:
- pneumonia, cystitis or pyelonephritis;
- during treatment of an associated bacterial infection in ARVI;
- in cases where during surgery it may be necessary to eliminate inflammation;
- in the treatment of diseases resulting from the action of specific microorganisms;
- in case of ear infections and eye diseases such as rhinotracheitis and purulent otitis media.
Cold
Colds, as a rule, can occur in cats as a result of hypothermia, which causes a malfunction in the immune system, and the animal becomes easy prey for germs and bacteria.
To help your pet heal faster, it is recommended to treat it with antibiotics.
In this case, it is better to use new generation drugs, since they have fewer contraindications and consequences than first generation drugs.
Note! Before starting treatment, it is necessary to make sure that the animal has a cold or runny nose, since allergic and viral diseases can have similar symptoms. In any case, for an accurate diagnosis it is better to consult a doctor.
During the course of treatment with antibacterial agents, it is necessary to regularly monitor the pet’s condition. If any side effects occur, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Types of broad-spectrum antibiotics for cats
These drugs are divided into several categories.
Spectrum of action
Stop cystitis for cats: tablets and suspension
Antibacterial agents can be of a narrow spectrum, which are used to treat certain diseases. Broad-spectrum drugs can resist various types of infections and microbes.
Action type
According to the type of action, antibiotics are divided into two groups:
- To destroy microbes, bactericidal agents are used;
- To slow down the development and spread of disease sources, bacteriostatic antibiotics are used.
Antibiotics of the first type help to quickly destroy the sources of the disease, and the second type slow down the development of infection. This does not mean that they are worse; if they are used, the bacteria will die and be guaranteed to disappear from the body, but this process will be lengthy.
Chemical composition
Antibiotics used to treat feline diseases differ in their chemical structure:
- penicillin;
- cephalosporin;
- tetracycline;
- macrolides;
- chloramphenicol;
- aminoglycoside
For your information! Only 25 types of antibiotics are used in veterinary medicine.
Place of impact on the body
Medicines can have both local and general effects. Depending on what exactly the pet is sick with, a specific antibiotic is used:
- if the skin is damaged, treatment is carried out with ointments or sprays;
- to cure bacterial conjunctivitis, the best remedies are eye drops or ointments;
- if the cat suffers from systemic infections, then tablets, intramuscular or intravenous injections should be used;
- when treating the respiratory system, aerosol agents are used;
- suppositories are used in the treatment of vaginitis.
Treatment
By release form
All types of medicines can be produced in various forms: suppositories, suspensions, ointments, drops and aerosols. When the disease affects the pet extensively, it is treated with injections or the animal is given tablets.
Basic rules for using drugs
Diabetes mellitus in cats: symptoms and treatment
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed only in the most extreme cases. Depending on the type of disease, medications can be prescribed either in tablets or in injections.
Instructions for use are always attached to each drug. It will indicate the dosage and duration of use of the medicine.
Typically, the course of treatment is completed within five days, and if the disease does not subside, it is extended by 7 or 14 days.
There are also antibiotics that need to be taken for no more than three days, and some require no more than one injection. In any case, before using medications, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Pills
If you independently shorten or, conversely, extend the course of taking the drug, this may negatively affect the health of your pet, and as a result you will have to resort to taking stronger drugs.
How and where can you inject a cat with an antibiotic?
Viral diseases in cats: infections, symptoms, treatment
Since it is quite difficult to inject antibiotics intravenously into an animal, it is prohibited to do this at home. Intramuscular injections also require special skills and dexterity, so it is better to consult a doctor. But as a last resort, you can perform this procedure yourself.
Injections
The procedure is as follows:
- To prevent the cat from escaping during the administration of the medicine, it must be securely secured in the hands.
- Take a syringe suitable for this case. An insulin syringe is suitable if you plan to administer a dose of no more than one cube of solution. If the medicine has an oily consistency, then a regular syringe with a medium needle will do.
- A solution at room temperature is drawn into a syringe.
- The needle is inserted into the animal's thigh to a depth of 1 cm.
- After the procedure, the pet must be constantly reassured and fed.
Possible side effects from using antibiotics
Antibiotics, just like any other medicine, can cause side effects. Dysbacteriosis is the most common of them.
Since during treatment, along with the infection, part of the natural microflora of the animal’s body is destroyed, as a result, the pet may experience disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, which can result in diarrhea.
To save your cat from this, after using antibiotics, you should give her prebiotics, which will restore the body's microflora.
The composition of any medicine always contains emulsifiers, stabilizers and preservatives. Some of them can contribute to the formation of allergic reactions in the cat, such as constant subcutaneous itching and rashes.
Note! Any antibiotic may cause your cat to become lethargic and sleep more than usual.
Depending on the type of drug, its dosage and duration of use, your pet may experience other side effects: swelling, vomiting, difficulty breathing and convulsions.
If an animal suffers from a disease of the urinary system, then with the use of certain types of drugs this disease may worsen.
Therefore, when prescribing antibiotics, it is necessary to take into account all possible side effects.
Important! After completing a course of treatment, the animal cannot mate, since antibiotics have a negative effect on reproductive function and, as a result, inferior offspring may be obtained.
What antibiotics can be given to cats and kittens?
The most popular drugs are listed below.
- Amikacin. This medication is used to treat infections caused by salmonella or E. coli. The medicine is administered intramuscularly three times a day, 10 mg per 1 kg of animal weight. If your pet has kidney disease, amikacin should not be used.
- Penicillin. It is used for purulent wounds, skin inflammations and burns. In rare cases, for the treatment of the urinary system.
- Enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. They belong to one group of fluoroquinols, which counteract any bacteria. Available in the form of solutions and tablets. The dosage is selected based on the weight of the animal - 0.5 ml per 5 kg of weight. The course of treatment can last 5-10 days.
- Sinulox. The main active ingredient of the drug is synthetic penicillin - amoxicillin. It copes well with many bacteria, as well as staphylococcus, clostridia and similar infections.
- Neomycin. Broad-spectrum drug. Used in the treatment of kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, skin infections. Produced in powders, ointments, solutions. It is administered once every 8 hours for seven days.
- Ceftriaxone. A third generation drug that has a wide spectrum of effects. Used for prophylaxis after operations, as well as in the treatment of sepsis, pneumonia, infections of bones and joints and many other diseases.
- Terramycin. Spray used for the treatment of skin diseases, treatment of wounds and postoperative sutures. The drug should be applied once. Repeated treatment is allowed after a week.
- Azithromycin. It is the most effective and safest remedy. It is used in the treatment of gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract infections.
- Lincomycin. In small doses it is a bacteriostatic agent. Used in the treatment of pneumonia, lung abscess and sepsis.
- Tetracycline. Used in the treatment of conjunctivitis and herpes. Tetracycline for cats is also used in the fight against pneumonia and diseases of the genitourinary system.
Important! Antibiotics should only be used to treat kittens after consultation with a veterinarian.
Advantages and disadvantages of antibiotic therapy in cats
Like any other medicine, antibiotics have both pros and cons. With their help, the pet will be healed faster, but additional harm will be caused to its health. In order for the animal to be negatively affected as little as possible, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the disease and select the appropriate drug for treatment.
Pros of antibiotics:
- improvement of the animal's condition;
- minimal side effects;
- effective even for advanced diseases.
Disadvantages of antibiotics:
- With a long course of treatment, addiction may occur.
- if the medicine or its dose is chosen incorrectly, the consequences can be very serious;
- the possibility of allergic reactions;
- After a course of treatment, the body's microflora needs to be restored.
Treatment
Thus, antibiotics can help treat a pet, but at the same time they should be used only if necessary and after accurately determining the source of the animal’s poor health. It is worth remembering that only a doctor can determine what exact antibiotic can be given to a cat.
Source: https://gafki.ru/koshki/antibiotiki.html